Changium smyrnioides
Changium smyrnioides
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.

Natural products/compounds from Changium smyrnioides
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
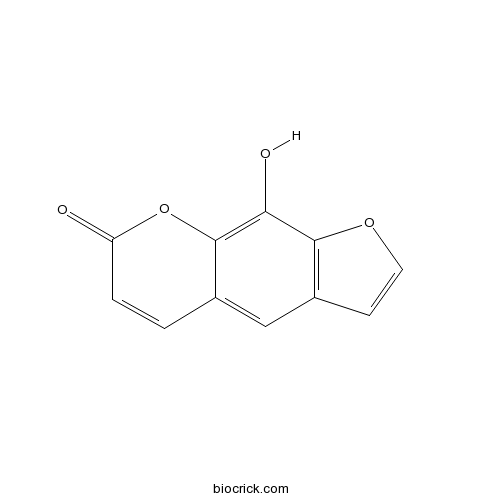
BCN4881
Xanthotoxol2009-24-7
Instructions
-
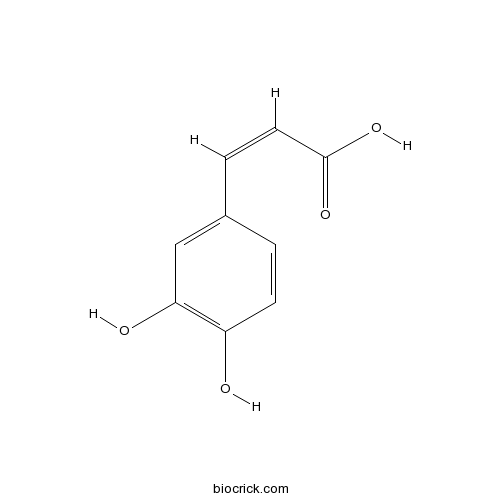
BCN5979
Caffeic acid331-39-5
Instructions
-
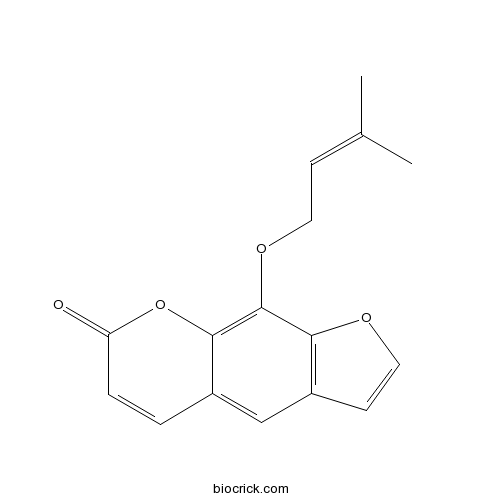
BCN5574
Imperatorin482-44-0
Instructions
[Analysis on character of mineral elements in Changium smyrnioides and rhizosphere soil].[Pubmed: 29751703]
The contents of 22 kinds of mineral elements in different parts of Changium smyrnioides and in the rhizosphere soil of 10 different populations were determined by microwave digestion-inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES). The characteristics of mineral elements in the plants and the soil of main distribution area of Ch. smyrnioides was analyzed and the mechanism of the quality formation of Ch. smyrnioides was explored to provide the basis for the quality evaluation and cultivation regulation of Ch. smyrnioides.The results showed that the quality of soil environment was better in the main distribution area of Ch. smyrnioides, the content of trace elements was higher, the contents of P and K were lower and the contents of mineral elements in the soil of each distribution area was significantly different. The three elements of Se, P and K are significantly accumulated in the root of Ch. smyrnioides. There were significant differences in the total contents of mineral elements in the roots of Ch. smyrnioides in different producing areas. The contents of mineral elements in different parts of Ch. smyrnioides were significantly different. Ch.smyrnioides of the main distribution area of Ch. smyrnioides belonged to the safety level, the distribution of mineral elements in the plants can be used as an indicator of the quality of medicinal herbs.
[Effects of methyl jasmonate on accumulation of furanocoumarins in Changium smyrnioides and its suspension cells].[Pubmed: 28945028]
Changium smyrnioides is an endangered and endemic medicinal herb in China which contains rich furanocoumarins. Bergaptol, bergapten and xanthotoxin are natural furanocoumarins in Ch. smyrnioides, among which bergaptol is mainly contained in in vitro cultures while the latter ones distribute in all organs and cultures of the plant. In this study, methyl jasmonate was used to elicit furanocoumarins in both cultivated plant and suspension cells. The accumulations of biomass and 3 furanocoumarins as well as the activity of cell, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and antioxidase were detected. The results showed that methyl jasmonate induced the biosynthesis of furanocoumarins markedly and suspension cells from petiole produced more furanocoumarins than those from leaf. In the case of suspension cells, the concentration at 100 μmol•L⁻¹ triggered the highest yield of furanocoumarins and the 10th day of the culture period was the proper time for treatment. After 4 days the yields of bergaptol, bergapten and xanthotoxin in suspension cells from petiole were enhanced to 2.83,14.04,0.62 mg•L⁻¹ respectively. The biomass and viability of treated suspension cells decreased. At the same time, the activity of antioxidase increased, which indicated that methyl jasmonate induced cell defense. In both in vivo and in vitro conditions, cells from petiole seemed to be more sensitive to methyl jasmonate treatment compared to those from leaf. Bergaptol and xanthotoxin mainly accumulated in medium and cell respectively. Bergapten was detected in both cell and medium. The elicitation treatment only enormously affected the yields but did not significantly involve the distributions of 3 furanocoumarins. This is the first systematic study focusing on the elicitation effects of methyl jasmonate and a series of changes which lead to the increase of furanocoumarins in Ch. smyrnioides cell suspension cultures. Methyl jasmonate appears to be an effective elicitor in the research and further efforts should be made to reveal the mechanism in detail.
Physiological characteristics, dry matter, and active component accumulation patterns of Changium smyrnioides in response to a light intensity gradient.[Pubmed: 27937676]
Changium smyrnioides Wolff (Apiaceae) is an endangered medicinal plant with numerous pharmacological uses.
[Effects of Browning Inhibitors on Suspension Cells Growth and Secondary Metabolites Production in Changium smyrnioides].[Pubmed: 27356372]
To study the effects of browning inhibitors on Changium smyrnioides suspension cells growth and secondary metabolites production.
Authentication of commercial processed Glehniae Radix (Beishashen) by DNA barcodes.[Pubmed: 26628908]
The radix of Glehnia littoralis Fr. Schmidt ex Miq. (Beishashen), is often misidentified and adultered in Chinese medicine. Its seven common adulterants include Chuanminshen violaceum Sheh et Shan (Chuanmingshen), Changium smyrnioides Wolff (Mingdangshen), Sphallerocarpus gracilis (Bess.) K.-Pol. (Miguoqin), Adenophora polyantha Nakai (Shishashen), Silene tatarinowii Regel (Shishengyingzicao), Adenophora tetraphylla (Thunb.) Fisch (Lunyeshashen) and Adenophora stricta Miq. (Shashen). This study aims to evaluate the feasibility of the second internal transcribed spacer (ITS2) DNA barcoding to discriminate between Glehniae Radix and its common adulterants.
Lipophilic constituents from two processed products and three different parts of Changium smyrnioides Wolff.[Pubmed: 25835784]
This article reports the lipophilic chemical composition of different processed products (Changii Radix, Changii Radix Alba) and parts (root bark, leaf and fruit) of Changium smyrnioides Wolff.. The lipophilic constituents were extracted with petroleum ether in Soxhlet apparatus, subsequently identified and determined by gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS). Yield of lipophilic constituents from Changii Radix (3.65%) was about three times more than Changii Radix Alba's (1.07%), which indicated processing by boiling in water had an impact on the content of lipophilic constituents. Moreover, the major compounds in different processed products and parts were found to be fatty acids and sesquiterpenes. The results are a contribution for the lipophilic chemical composition and can serve as a reference for product development of Changium smyrnioides Wolff..
Authentication of an endangered herb Changium smyrnioides from different producing areas based on rDNA ITS sequences and allele-specific PCR.[Pubmed: 22553063]
The rDNA ITS region of 18 samples of Changium smyrnioides from 7 areas and of 2 samples of Chuanminshen violaceum were sequenced and analyzed. The amplified ITS region of the samples, including a partial sequence of ITS1 and complete sequences of 5.8S and ITS2, had a total length of 555 bp. After complete alignment, there were 49 variable sites, of which 45 were informative, when gaps were treated as missing data. Samples of C. smyrnioides from different locations could be identified exactly based on the variable sites. The maximum parsimony (MP) and neighbor joining (NJ) tree constructed from the ITS sequences based on Kumar's two-parameter model showed that the genetic distances of the C. smyrnioides samples from different locations were not always related to their geographical distances. A specific primer set for Allele-specific PCR authentication of C. violaceum from Jurong of Jiangsu was designed based on the SNP in the ITS sequence alignment. C. violaceum from the major genuine producing area in Jurong of Jiangsu could be identified exactly and quickly by Allele-specific PCR.
[Change of chemical constituents in Changium smyrnioides at different ages].[Pubmed: 21355257]
To analyze the dynamic change of chemical constituents in Changium smyrnioides at different ages and give a reference for standard cultivation.
[Analysis on water-soluble components in roots of Changium smyrnioides among different populations by HPLC].[Pubmed: 21355227]
To analyze water-soluble components in the roots of Ch. smyrnioides among different populations that distributed in the main areas and give a reference for germplasm evaluation and quality control.


