Gentisic acidCAS# 490-79-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 490-79-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3469 | Appearance | Powder |
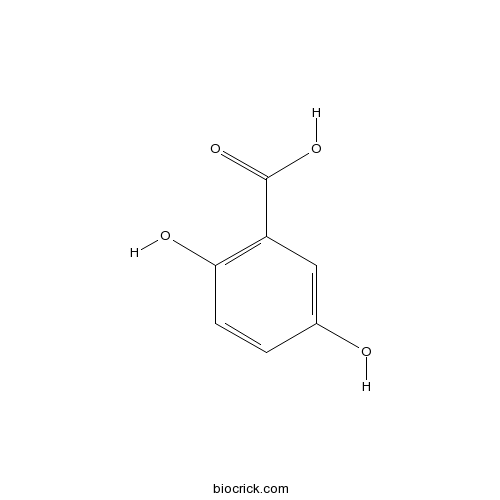
| Formula | C7H6O4 | M.Wt | 154.1 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (648.85 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1O)C(=O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WXTMDXOMEHJXQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C7H6O4/c8-4-1-2-6(9)5(3-4)7(10)11/h1-3,8-9H,(H,10,11) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Gentisic acid, an active metabolite of salicylic acid degradation, has a broad spectrum of biological activity, such as antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, antirheumatic and antioxidant properties; it also has antimutagenic/protective effects that may contribute to human health. Gentisic acid has protective effect against cyclophosphamide induced genotoxicity and hepatotoxicity in Swiss albino mice. |
| Targets | LDL | Immunology & Inflammation related |
| In vitro | Cytotoxicity, mutagenicity, and antimutagenicity of the gentisic acid on HTC cells.[Pubmed: 28511592 ]Drug Chem Toxicol. 2017 May 16:1-7.Gentisic acid (GA) exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibiotic activities. This substance can be found in citrus fruits, grapes, olive oil, and peas. Gentisic acid, an aspirin metabolite, inhibits oxidation of low-density lipoprotein and the formation of cholesterol ester hydroperoxides in human plasma.[Pubmed: 15862799]Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Apr 25;513(3):173-9.Gentisic acid, an aspirin metabolite, has an antioxidant effect, although its detailed mechanism remains elusive. |
| Animal Research | Modulatory effects of gentisic acid against genotoxicity and hepatotoxicity induced by cyclophosphamide in Swiss albino mice.[Pubmed: 22221102 ]J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;64(2):259-67.This study evaluated the protective effects of Gentisic acid (GA) against genotoxicity and hepatotoxicity induced by cyclophosphamide (CP) in Swiss albino mice. |

Gentisic acid Dilution Calculator

Gentisic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.4893 mL | 32.4465 mL | 64.8929 mL | 129.7859 mL | 162.2323 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2979 mL | 6.4893 mL | 12.9786 mL | 25.9572 mL | 32.4465 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6489 mL | 3.2446 mL | 6.4893 mL | 12.9786 mL | 16.2232 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1298 mL | 0.6489 mL | 1.2979 mL | 2.5957 mL | 3.2446 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0649 mL | 0.3245 mL | 0.6489 mL | 1.2979 mL | 1.6223 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 2,5-Dihydroxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3825
CAS No.:490-78-8
- Homoquinolinic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6570
CAS No.:490-75-5
- Gaultherin
Catalog No.:BCN2482
CAS No.:490-67-5
- Epicatechin
Catalog No.:BCN5597
CAS No.:490-46-0
- Robinetin
Catalog No.:BCN5596
CAS No.:490-31-3
- Beta-Tocotrienol
Catalog No.:BCN3725
CAS No.:490-23-3
- a-Truxilline
Catalog No.:BCN1947
CAS No.:490-17-5
- SBC-115076
Catalog No.:BCC6440
CAS No.:489415-96-5
- ML 213
Catalog No.:BCC6213
CAS No.:489402-47-3
- Guaiol
Catalog No.:BCN6619
CAS No.:489-86-1
- Guaiazulen
Catalog No.:BCC8180
CAS No.:489-84-9
- Globulol
Catalog No.:BCN6901
CAS No.:489-41-8
- Valeroidine
Catalog No.:BCN1920
CAS No.:490-96-0
- 4-HQN
Catalog No.:BCC2448
CAS No.:491-36-1
- Quercetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1261
CAS No.:491-50-9
- Kaempferide
Catalog No.:BCN5598
CAS No.:491-54-3
- Baicalein
Catalog No.:BCN5599
CAS No.:491-67-8
- Isosakuranin
Catalog No.:BCN3712
CAS No.:491-69-0
- Luteolin
Catalog No.:BCN5600
CAS No.:491-70-3
- Chrysoeriol
Catalog No.:BCN5601
CAS No.:491-71-4
- Iridin
Catalog No.:BCN6868
CAS No.:491-74-7
- Biochanin A
Catalog No.:BCN1224
CAS No.:491-80-5
- Hemokinin 1 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5923
CAS No.:491851-53-7
- TCS PIM-1 1
Catalog No.:BCC2447
CAS No.:491871-58-0
Cytotoxicity, mutagenicity, and antimutagenicity of the gentisic acid on HTC cells.[Pubmed:28511592]
Drug Chem Toxicol. 2018 Apr;41(2):155-161.
Gentisic acid (GA) exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibiotic activities. This substance can be found in citrus fruits, grapes, olive oil, and peas. Considering that there are few studies in the literature on the toxicity of GA, the present work aimed to investigate its cytotoxic, mutagenic, and antimutagenic activities on HTC cells. GA was diluted in culture medium at the final concentration of 0.08, 0.16, 0.8, 1.6, and 8 mug/mL. The cytotoxicity was determined by the MTT assay and Trypan Blue exclusion method, with methyl methanesulfonate and doxorubicin as positive controls, respectively. The cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay determined the mutagenic/antimutagenic activity with benzo[a]pyrene as positive control. Negative control received culture medium only. GA (0.08-8 mug/mL) was not cytotoxic to HTC cells by the MTT assay nor the Trypan Blue exclusion method as no statistical difference was observed when compared to the control. Concentration of 0.08 and 0.8 mug/mL showed no mutagenic or clastogenic effects, as no significant micronuclei inductions were observed, different from 8 mug/mL, that was mutagenic. Furthermore, none of the concentrations presented an antiproliferative activity. The antimutagenic activity of GA (0.08 mug/mL) was observed at the simultaneous treatment, as it reduced the frequency of micronuclei by 76% (24 h) and 79% (48 h). Although pre- and post-treatments were not statistically different from the mutagen, they reduced the induced-damage by 11% and 21%, respectively. The present study indicated the absence of cytotoxicity and antiproliferative activities of GA, in addition to their antimutagenic/protective effects that may contribute to human health.
Modulatory effects of gentisic acid against genotoxicity and hepatotoxicity induced by cyclophosphamide in Swiss albino mice.[Pubmed:22221102]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;64(2):259-67.
OBJECTIVES: This study evaluated the protective effects of Gentisic acid (GA) against genotoxicity and hepatotoxicity induced by cyclophosphamide (CP) in Swiss albino mice. METHODS: Mice were pretreated with GA orally at doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg for 14 consecutive days before the administration of a single intraperitoneal dose of 50 mg/kg CP. The ameliorative effect of GA on genotoxicity was studied using the in-vivo bone marrow micronuclei induction test, DNA integrity and alkaline unwinding assay. The activity of various oxidative stress enzymes were estimated in hepatic tissue. KEY FINDINGS: A single intraperitoneal administration of CP in mice increased the malondialdehyde level, depleted the glutathione content and antioxidant enzyme activity (glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, catalase and quinone reductase), and induced DNA strand breaks and micronuclei induction. Oral pretreatment with GA at both doses caused a significant reduction in malondialdehyde and glutathione levels, restoration of antioxidant enzyme activity, reduction in micronuclei formation and DNA fragmentation. Serum toxicity marker enzymes such as aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase and lactate dehydrogenase were increased after CP treatment but restored in GA pretreated groups. CONCLUSION: The results support the protective effect of GA against CP induced genotoxicity and hepatotoxicity.
Gentisic acid, an aspirin metabolite, inhibits oxidation of low-density lipoprotein and the formation of cholesterol ester hydroperoxides in human plasma.[Pubmed:15862799]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Apr 25;513(3):173-9.
Gentisic acid, an aspirin metabolite, has an antioxidant effect, although its detailed mechanism remains elusive. The present study was designed to determine whether it inhibits low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation and the formation of lipid hydroperoxides in human plasma. The susceptibility of LDL oxidative modification was investigated by a method using 2,2'-azobis or Cu2+. To study the effect of Gentisic acid on free radical-induced damage to plasma lipids, cholesterol ester hydroperoxides generated by incubating human fresh plasma with Cu2+ and Gentisic acid was analyzed. Gentisic acid inhibited LDL oxidation in a concentration-dependent manner. It significantly inhibited the formation of cholesterol ester hydroperoxides in plasma, and was consumed after the depletion of ascorbic acid and reduced form of coenzyme Q-10 (CoQH2-10), whereas concentrations of other antioxidants remained unchanged. Gentisic acid had a potent free radical scavenging activity with a minimal chelating effect. The potent antioxidant property of Gentisic acid may partly account for the anti-atherogenic effects of aspirin.


