Callicarpa macrophylla
Callicarpa macrophylla
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Callicarpa macrophylla
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
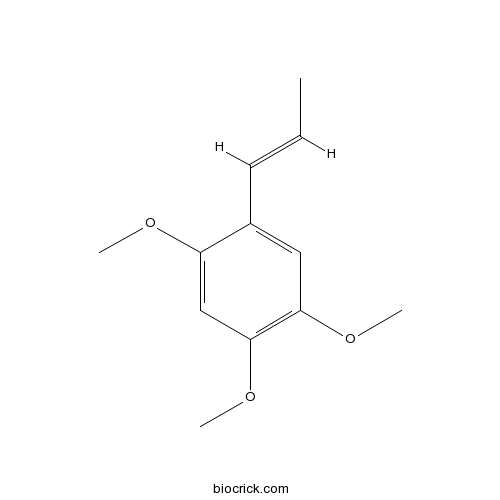
BCN3837
alpha-Asarone2883-98-9
Instructions
-
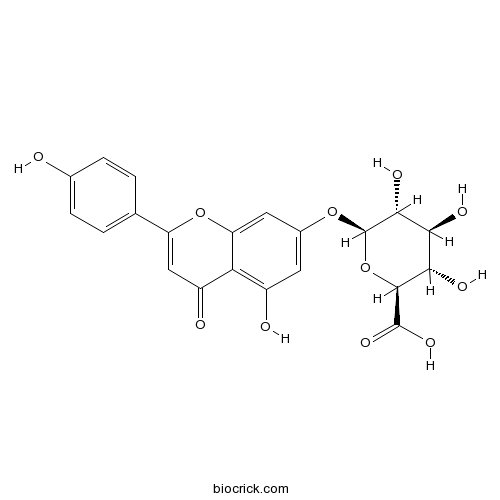
BCN5326
Apigenin-7-glucuronide29741-09-1
Instructions
-
BCN5338
Luteolin-7-O-glucuronide29741-10-4
Instructions

-
BCN4136
Acteoside61276-17-3
Instructions

β-Selinene-Rich Essential Oils from the Parts of Callicarpa macrophylla and Their Antioxidant and Pharmacological Activities.[Pubmed: 28930267]
None
Three New Abietane-Type Diterpenoids from Callicarpa macrophylla Vahl.[Pubmed: 28534843]
None
Bioactive Diterpenoids from the Leaves of Callicarpa macrophylla.[Pubmed: 26110519]
A phytochemical investigation of the leaves of Callicarpa macrophylla led to the isolation of five new diterpenoids (1-5), macrophypenes A-E, and nine known analogues (6-14). The structures of 1-5 were established on the basis of extensive analysis of NMR spectroscopic data, X-ray diffraction data, and experimental and calculated electronic circular dichroism spectra. Compound 1 is a spiroditerpenoid with a novel skeleton, and compound 5 is a rare ent-abietane diterpenoid possessing a peroxide bridge. Compounds 1, 5-7, and 11-14 stimulate nerve growth factor mediated neurite outgrowth from PC12 cells.
Comparative analysis of three Callicarpa herbs using high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector and electrospray ionization-trap mass spectrometry method.[Pubmed: 23277156]
Three Callicarpa species, namely Callicarpa nudiflora Hook. et Arn., Callicarpa macrophylla Vahl. and Callicarpa kwangtungensis Chun. are astringency and hemostasis herbs in the traditional Chinese medical systems. Despite their wide use in Chinese medicine, no report on system comparison on their chemical constituents is available so far. High-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detector and electrospray ionization trap mass spectrometry (HPLC-DAD-ESI-Trap MS) technique was used for qualitative and quantitative analyses of the three Callicarpa herbs. Phenylpropanoid glycosides, flavonoids and organic acids were identified by comparing with reference standards or according to their MS/MS fragmentation behaviors. A total of 33 compounds were identified identified or tentatively identified, and 23 of them were reported from these herbs for the first time. Phenylpropanoid glycosides were featured in the three species with their types and contents presenting significant differences. Furthermore, quantitative analysis was conducted by determining four marker phenylpropanoid glycosides (forsythoside B (14), acteoside (15), poliumoside (19), isoacteoside (21)) and two flavonoids (luteolin (30), apigenin (32)). Three flavonoid glucuronides (luteolin-diglucuronide-glucuronide (5), luteolin-diglucuronide (12), apigenin-7-O-β-glucuronide (24)) were semi-quantified according to their corresponding aglycones. The total contents of the nine major compounds in the three species varied significantly from 8.92 to 40.89 mg/g.
A natural plant growth promoter calliterpenone from a plant Callicarpa macrophylla Vahl improves the plant growth promoting effects of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs).[Pubmed: 23271460]
Experiments were conducted to evaluate the efficacy of calliterpenone, a natural plant growth promoter from a shrub Callicarpa macrophylla Vahl., in enhancing the growth and yield promoting effects of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs), in menthol mint (Mentha arvensis L).This study is based on our previous results indicating the microbial growth promotion by calliterpenone and assumption that application of calliterpenone along with PGPRs will improve the population of PGPRs resulting in higher impacts on plant growth and yield. Of the 15 PGPRs (identified as potent ones in our laboratory), 25 μl of 0.01 mM calliterpenone (8.0 μg/100 ml) was found to be useful in improving the population of nine PGPRs in culture media. The five selected strains of PGPRs exhibiting synergy with calliterpenone in enhancing growth of maize compared to PGPR or calliterpenone alone were selected and tested on two cultivars (cvs. Kosi and Kushal) of M. arvensis. Of the five strains, Bacillus subtilis P-20 (16S rDNA sequence homologous to Accession No NR027552) and B. subtilis Daz-26 (16SrDNA sequence homologuos to Accession No GU998816) were found to be highly effective in improving the herb and essential oil yield in the cultivars Kushal and Kosi respectively when co-treated with calliterpenone. The results open up the possibilities of using a natural growth promoter along with PGPRs as a bio-agri input for sustainable and organic agriculture.
Volatiles of Callicarpa macrophylla: a rich source of selinene isomers.[Pubmed: 20334142]
Variations in volatile composition of the leaf and fruit oils from Callicarpa macrophylla were compared, using GC-FID, Kovat's Index calculation, and GC/MS. The oils were rich in selinene derivatives. The fruit oil was comprised of 41.6% beta-selinene and 6% alpha-selinene. The leaves from both the harvests contained 29% and 20% beta-selinene and 1.7% alpha-selinene. In addition, dendrolasin, a potential perfumery natural furanoid sesquiterpenoid, was a characteristic of both leaf and fruit essential oils.
[RP-HPLC determination of betulinic acid in Callicarpa macrophylla].[Pubmed: 18589770]
To establish an RP-HPLC method for determination of betulinic acid in Callicarpa macrophylla, a commonly used herbal in Yunnan.


