Baicalein5- and 12-Lipoxygenase inhibitor CAS# 491-67-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 491-67-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281605 | Appearance | Yellow-brown powder |
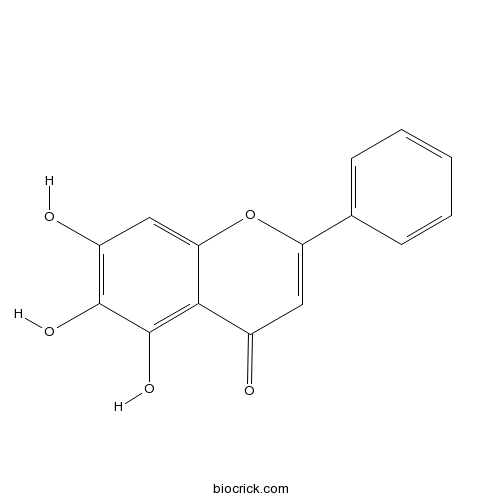
| Formula | C15H10O5 | M.Wt | 270.2 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 5,6,7-Trihydroxyflavone | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 34 mg/mL (125.81 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,6,7-trihydroxy-2-phenylchromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FXNFHKRTJBSTCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Baicalein has neuroprotective, anticancer, antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects, it inhibits mTORC1 pathway and PI3K kinase activity. Baicalein is mainly due to autophagic cell death through activation of the AMPK/ULK1 pathway and inhibition of mTOR/Raptor complex 1 expression; it can induce cancer cell death and proliferation retardation by the inhibition of CDC2 kinase and survivin associated with opposite role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and AKT. |
| Targets | p53 | PI3K | mTOR | ERK | Calcium Channel | p38MAPK | Akt | AMPK | Wnt/β-catenin | GSK-3 |
| In vitro | Baicalein upregulates DDIT4 expression which mediates mTOR inhibition and growth inhibition in cancer cells.[Pubmed: 25543165]Cancer Lett. 2015 Mar 28;358(2):170-9.Baicalein is a natural flavone that exhibits anticancer properties. Using microarrays we found that DDIT4 was the highest transcript induced by Baicalein in cancer cells. Baicalein inhibits agonist- and tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation while suppressing pulmonary tumor metastasis via cAMP-mediated VASP phosphorylation along with impaired MAPKs and PI3K-Akt activation.[Pubmed: 25268843]Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Nov 15;92(2):251-65.Recently, the importance of platelet activation in cancer metastasis has become generally accepted. As a result, the development of new platelet inhibitors with minimal adverse effects is now a promising area of targeted cancer therapy. Baicalein is a functional ingredient derived from the root of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, a plant used intraditional medicine. The pharmacological effects of this compound including anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory activities have already been demonstrated. However, its effects on platelet activation are unknown. We therefore investigated the effects of Baicalein on ligand-induced platelet aggregation and pulmonary cancer metastasis. Anticancer effects of baicalein on hepatocellular carcinoma cells.[Pubmed: 24596136]Phytother Res. 2014 Sep;28(9):1342-8.The therapeutic potential of Baicalein against hepatoma cells was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects of baicalein, baicalin and wogonin.[Pubmed: 11062694]Anticancer Res. 2000 Sep-Oct;20(5A):2861-5.Xanthine oxidase inhibitors are known to be therapeutically useful for the treatment of hepatitis and brain tumor. Baicalein, baicalin and wogonin, isolated from Scutellaria rivularis, have been reported to exhibit a strong activity on xanthine oxidase inhibition. |
| In vivo | Ameliorative effects of baicalein in MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson's disease: A microarray study.[Pubmed: 25895692 ]Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Jun;133:155-63.Baicalein, a flavonoid from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, has been shown to possess neuroprotective properties. |
| Kinase Assay | Baicalein induces cancer cell death and proliferation retardation by the inhibition of CDC2 kinase and survivin associated with opposite role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and AKT.[Pubmed: 18025287 ]Baicalein induces autophagic cell death through AMPK/ULK1 activation and downregulation of mTORC1 complex components in human cancer cells.[Pubmed: 25132405 ]FEBS J. 2014 Oct;281(20):4644-58.Baicalein, a flavonoid and aglycon hydrolyzed from baicalin, has anticancer properties in several human carcinomas, but its molecular mechanisms of action remain unclear. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Nov;6(11):3039-48.The bioactive flavonoid Baicalein has been shown to have in vitro growth-inhibitory activity in human cancer cells, although the mechanism of action is poorly understood. |
| Animal Research | The anti-inflammatory activity of Scutellaria rivularis extracts and its active components, baicalin, baicalein and wogonin.[Pubmed: 8739179 ]Am J Chin Med. 1996;24(1):31-6.
|

Baicalein Dilution Calculator

Baicalein Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.701 mL | 18.5048 mL | 37.0096 mL | 74.0192 mL | 92.5241 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7402 mL | 3.701 mL | 7.4019 mL | 14.8038 mL | 18.5048 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3701 mL | 1.8505 mL | 3.701 mL | 7.4019 mL | 9.2524 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.074 mL | 0.3701 mL | 0.7402 mL | 1.4804 mL | 1.8505 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.037 mL | 0.185 mL | 0.3701 mL | 0.7402 mL | 0.9252 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Baicalein (5,6,7-Trihydroxyflavone) is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor with an IC50 value of 3.12 mM.
In Vitro:Baicalein suppresses mitogen induced T cell proliferation and cytokine secretion in vitro. Pre-treatment with baicalein significantly suppresses Con A or anti-CD3/CD28 mAb induced proliferation as well as cytokine secretion at 25 μM. Baicalein treatment induces DNA binding of NF-κB but inhibits thioredoxin activity in the nuclear compartment[2]. Baicalein suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Baicalein significantly decreases the expression of SATB1 in MDA-MB-231 cells. Baicalein also downregulates the expression of Wnt1 and β-catenin proteins and transcription level of Wnt/β-catenin-targeted genes[3].
In Vivo:Baicalein suppresses induction of graft versus host disease but does not inhibit homeostatic proliferation of T-cells in mice. This observation clearly shows potent anti-inflammatory activity of baicalein in vivo[2]. Rats treated with baicalein are protected against an increase in heart to body weight ratio, plasma level of brain natriuretic peptides, intraventricular septum thickness, myocardial collagen volume of left ventricle (all P<0.05, respectively). The antifibrotic effects of baicalein are further illustrated by the suppressed expression of left ventricle pro-collagens I and III accompanied by the decreased expression of 12-lipoxygenase, and by reduced expression and activity of matrix metallopeptidase 9 and extracellular signal-regulated kinases. Baicalein can inhibit cardiac fibrosis in hypertensive rats[4].
References:
[1]. Shieh DE,et al. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects of baicalein, baicalin and wogonin. Anticancer Res. 2000 Sep-Oct;20(5A):2861-5.
[2]. Patwardhan RS, et al. Baicalein exhibits anti-inflammatory effects via inhibition of NF-κB transactivation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 May 15;108:75-89.
[3]. Ma X, et al. Baicalein suppresses metastasis of breast cancer cells by inhibiting EMT via downregulation of SATB1 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Apr 18;10:1419-41.
[4]. Kong EK, et al. A novel anti-fibrotic agent, baicalein, for the treatment of myocardial fibrosis in spontaneously hypertensiverats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 May 11;658(2-3):175-81.
- Kaempferide
Catalog No.:BCN5598
CAS No.:491-54-3
- Quercetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1261
CAS No.:491-50-9
- 4-HQN
Catalog No.:BCC2448
CAS No.:491-36-1
- Valeroidine
Catalog No.:BCN1920
CAS No.:490-96-0
- Gentisic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3408
CAS No.:490-79-9
- 2,5-Dihydroxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3825
CAS No.:490-78-8
- Homoquinolinic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6570
CAS No.:490-75-5
- Gaultherin
Catalog No.:BCN2482
CAS No.:490-67-5
- Epicatechin
Catalog No.:BCN5597
CAS No.:490-46-0
- Robinetin
Catalog No.:BCN5596
CAS No.:490-31-3
- Beta-Tocotrienol
Catalog No.:BCN3725
CAS No.:490-23-3
- a-Truxilline
Catalog No.:BCN1947
CAS No.:490-17-5
- Isosakuranin
Catalog No.:BCN3712
CAS No.:491-69-0
- Luteolin
Catalog No.:BCN5600
CAS No.:491-70-3
- Chrysoeriol
Catalog No.:BCN5601
CAS No.:491-71-4
- Iridin
Catalog No.:BCN6868
CAS No.:491-74-7
- Biochanin A
Catalog No.:BCN1224
CAS No.:491-80-5
- Hemokinin 1 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5923
CAS No.:491851-53-7
- TCS PIM-1 1
Catalog No.:BCC2447
CAS No.:491871-58-0
- Thermopsidine
Catalog No.:BCN7923
CAS No.:492-02-4
- (+)-Sparteine
Catalog No.:BCC9249
CAS No.:492-08-0
- Plathymenin
Catalog No.:BCN6810
CAS No.:492-12-6
- Butin
Catalog No.:BCN4630
CAS No.:492-14-8
- Kynurenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2228
CAS No.:492-27-3
Ameliorative effects of baicalein in MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson's disease: A microarray study.[Pubmed:25895692]
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Jun;133:155-63.
Baicalein, a flavonoid from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, has been shown to possess neuroprotective properties. The purpose of this study was to explore the effects of Baicalein on motor behavioral deficits and gene expression in N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced mice model of Parkinson's disease (PD). The behavioral results showed that Baicalein significantly improves the abnormal behaviors in MPTP-induced mice model of PD, as manifested by shortening the total time for climbing down the pole, prolonging the latent periods of rotarod, and increasing the vertical movements. Using cDNA microarray and subsequent bioinformatic analyses, it was found that Baicalein significantly promotes the biological processes including neurogenesis, neuroblast proliferation, neurotrophin signaling pathway, walking and locomotor behaviors, and inhibits dopamine metabolic process through regulation of gene expressions. Based on analysis of gene co-expression networks, the results indicated that the regulation of genes such as LIMK1, SNCA and GLRA1 by Baicalein might play central roles in the network. Our results provide experimental evidence for the potential use of Baicalein in the treatment of PD, and revealed gene expression profiles, biological processes and pathways influenced by Baicalein in MPTP-treated mice.
The anti-inflammatory activity of Scutellaria rivularis extracts and its active components, baicalin, baicalein and wogonin.[Pubmed:8739179]
Am J Chin Med. 1996;24(1):31-6.
Five extracts (n-hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, n-butanol and water) of Scutellaria rivularis Benth. were evaluated for their anti-inflammatory activity against carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats and compared with indomethacin. The result indicated that chloroform extract proved to be the most effective in all of the extracts. Consequently, three major components (baicalin, Baicalein and wogonin) of the chloroform extract were further tested for their anti-inflammatory activity using the same model. It was found that baicalin exhibits the greatest inhibition activity against carrageenan-induced rat paw edema.
Baicalein inhibits agonist- and tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation while suppressing pulmonary tumor metastasis via cAMP-mediated VASP phosphorylation along with impaired MAPKs and PI3K-Akt activation.[Pubmed:25268843]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Nov 15;92(2):251-65.
Recently, the importance of platelet activation in cancer metastasis has become generally accepted. As a result, the development of new platelet inhibitors with minimal adverse effects is now a promising area of targeted cancer therapy. Baicalein is a functional ingredient derived from the root of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, a plant used intraditional medicine. The pharmacological effects of this compound including anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory activities have already been demonstrated. However, its effects on platelet activation are unknown. We therefore investigated the effects of Baicalein on ligand-induced platelet aggregation and pulmonary cancer metastasis. In the present study, Baicalein inhibited agonist-induced platelet aggregation, granule secretion markers (P-selectin expression and ATP release), [Ca(2+)]i mobilization, and integrin alphaIIbbeta3 expression. Additionally, Baicalein attenuated ERK2, p38, and Akt activation, and enhanced VASP phosphorylation. Indeed, Baicalein was shown to directly inhibit PI3K kinase activity. Moreover, Baicalein attenuated the platelet aggregation induced by C6 rat glioma tumor cells in vitro and suppressed CT26 colon cancer metastasis in mice. These features indicate that Baicalein is a potential therapeutic drug for the prevention of cancer metastasis.
Baicalein upregulates DDIT4 expression which mediates mTOR inhibition and growth inhibition in cancer cells.[Pubmed:25543165]
Cancer Lett. 2015 Mar 28;358(2):170-179.
Baicalein is a natural flavone that exhibits anticancer properties. Using microarrays we found that DDIT4 was the highest transcript induced by Baicalein in cancer cells. We confirmed in multiple cancer cell lines large, dose-related expression of DDIT4 by quantitative RT-PCR and immunoblot, which correlates with growth inhibition. Time course experiments demonstrate that DDIT4 is rapidly inducible, with high expression maintained for several days in vitro. Induction of DDIT4 expression is p53 independent based on evaluation of p53 knockout cells. Since DDIT4 is known to inhibit mTORC1 activity we confirmed that Baicalein suppresses phosphorylation of mTORC1 targets. Using RNA interference we demonstrate that mTORC1 activity and growth inhibition by Baicalein is attenuated by knockdown of DDIT4. We furthermore demonstrate suppression of established tumors by Baicalein in a mouse model of breast cancer with increased DDIT4 expression in the tumors. Finally, we demonstrate that Baicalein upregulates DDIT4 and causes mTORC1 and growth inhibition in platinum resistant cancer cells in marked contrast to platinum chemotherapy treatment. These studies demonstrate that Baicalein inhibits mTORC1 through DDIT4 expression, and may be useful in cancer chemotherapy and chemoprevention.
Baicalein induces cancer cell death and proliferation retardation by the inhibition of CDC2 kinase and survivin associated with opposite role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and AKT.[Pubmed:18025287]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Nov;6(11):3039-48.
The bioactive flavonoid Baicalein has been shown to have in vitro growth-inhibitory activity in human cancer cells, although the mechanism of action is poorly understood. Baicalein (40-80 mumol/L for 24 h) more effectively induced cytotoxicity compared with other flavonoids (baicalin, catechin, genistein, quercetin, and rutin) in bladder cancer cells. Baicalein induced cell proliferation inhibition and apoptosis. The levels of cyclin B1 and phospho-CDC2 (Thr(161)) were reduced, whereas the G(2)-M phases were elevated by Baicalein. Treatment of CDC2 kinase or CDC25 phosphatase inhibitors augments the Baicalein-induced cytotoxicity. A variety of human bladder cancer cell lines expressed survivin proteins, which were located on the mitotic phases and regulated mitotic progression. Baicalein markedly reduced survivin protein expression. Transfection of a survivin small interfering RNA diminished the level of survivin proteins and increased the Baicalein-mediated cell death. Overexpression of survivin enhanced cell proliferation and resisted the Baicalein-induced cytotoxicity. Interestingly, Baicalein induced the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and AKT. SB203580, a specific p38 MAPK inhibitor, attenuated proliferation inhibition and restored the protein levels of phospho-CDC2 (Thr(161)) and survivin in the Baicalein-exposed cells; conversely, blockade of AKT activation enhanced cytotoxicity and the reduction of phospho-CDC2 (Thr(161)) and survivin proteins. As a whole, these findings provide that the opposite role of p38 MAPK and AKT regulates CDC2 kinase and survivin and the inhibition of CDC2-survivin pathway by Baicalein contributes to apoptosis and proliferation retardation in cancer cells.
Anticancer effects of baicalein on hepatocellular carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:24596136]
Phytother Res. 2014 Sep;28(9):1342-8.
The therapeutic potential of Baicalein against hepatoma cells was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. In cell viability assays, Baicalein showed significant cytotoxicity against the hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines H22, Bel-7404, and Hep G2 and moderate cytotoxicity against immortalized human hepatocytes. Baicalein induced G0/G1-phase arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, inhibited AKT, and promoted the degradation of beta-catenin and cyclin D1 without activation of GSK-3beta. Furthermore, Baicalein significantly inhibited H22 xenograft tumor growth without causing obvious adverse effects on weight or liver and spleen weight indexes in ICR mice. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that the inhibition of tumor growth in Baicalein-treated mice was associated with decreased AKT, beta-catenin, and cyclin D1 expression ex vivo. Our data indicate that Baicalein might regulate cyclin D1 transcription via a beta-catenin-dependent mechanism, leading to cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase and impaired cancer cell proliferation. These results suggest that Baicalein is a potential candidate for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects of baicalein, baicalin and wogonin.[Pubmed:11062694]
Anticancer Res. 2000 Sep-Oct;20(5A):2861-5.
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors are known to be therapeutically useful for the treatment of hepatitis and brain tumor. Baicalein, baicalin and wogonin, isolated from Scutellaria rivularis, have been reported to exhibit a strong activity on xanthine oxidase inhibition. In this study, their antioxidant activity was evaluated by modified xanthine oxidase inhibition and cytochrome c reduced methods. The results showed that the order of activity on xanthine oxidase inhibition was Baicalein > wogonin > baicalin, IC50 = 3.12, 157.38 and 215.19 microM, respectively, whereas the activity on cytochrome c reduction was baicalin > wogonin > Baicalein (IC50 = 224.12, 300.10 and 370.33 microM, respectively). In another study, an electron spin resonance (ESR) technique was used to further confirm the direct free radical scavenging activity. Both Baicalein and baicalin demonstrated a strong activity on eliminating the superoxide radical (.O2-) (Baicalein: 7.31 x 10(4) u/g; baicalin: 1.19 x 10(5) u/g). The IC50 of Baicalein was 2.8 fold higher than that of baicalin. However they had no significant effect on scavenging hydroxyl radical (.OH). The present results demonstrated that Baicalein and baicalin posed a different pathological pathway. The antioxidant function of baicalin was mainly based on scavenging superoxide radical whilst Baicalein was a good xanthine oxidase inhibitor.
Baicalein induces autophagic cell death through AMPK/ULK1 activation and downregulation of mTORC1 complex components in human cancer cells.[Pubmed:25132405]
FEBS J. 2014 Oct;281(20):4644-58.
Baicalein, a flavonoid and aglycon hydrolyzed from baicalin, has anticancer properties in several human carcinomas, but its molecular mechanisms of action remain unclear. Here, we show that Baicalein leads to human cancer cell death by inducing autophagy rather than apoptosis, because cell death induced by Baicalein was completely reversed by suppressing the expression levels of key molecules in autophagy such as Beclin 1, vacuolar protein sorting 34 (Vps34), autophagy-related (Atg)5 and Atg7, but not by pan-caspase inhibitor. Our data revealed that Baicalein significantly increased the number of green fluorescence protein-cytosol-associated protein light chain 3 (GFP-LC3)-containing puncta and LC3B-II expression levels, which were further enhanced by chloroquine treatment. Furthermore, a luciferase-based reporter assay showed that the ratio of RLuc-LC3wt/RLuc-LC3G120A was greatly reduced. The data suggested that Baicalein induced not only autophagosome formation, but also autophagic flux. Experiments using short interfering RNAs and pharmacological inhibitors revealed that Beclin 1, Vps34, Atg5, Atg7 and UNC-51 (Caenorhabditis elegans)-like kinase 1 (ULK1) play pivotal roles in mediating Baicalein-induced autophagy. Moreover, Baicalein activated AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)alpha, leading to ULK1 activation through phosphorylation at Ser555, whereas both protein and mRNA levels of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and Raptor, upstream inhibitors of ULK1 and autophagy, were markedly downregulated by Baicalein. Our data suggest that the anticancer effects of Baicalein are mainly due to autophagic cell death through activation of the AMPK/ULK1 pathway and inhibition of mTOR/Raptor complex 1 expression. These results provide new mechanistic insights into the anticancer functions of autophagy inducers, such as Baicalein, which may be used as potential therapeutics for cancer treatment.
Baicalein inhibits IL-1beta- and TNF-alpha-induced inflammatory cytokine production from human mast cells via regulation of the NF-kappaB pathway.[Pubmed:18039391]
Clin Mol Allergy. 2007 Nov 26;5:5.
BACKGROUND: Human mast cells are multifunctional cells capable of a wide variety of inflammatory responses. Baicalein (BAI), isolated from the traditional Chinese herbal medicine Huangqin (Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi), has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. We examined its effects and mechanisms on the expression of inflammatory cytokines in an IL-1beta- and TNF-alpha-activated human mast cell line, HMC-1. METHODS: HMC-1 cells were stimulated either with IL-1beta (10 ng/ml) or TNF-alpha (100 U/ml) in the presence or absence of BAI. We assessed the expression of IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 by ELISA and RT-PCR, NF-kappaB activation by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA), and IkappaBalpha activation by Western blot. RESULTS: BAI (1.8 to 30 muM) significantly inhibited production of IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 in a dose-dependent manner in IL-1beta-activated HMC-1. BAI (30 muM) also significantly inhibited production of IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 in TNF-alpha-activated HMC-1. Inhibitory effects appear to involve the NF-kappaB pathway. BAI inhibited NF-kappaB activation in IL-1beta- and TNF-alpha-activated HMC-1. Furthermore, BAI increased cytoplasmic IkappaBalpha proteins in IL-1beta- and TNF-alpha-activated HMC-1. CONCLUSION: Our results showed that BAI inhibited the production of inflammatory cytokines through inhibition of NF-kappaB activation and IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and degradation in human mast cells. This inhibitory effect of BAI on the expression of inflammatory cytokines suggests its usefulness in the development of novel anti-inflammatory therapies.
Baicalein inhibits Raf-1-mediated phosphorylation of MEK-1 in C6 rat glioma cells.[Pubmed:12568909]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2003 Feb 7;461(1):1-7.
Baicalein is a flavonoid derived from the Scutellaria root. In investigations of the inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis in C6 rat glioma cells, we found that Baicalein had a potent inhibitory activity on prostaglandin synthesis induced by either histamine or A23187, a Ca(2+) ionophore. Baicalein inhibited histamine- or A23187-induced phosphorylation of p42/p44 extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), which causes the phosphorylation of cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (PLA(2)). Baicalein also inhibited the phosphorylation of MAPK kinase-1 (MEK-1) induced by histamine or A23187 in the cells. To examine the site of action of Baicalein, MEK-1 and Raf-1 were prepared by immunoprecipitation with anti-MEK-1 and anti-Raf-1 antibodies, respectively. Baicalein inhibited the phosphorylation of exogenous MEK-1 by Raf-1 under cell-free conditions, while it did not change the phosphorylation of exogenous p42 MAPK by MEK-1. These results imply that Baicalein inhibits the ERK/MAPK cascade, acting on the phosphorylation of MEK-1 by Raf-1.
Baicalein induces a dual growth arrest by modulating multiple cell cycle regulatory molecules.[Pubmed:11513834]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Aug 17;425(3):165-71.
Baicalein, a flavonoid present in the root of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, has been reported to inhibit cell proliferation in several types of cells. In this study, the effect of Baicalein on cell growth and the mechanism of growth modulation were examined in primary cultured rat heart endothelial cells. Here, we report that treatment with 100-microM Baicalein caused an almost complete inhibition of cell proliferation after 5 days of incubation. Baicalein mediated G1 and G2 growth arrest accompanied by the down-regulation of cyclin D2, cyclin A, cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) and cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (Cdk2), and up-regulation of p15(Ink4B), p21(CIP1/Waf1), p53 and cyclin E. Evaluation of the kinase activity of cyclin-Cdk complexes showed that Baicalein decreased Cdk1, Cdk2, cyclin D2 and cyclin A expression in endothelial cells, leading to markedly reduced Cdk/cyclin-associated kinase activities. These results suggest that Baicalein inhibits the proliferation of rat heart endothelial cells via G1 and G2 arrest in association with the down-regulation of the expression and function of Cdk1, Cdk2, cyclin D2 and cyclin A proteins, and up-regulation of cyclin E, p15(Ink4B), p53 and p21(CIP1/Waf1).


