Bauhinia variegata
Bauhinia variegata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Bauhinia variegata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
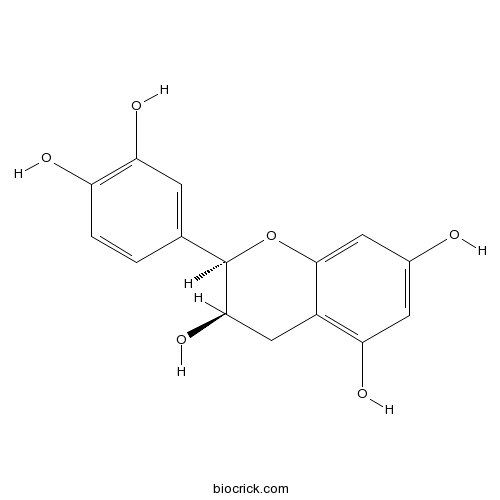
BCN5597
Epicatechin490-46-0
Instructions
-
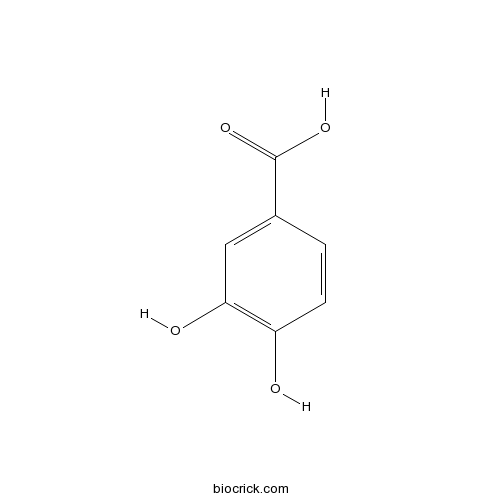
BCN4537
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
FORMULATION AND STABILITY EVALUATION OF BAUHINIA VARIEGATA EXTRACT TOPICAL EMULSION.[Pubmed: 29513965]
This study presents the results for the development of water in oil (W/O) emulsion containing 2 % Bauhinia variegata (BV) extract with good antioxidant potential for cosmetic application. Different ratios of surfactant, oil and water were investigated to optimize the ratio of ingredients. It was found that emulsifier and oil4ratio were important in improving the stability of emulsion. The formulation having 2.5% Abil EM90, 12% liquid paraffin, 83.5% distilled water and 2% BV extract was found to be most stable. Stability of the formulation was further evaluated by characterizing for organoleptic, sedimentation, microscopic and rheological properties at a range of storage conditions for a period of 12 weeks. Experimental findings showed stable formulation behavior with respect to color change, liquefaction and phase separation. Centrifugation test was carried out to predict the long term stability..The rheological parameters were evaluated from Power Law and the flow index value less than 1 suggested non-Newtonian behavior of the W/O emulsion. The mean droplet size of the internal phase of freshly prepared formulation was 4.06 ? 1.99 pm that did not change significantly (p > 0.05) during the storage. The newly developed formulation exhibited promising attributes over long term storage and open opportunities for the topical delivery of natural antioxidants for cosmetic and pharmaceutical objectives.
Elucidating Bauhinia variegata lectin/phosphatidylcholine interactions in lectin-containing liposomes.[Pubmed: 29501995]
None
The influence of electron beam radiation in the nutritional value, chemical composition and bioactivities of edible flowers of Bauhinia variegata L. var. candida alba Buch.-Ham from Brazil.[Pubmed: 28958515]
As edible flowers are highly perishable, irradiation technology can be applied to increase their shelf life, as also for phytosanitary purposes. Herein, flowers of Bauhinia variegata L. var. candida alba Buch.-Ham were submitted to electron beam irradiation at the doses of 0.5, 0.8 and 1kGy, to study the effects in the nutritional and chemical profiles, and also in antioxidant, cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory activities. The petals of white flowers revealed interesting bioactive properties being kaempferol derivatives the most abundant compounds, especially kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside. The applied irradiation doses did not highly affect the nutritional profile. No changes were produced in cytotoxicity, but the anti-inflammatory activity slightly decreased. However, the antioxidant activity was increased, especially in the dose of 0.5kGy, in agreement with the higher content in phenolic compounds found at this dose.
Rapid biosynthesis of Bauhinia variegata flower extract-mediated silver nanoparticles: an effective antioxidant scavenger and α-amylase inhibitor.[Pubmed: 28885044]
None
Palatability of nine fodders species used by guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus).[Pubmed: 28884404]
Nine fodders commonly offered to the guinea pigs by the breeders in Lubumbashi (Democratic Republic of Congo) were compared for chemical composition and for both daily dry matter intake and palatability indices by using 13 three-month-old guinea pigs. Four different plant families were provided to each guinea pig, and each animal was exposed to all the experimental diets studied for 8 consecutive days. The fodder species were three grasses: Trypsacum laxum, Panicum maximum, and Pennisetum purpureum; three trees or bushes Moringa oleifera, Leucaena leucocephala, and Bauhinia variegata; and three flowering plants Bidens oligoflora, Bidens pilosa, and Commelina diffusa. Dry matter content varied from 14 to 44/100 g FM, and CP from 13 to 28/100 g DM. B. variegata and P. purpureum showed the lowest CP value and L. leucocephala the highest. The grasses and the Commelina had higher levels of hemicelluloses than the tree fodders, especially P. maximum (45/100 g DM). High levels of K were found in the grasses and Bidens, and high Ca in the tree fodders and Bidens. The guinea pigs preferred, in a descending order, P. purpureum (0.79), B. pilosa (0.78), C. diffusa (0.78), T. laxum (0.77), P. maximum (0.76), B. oligoflora (0.75), M. oleifera (0.45), L. leucocephala (0.37), and B. variegata (0.33). The DMI and the palatability index were strongly correlated to the ash (r = 0.82; p ˂ 0.05) and the potassium (r = 0.88; p ˂ 0.05) contents in fodders.
Histochemistry and immunolocalisation of glucokinin in antidiabetic plants used in traditional Mexican medicine.[Pubmed: 28735523]
Mexico is a megadiverse country that has 3,600 to 4,000 species of medicinal plants, of which approximately 800 are used to treat conditions related to diabetes mellitus (DM). DM is a chronic degenerative disease of energy metabolism that exists as two types: type 1 (DM1) and type 2 (DM2). DM is considered a public health problem that affects 7% of the Mexican population older than 20 years. DM is clinically controlled with hypoglycaemic drugs, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, insulin secretion stimulants or the direct application of insulin. The hypoglycaemic effectiveness of specific molecules has been determined only for some medicinal plants in Mexico used to treat DM2. The presence of molecules called glucokinins, wich are similar to animal insulin molecules, has been reported in some plant species; glucokinins act as both growth factors and regulators of glucose metabolism in plants. Therefore, we hypothesized that the hypoglycaemic effectiveness of some of the popularly used species for the control of DM could be due to the presence of glucokinin, as reported for Bauhinia variegata. The goal of this work was to use histochemistry to detect, the accumulation of protein that is immunocytochemically compatible with glucokinin in slide sections of hypoglycaemic species used as remedies for DM2. The top fourteen most used medicinal plants in Mexico were selected for study via microscopic sections. Proteins were histochemically detected using naphthol blue black and Johansen's quadruple stain, and the immunocytochemical correspondence of the proteins with glucokinin was investigated using an insulin antibody. All species studied reacted positively to proteins and glucokinin in the same structures. The presence of glucokinin in these structures and the corresponding hypoglycaemic effects are discussed in the contex of the actions of other compounds.
Morphoanatomical and physiological changes in Bauhinia variegata L. as indicators of herbicide diuron action.[Pubmed: 28359990]
None
Lectin I from Bauhinia variegata (BVL-I) expressed by Pichia pastoris inhibits initial adhesion of oral bacteria in vitro.[Pubmed: 27651277]
Lectins are non-immune proteins that reversibly bind to carbohydrates in a specific manner. Bauhinia variegata lectin I (BVL-I) is a Gal/GalNAc-specific, single-chain lectin isolated from Bauhinia variegata seeds that has been implicated in the inhibition of bacterial adhesion and the healing of damaged skin. Since the source of the native protein (nBVL) is limited, this study aimed to produce recombinant BVL-I in Pichia pastoris (rBVL-Ip). The coding sequence for BVL-I containing preferential codons for P. pastoris was cloned into the pPICZαB plasmid. A single expressing clone was selected and fermented, resulting in the secretion and glycosylation of the protein. Fed-batch fermentation in 7L-scale was performed, and the recombinant lectin was purified from culture supernatant, resulting in a yield of 1.5mg/L culture. Further, rBVL-Ip was compared to nBVL and its recombinant version expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) (rBVL-Ie). Although it was expressed as a monomer, rBVL-Ip retained its biological activity since it was able to impair the initial adhesion of Streptococcus mutans and S. sanguinis in an in vitro model of biofilm formation and bacterial adhesion. In summary, rBVL-Ip produced in Pichia pastoris represents a viable alternative to large-scale production, encouraging further biological application studies with this lectin.


