Chaenomeles sinensis
Chaenomeles sinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Chaenomeles sinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
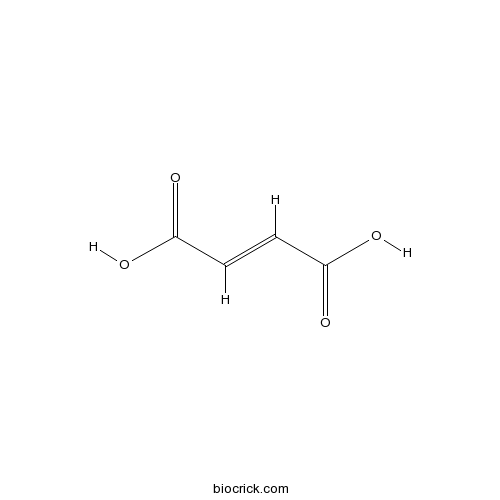
BCN5989
Fumaric acid110-17-8
Instructions
-
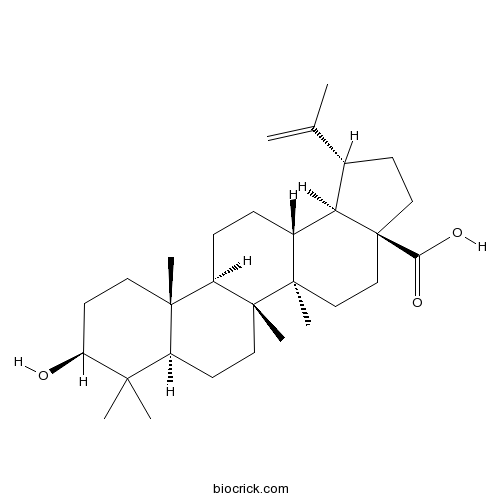
BCN5524
Betulinic acid472-15-1
Instructions
-
BCN5528
Betulin473-98-3
Instructions

-
BCN3820
Stearic Acid57-11-4
Instructions

Structural elucidation of lignin-carbohydrate complexes (LCCs) from Chinese quince (Chaenomeles sinensis) fruit.[Pubmed: 29778878]
The lignin-carbohydrate complexes (LCCs) of the mesocarp (MS) and near the endocarp (NE) of Chinese quince (Chaenomeles sinensis) fruits were analyzed using three different methods of fractioning: milled wood lignin (MWL), LCC extracted from crude MWL with acetic acid (LCC-AcOH), and Bjorkman LCC. The MWL and LCC fractions were characterized by carbohydrate composition analysis, SEC, FT-IR, Py-GC/MS, thermal analysis and 2D HSQC NMR. Notably, large amounts of arabinose and galactose remained in the Björkman LCC fractions suggesting a chemical bond between the lignin and pectin. MWL and LCC-AcOH fractions showed better thermal stability than the Björkman LCC fractions. The structure of MS lignin was similar to that of NE lignin; however, fractions from the different fractionation methods revealed differences. The MWL fractions were rich in benzyl ether and γ-ester linkages, while the Björkman LCC fractions contained phenyl glycoside and γ-ester linkages, and the LCC-AcOH fractions contained phenyl glycoside and benzyl ether linkages. These findings are helpful in understanding the nature of lignin and LCC in Chinese quince fruits and provide a theoretical support for their potential application.
Standardization of extract mixture of Chaenomeles sinensis and Phyllostachys bambusoides for anti-obesity by HPLC-UV.[Pubmed: 28965327]
JM-101 is a developed functional food formula using water extract of Chaenomeles sinensis and Phyllostachys bambusoides for anti-obesity. Standardization and quality control of herb mixture is more difficult than those of single herb. Additionally, the estimation of mixing ratio is an essential requirement for standardization. This study aimed to develop an efficient analytical method for the standardization of JM-101 based on C. sinensis and P. bambusoides. Protocatechuic acid and p-coumaric acid were selected as marker compounds of JM-101. A mixture of the two medicinal materials (1:1 w/w) was extracted by water and then liquid-liquid extracted (LLE) by ethyl acetate. The supernatant was evaporated to dryness and dissolved in methanol for analysis. The extraction time, material-to-water ratio and ethyl acetate-to-water ratio were optimized by multi-response optimization based on response surface methodology (RSM). The established methods were validated in terms of linearity, precision, accuracy, repeatability, stability and recovery. The novel method based on LLE and RSM provides a sensitive, accurate analysis and excellent extraction efficiency of marker compounds in JM-101, without interruption of other compounds in JM-101. In conclusion, the developed simultaneous analytical method contributes to the standardization of two materials (C. sinensis and P. bambusoides) and JM-101.


