Croton crassifolius
Croton crassifolius
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Croton crassifolius
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
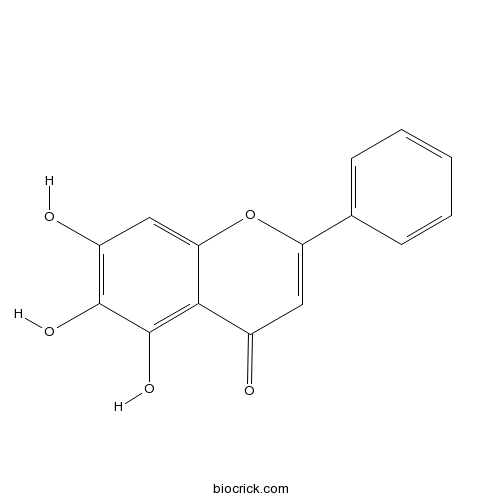
BCN5599
Baicalein491-67-8
Instructions
-
BCN4171
Wogonin632-85-9
Instructions

-
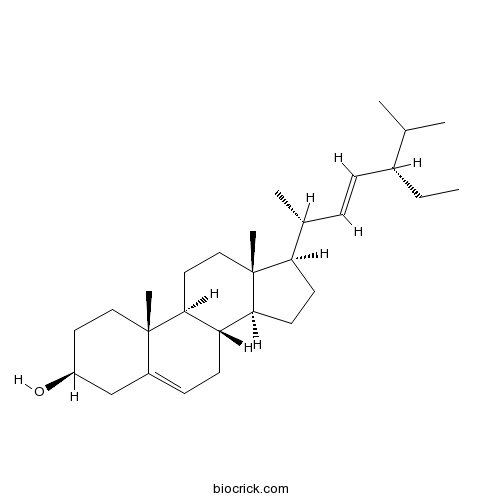
BCN4376
Stigmasterol83-48-7
Instructions
Sesquiterpenoids from the roots of Croton crassifolius.[Pubmed: 29888617]
Phytochemical investigation of Croton crassifolius roots afforded five sesquiterpenes (1-5), including two new sesquiterpenes 6S-hydroxy-cyperenoic acid (1) and crassifterpenoid A (5), together with three known compounds (2-4). The structures of the new compounds were determined by comprehensive spectroscopic methods, and their absolute configurations were determined by quantum chemical ECD calculation. Crassifterpenoid A (5) is the first germacrane-type sesquiterpene isolated from C. crassifolius, which enriched the diversity of chemical constituents in Croton crassifolius. In addition, the cytotoxicities of all compounds against human liver cancer lines HepG2 and Hep3B were determined, but none showed significant activity.
Pyran-2-one derivatives from Croton crassifolius as potent apoptosis inducers in HepG2 cells via p53-mediated Ras/Raf/ERK pathway.[Pubmed: 29852310]
None
Diterpenoids from Croton crassifolius include a novel skeleton possibly generated via an intramolecular [2+2]-photocycloaddition reaction.[Pubmed: 29117577]
Five previously undescribed terpenoids (cracrosons D-H), including three clerodane diterpenoids, together with 16 known diterpenoids were isolated from Croton crassifolius (Euphorbiaceae). Cracroson D features a previously undescribed carbon skeleton with an unprecedented cyclobutane ring. Their structures, including their absolute configurations, were elucidated using spectroscopic and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analyses along with CD calculations. A plausible biogenetic pathway for cracroson D is also proposed, which was supported by the experimental results. Additionally, all of the compounds were evaluated in vitro for cytotoxicity against T24 and A549 cells using the CCK-8 method.
Biotransfomation of cyperenoic acid by Cunninghamella elegans AS 3.2028 and the potent anti-angiogenic activities of its metabolites.[Pubmed: 28216250]
Cyperenoic acid (1) is one of the major sesquiterpenes isolated from Croton crassifolius, which exhibited potent anti-angiogenic activity. Traditional structural modification of 1 is difficult to perform by chemical technology due to the remarkable stability of the patchoulane skeleton. In order to overcome chemical synthesis difficulties and obtain structurally diverse derivations, microbial transformation of 1 by using Cunninghamella elegans AS 3.2028 was studied for the first time. Five new hydroxylated products 2-6 were obtained. Furthermore, cytotoxicity and anti-angiogenic activities of all the biotransformation products were evaluated by MTT assay and ELISA in HepG2 and MCF-7 cells. These results indicated that hydroxylated modification products 2-4 significantly inhibited VEGF release, which suggest the potential use of hydroxylated modification products for cancer therapy.
Cytotoxic clerodane diterpenoids from Croton crassifolius.[Pubmed: 28174107]
None
Crassins A-H, Diterpenoids from the Roots of Croton crassifolius.[Pubmed: 28150949]
None
Penduliflaworosin, a Diterpenoid from Croton crassifolius, Exerts Anti-Angiogenic Effect via VEGF Receptor-2 Signaling Pathway.[Pubmed: 28098802]
None


