CinnamamideCAS# 22031-64-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 22031-64-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5273472 | Appearance | Powder |
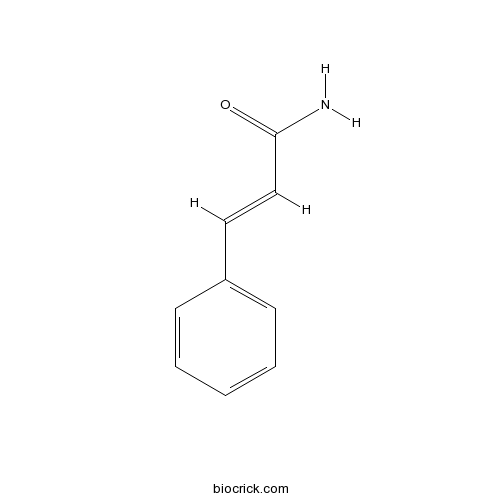
| Formula | C9H9NO | M.Wt | 147.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 621-79-4 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-3-phenylprop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C=CC(=O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | APEJMQOBVMLION-VOTSOKGWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H9NO/c10-9(11)7-6-8-4-2-1-3-5-8/h1-7H,(H2,10,11)/b7-6+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Cinnamamide, a non-lethal repellent, deters feeding by a wide range of avian species;cinnamamide has the potential for use against the commensal rodent Mus musculus in situations where use of lethal control methods could be hazardous (e.g. food stores). 2. Cinnamamide is an antitumor agent with low cytotoxicity acting on matrix metalloproteinase, and may serve as a lead compound in the development of antitumor drugs. 3. Cinnamamide and betaine cinnamamide have growth-regulating activity on wheat. |
| Targets | MMP(e.g.TIMP) |

Cinnamamide Dilution Calculator

Cinnamamide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.7935 mL | 33.9674 mL | 67.9348 mL | 135.8696 mL | 169.837 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.3587 mL | 6.7935 mL | 13.587 mL | 27.1739 mL | 33.9674 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6793 mL | 3.3967 mL | 6.7935 mL | 13.587 mL | 16.9837 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1359 mL | 0.6793 mL | 1.3587 mL | 2.7174 mL | 3.3967 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0679 mL | 0.3397 mL | 0.6793 mL | 1.3587 mL | 1.6984 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Triptohairic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8060
CAS No.:220209-71-2
- O-Methyldauricine
Catalog No.:BCC8225
CAS No.:2202-17-7
- Eichlerialactone
Catalog No.:BCN4941
CAS No.:2202-01-9
- Imatinib Mesylate (STI571)
Catalog No.:BCC1115
CAS No.:220127-57-1
- Vincetoxicoside B
Catalog No.:BCN2864
CAS No.:22007-72-3
- Nu 6027
Catalog No.:BCC1154
CAS No.:220036-08-8
- Ixabepilone
Catalog No.:BCC1666
CAS No.:219989-84-1
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Tyr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2621
CAS No.:219967-69-8
- Isoescin IB
Catalog No.:BCN2969
CAS No.:219944-46-4
- Isoescin IA
Catalog No.:BCN2968
CAS No.:219944-39-5
- 3-Methyl-1-(2-piperidinophenyl)butylamine N-acetylglutamate salt
Catalog No.:BCC8635
CAS No.:219921-94-5
- 5,8,9,14-Tetraacetoxy-3-benzoyloxy-10,15-dihydroxypepluane
Catalog No.:BCN7657
CAS No.:219916-77-5
- 5-[2-[Tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxyethyl]-2,2-dimethyl-3a,6a-dihydrofuro[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-6-one
Catalog No.:BCC8592
CAS No.:220328-03-0
- 3,11,12-Trihydroxyspirovetiv-1(10)-en-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN1487
CAS No.:220328-04-1
- TRO 19622
Catalog No.:BCC5288
CAS No.:22033-87-0
- DH 97
Catalog No.:BCC6973
CAS No.:220339-00-4
- 5-Epicanadensene
Catalog No.:BCN7349
CAS No.:220384-17-8
- ShK-Dap22
Catalog No.:BCC5990
CAS No.:220384-25-8
- Polycephalin C
Catalog No.:BCN1852
CAS No.:220422-37-7
- Kaempferol 5-methyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN3426
CAS No.:22044-80-0
- Leptomerine
Catalog No.:BCN1486
CAS No.:22048-97-1
- 1-Methyl-2-pentyl-4(1H)-quinolinone
Catalog No.:BCN4943
CAS No.:22048-98-2
- Caspase-3/7 Inhibitor I
Catalog No.:BCC1140
CAS No.:220509-74-0
- Diphyllin
Catalog No.:BCN8066
CAS No.:22055-22-7
Cinnamamide, an antitumor agent with low cytotoxicity acting on matrix metalloproteinase.[Pubmed:10757563]
Anticancer Drugs. 2000 Jan;11(1):49-54.
The antitumor activity of Cinnamamide (CNM), an agent acting on matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), was investigated in the present study. CNM displayed low cytotoxicity. By the MTT assay the IC50 (50% inhibitory concentration) values of CNM on cell proliferation ranged from 1.29 to 1.94 mM in human oral epidermoid carcinoma KB cells, human hepatoma BEL-7402 cells and human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells. Moreover, the IC50 for human fetal lung 2BS cells reached 4.33 mM. The administration of CNM in the range of 50-150 mg/kg (i.p. or p.o.) showed moderate antitumor effects in mice. When administered i.p. or p.o., CNM (150 mg/kg) inhibited the growth of transplanted hepatoma 22 by 48.8 or 40.5%, respectively. At the dose of 100 mg/kg, CNM inhibited the growth of colon 26 carcinoma by 39.0% and that of Lewis lung carcinoma by 53.9%. In the Lewis lung carcinoma model, CNM at the dose of 100 mg/kg (i.p.) also reduced the lung metastasis by 59.1%. Gelatine zymography revealed that CNM was able to decrease the level of MMP-2 in conditioned medium of HT-1080 tumor cells in a concentration-dependent manner. These results indicate that CNM is an antitumor agent with low cytotoxicity acting on MMP and may serve as a lead compound in the development of antitumor drugs.
Cinnamamide Derivatives for Central and Peripheral Nervous System Disorders--A Review of Structure-Activity Relationships.[Pubmed:26083325]
ChemMedChem. 2015 Aug;10(8):1302-25.
The Cinnamamide scaffold has been incorporated in to the structure of numerous organic compounds with therapeutic potential. The scaffold enables multiple interactions, such as hydrophobic, dipolar, and hydrogen bonding, with important molecular targets. Additionally, the scaffold has multiple substitution options providing the opportunity to optimize and modify the pharmacological activity of the derivatives. In particular, Cinnamamide derivatives have exhibited therapeutic potential in animal models of both central and peripheral nervous system disorders. Some have undergone clinical trials and were introduced on to the pharmaceutical market. The diverse activities observed in the nervous system included anticonvulsant, antidepressant, neuroprotective, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. Over the last decade, research has focused on the molecular mechanisms of action of these derivatives, and the data reported in the literature include targeting the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA ) receptors, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, transient receptor potential (TRP) cation channels, voltage-gated potassium channels, histone deacetylases (HDACs), prostanoid receptors, opioid receptors, and histamine H3 receptors. Here, the literature data from reports evaluating cinnamic acid amide derivatives for activity in target-based or phenotypic assays, both in vivo and in vitro, relevant to disorders of the central and peripheral nervous systems are analyzed and structure-activity relationships discussed.


