KaempferideO-methylated flavonol CAS# 491-54-3 |
- SB 431542
Catalog No.:BCC3658
CAS No.:301836-41-9
- SB-505124 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1930
CAS No.:356559-13-2
- SB525334
Catalog No.:BCC2531
CAS No.:356559-20-1
- A 77-01
Catalog No.:BCC1318
CAS No.:607737-87-1
- LY2109761
Catalog No.:BCC3806
CAS No.:700874-71-1
- LY2157299
Catalog No.:BCC3709
CAS No.:700874-72-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 491-54-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281666 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C16H12O6 | M.Wt | 300.3 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Kaempferol 4'-O-methyl ether | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 20 mg/mL (66.61 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
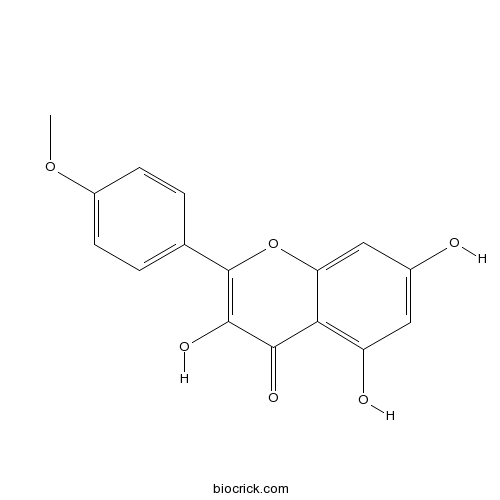
| Chemical Name | 3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=C(C(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SQFSKOYWJBQGKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H12O6/c1-21-10-4-2-8(3-5-10)16-15(20)14(19)13-11(18)6-9(17)7-12(13)22-16/h2-7,17-18,20H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Kaempferide has a variety of effects including anti-carcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-bacterial and anti-viral properties.it can protect DNA from radiation induced lesions resulting from radiation exposures under in vitro and ex vivo conditions. |
| Targets | Caspase | PARP | BMP-2 |
| In vitro | Comparison of effects of kaempferide and anhydroicaritin on biomineralization of cultured osteoblasts[Pubmed: 22993853]Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012 Jul;47(7):890-6.This study is to compare the effects of Kaempferide and anhydroicaritin on biomineralization of rat osteoblasts (ROB) in vitro.
Antioxidant capacity and radioprotective propertiesof the flavonoids galangin and kaempferide isolated from Alpinia galanga L. (Zingiberaceae) against radiation induced cellular DNA damage[Reference: WebLink]Int.J.Radiat. Res.,2013, 11(2):81-9.Alpinia galanga L belonging to the family Zingiberaceae is widely grown in the state of Kerala, India. They are effective antioxidant and free radical scavenger under both in vitro and in vivo condition. The efficacy of the isolated flavonoids in conferring protection from radiation induced damages to genomic DNA was studied.
|
| Cell Research | Kaempferide, the most active among the four flavonoids isolated and characterized from Chromolaena odorata, induces apoptosis in cervical cancer cells while being pharmacologically safe[Reference: WebLink]Inhibition of in vitro growth and arrest in the G0/G1 phase of HCT8 line human colon cancer cells by kaempferide triglycoside from Dianthus caryophyllus.[Pubmed: 20104502]Phytother Res. 2010 Sep;24(9):1302-8.The effects of phytoestrogens have been studied in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and in various non-gonadal targets. Epidemiologic and experimental evidence indicates a protective effect of phytoestrogens also in colorectal cancer. The mechanism through which estrogenic molecules control colorectal cancer tumorigenesis could possibly involve estrogen receptor beta, the predominantly expressed estrogen receptor subtype in colon mucosa.
Rsc Adv., 2015, 5(122):100912-22.Chromolaena odorata, commonly known as Siam weed, is popular as a traditional medicine. We report the isolation and characterization of four compounds from a cytotoxic fraction, F-17, isolated from the dichloromethane (DCM) extract of C. odorata by bioactivity-guided fractionation.
|

Kaempferide Dilution Calculator

Kaempferide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.33 mL | 16.65 mL | 33.3 mL | 66.6001 mL | 83.2501 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.666 mL | 3.33 mL | 6.66 mL | 13.32 mL | 16.65 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.333 mL | 1.665 mL | 3.33 mL | 6.66 mL | 8.325 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0666 mL | 0.333 mL | 0.666 mL | 1.332 mL | 1.665 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0333 mL | 0.1665 mL | 0.333 mL | 0.666 mL | 0.8325 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
The effects of phytoestrogens have been studied in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and various non-gonadal targets. Epidemiologic and experimental evidence indicates a protective effect of phytoestrogens also in colorectal cancer. The mechanism through which estrogenic molecules control colorectal cancer tumorigenesis could possibly involve estrogen receptor β, which is the predominantly expressed estrogen receptor subtype in colon mucosa.
In vitro: Kaempferide triglycoside proved to inhibit the proliferation of native and estrogen receptor β overexpressing colon cancer cells via a mechanism not mediated by ligand binding dependent estrogen receptor activation. It affected HCT8 cell cycle progression through increasing the G0/G1 cell fraction and in estrogen receptor β overexpressing cells increased two antioxidant enzymes [1].
In vivo: The aim of one previous study was to evaluate the effect of kaempferol on tissue lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine induced colorectal cancer in male Wistar rats and to compare its efficacy with irinotecan. This study revealed that kaempferol could be safely used as a chemopreventive agent in colorectal cancer [2].
Clinical trial: Up to now, kaempferide is still in the preclinical development stage.
Reference:
[1] Martineti V, Tognarini I, Azzari C, Carbonell Sala S, Clematis F, Dolci M, Lanzotti V, Tonelli F, Brandi ML, Curir P. Inhibition of in vitro growth and arrest in the G0/G1 phase of HCT8 line human colon cancer cells by kaempferide triglycoside from Dianthus caryophyllus. Phytother Res. 2010 Sep;24(9):1302-8.
[2] Nirmala P, Ramanathan M. Effect of kaempferol on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine induced colorectal carcinoma in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Mar 1;654(1):75-9.
- Quercetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1261
CAS No.:491-50-9
- 4-HQN
Catalog No.:BCC2448
CAS No.:491-36-1
- Valeroidine
Catalog No.:BCN1920
CAS No.:490-96-0
- Gentisic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3408
CAS No.:490-79-9
- 2,5-Dihydroxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3825
CAS No.:490-78-8
- Homoquinolinic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6570
CAS No.:490-75-5
- Gaultherin
Catalog No.:BCN2482
CAS No.:490-67-5
- Epicatechin
Catalog No.:BCN5597
CAS No.:490-46-0
- Robinetin
Catalog No.:BCN5596
CAS No.:490-31-3
- Beta-Tocotrienol
Catalog No.:BCN3725
CAS No.:490-23-3
- a-Truxilline
Catalog No.:BCN1947
CAS No.:490-17-5
- SBC-115076
Catalog No.:BCC6440
CAS No.:489415-96-5
- Baicalein
Catalog No.:BCN5599
CAS No.:491-67-8
- Isosakuranin
Catalog No.:BCN3712
CAS No.:491-69-0
- Luteolin
Catalog No.:BCN5600
CAS No.:491-70-3
- Chrysoeriol
Catalog No.:BCN5601
CAS No.:491-71-4
- Iridin
Catalog No.:BCN6868
CAS No.:491-74-7
- Biochanin A
Catalog No.:BCN1224
CAS No.:491-80-5
- Hemokinin 1 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5923
CAS No.:491851-53-7
- TCS PIM-1 1
Catalog No.:BCC2447
CAS No.:491871-58-0
- Thermopsidine
Catalog No.:BCN7923
CAS No.:492-02-4
- (+)-Sparteine
Catalog No.:BCC9249
CAS No.:492-08-0
- Plathymenin
Catalog No.:BCN6810
CAS No.:492-12-6
- Butin
Catalog No.:BCN4630
CAS No.:492-14-8
[Comparison of effects of kaempferide and anhydroicaritin on biomineralization of cultured osteoblasts].[Pubmed:22993853]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012 Jul;47(7):890-6.
This study is to compare the effects of Kaempferide and anhydroicaritin on biomineralization of rat osteoblasts (ROB) in vitro. Calvarias were dissected aseptically from newborn SD rats, the osteoblasts were obtained by enzyme digestion and were cultured in MEM containing 10% FBS. The medium was changed every three days, and serial subculture was performed when cells covered with 90% of the dish. Kaempferide and anhydroicaritin were separately added with final concentrations of 1 x 10(-4), 1 x 10(-5), 1 x 10(-6) and 1 x 10(-7) mol x L(-1) under the conditions of osteogenic differentiation. The proliferation was measured by MTT, and the optimal concentration was detected by the ALP activity at the 9th day after osteogenic induction culture. The osteogenic indexes of Kaempferide, anhydroicaritin and control group with the optimal concentration were compared. The result showed that the anhydroicaritin at concentration of 1 x 10(-5) mol x L(-1) had significantly promoted the activity of ALP, calcium content and osteocalcin content, increased the number of CFU-F(ALP) and mineralized nodules, enhanced the mRNA level of BMP-2, OSX and Runx-2, which are key genes of osteogenic differentiation, and raised the protein content of collagen-I. However, the Kaempferide group had not significantly represented the ability that promoted osteogenic differentiation of ROB. The difference of osteogenic differentiation on ROB between Kaempferide and anhydroicaritin was caused by the prenyl group on C-8 of icariin.
Inhibition of in vitro growth and arrest in the G0/G1 phase of HCT8 line human colon cancer cells by kaempferide triglycoside from Dianthus caryophyllus.[Pubmed:20104502]
Phytother Res. 2010 Sep;24(9):1302-8.
The effects of phytoestrogens have been studied in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and in various non-gonadal targets. Epidemiologic and experimental evidence indicates a protective effect of phytoestrogens also in colorectal cancer. The mechanism through which estrogenic molecules control colorectal cancer tumorigenesis could possibly involve estrogen receptor beta, the predominantly expressed estrogen receptor subtype in colon mucosa.To validate this hypothesis, we therefore used an engineered human colon cancer cell line induced to overexpress estrogen receptor beta, beside its native cell line, expressing very low levels of ERbeta and not expressing ERalpha; as a phytoestrogenic molecule, we used Kaempferide triglycoside, a glycosylated flavonol from a Dianthus caryophyllus cultivar. The inhibitory properties of this molecule toward vegetal cell growth have been previously demonstrated: however, no data on its activity on animal cell or information about the mechanism of this activity are available. Kaempferide triglycoside proved to inhibit the proliferation of native and estrogen receptor beta overexpressing colon cancer cells through a mechanism not mediated by ligand binding dependent estrogen receptor activation. It affected HCT8 cell cycle progression by increasing the G(0)/G(1) cell fraction and in estrogen receptor beta overexpressing cells increased two antioxidant enzymes. Interestingly, the biological effects of this Kaempferide triglycoside were strengthened by the presence of high levels of estrogen receptor beta.Pleiotropic molecular effects of phytoestrogens may explain their protective activity against colorectal cancer and may represent an interesting area for future investigation with potential clinical applications.


