LY2109761TβRI/II kinase inhibitor CAS# 700874-71-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 700874-71-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11655119 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H27N5O2 | M.Wt | 441.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 30 mg/mL (67.95 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
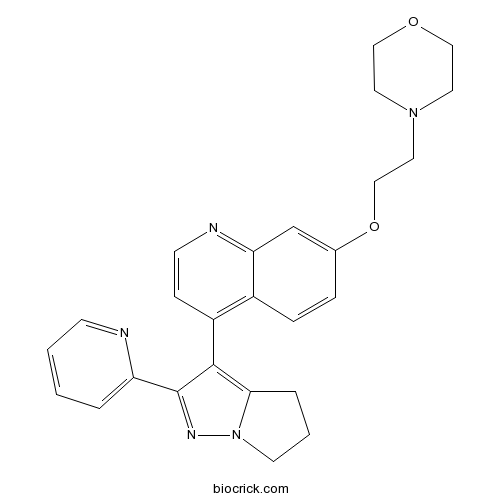
| Chemical Name | 4-[2-[4-(2-pyridin-2-yl-5,6-dihydro-4H-pyrrolo[1,2-b]pyrazol-3-yl)quinolin-7-yl]oxyethyl]morpholine | ||
| SMILES | C1CC2=C(C(=NN2C1)C3=CC=CC=N3)C4=C5C=CC(=CC5=NC=C4)OCCN6CCOCC6 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IHLVSLOZUHKNMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H27N5O2/c1-2-9-27-22(4-1)26-25(24-5-3-11-31(24)29-26)21-8-10-28-23-18-19(6-7-20(21)23)33-17-14-30-12-15-32-16-13-30/h1-2,4,6-10,18H,3,5,11-17H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | LY2109761 is a novel selective dual inhibitor of TGF-β receptor type I/II (TβRI/II) with Ki of 38 nM and 300 nM, respectively. | |||||
| Targets | TβRI | TβRII | ||||
| IC50 | 38 nM (Ki) | 300 nM (Ki) | ||||
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | Human cell MDA PCa 2b, PC-3 lines. |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is <10 mm. general tips for obtaining a higher concentration: please warm the tube at 37 °c 10 minutes and> |
| Reacting condition | 24h; 4 μM |
| Applications | A crucial step in the transduction of TGF-β 1 signals is the phosphorylation of receptor-activated Smad2 and Smad3. We thus assessed the phosphorylation of Smad2 in lysates of MDA PCa 2b cells, PC-3 cells, and PMOs treated with rhTGF- β1. We found that TGF-β1 induces phosphorylation of Smad2 in PC-3 cells and PMOs but not in MDA PCa 2b cells. Further, treatment with LY2109761 reverses the Smad2 phosphorylation induced by rhTGF-β1. In other words, LY2109761 inhibits TGF-β1–induced Smad2 activation in PC-3 cells and PMOs. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
| Animal models | Male SCID mice |
| Dosage form | 200 mg/kg/day; oral taken |
| Application | After 3 weeks of treatment, X-ray analysis of the vehicle control group revealed two broken bones and loss of 30%–70% of the radiopaque areas in the tumor-bearing bones. MRI analysis showed a significantly smaller tumor volume in the treated group than in the controls (p =0.012). Micro-CT analysis of the tumor-bearing bones of the controls and treated mice demonstrated significantly lower BV (p=0.00043), BMC (p =0.000132), and BMD (p = 0.000085) in the control mice. Furthermore, BV, BMC, and BMD in the treated group were restored to values found in the normal (uninjected) femurs, which supports the efficacy of treatment. Finally, bone histomorphometric analysis demonstrated that LY2109761 inhibited PC-3-induced activation of osteoclasts. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Wan X, Li Z G, Yingling J M, et al. Effect of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) receptor I kinase inhibitor on prostate cancer bone growth[J]. Bone, 2012, 50(3): 695-703. | |

LY2109761 Dilution Calculator

LY2109761 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2649 mL | 11.3245 mL | 22.649 mL | 45.2981 mL | 56.6226 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.453 mL | 2.2649 mL | 4.5298 mL | 9.0596 mL | 11.3245 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2265 mL | 1.1325 mL | 2.2649 mL | 4.5298 mL | 5.6623 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0453 mL | 0.2265 mL | 0.453 mL | 0.906 mL | 1.1325 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0226 mL | 0.1132 mL | 0.2265 mL | 0.453 mL | 0.5662 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
LY2109761 is a small-molecule inhibitor selectively targeting both TGF-β receptor type I and II ((TβRI/II)) with Ki of 38 nM and 300 nM, respectively [1]. It gave IC50 value of 69 nM in TβRI enzymatic assay [2]. Crystal structure showed the binding of LY2109761 to the ATP binding site of the TGF-β R1 kinase domain [2]. Weak inhibitory activities were reported for other kinases, including Lck, Sapk2α, MKK6, Fyn, and JNK3 (18–89% inhibition at 20 µM) [2].
LY2109761 has shown potential anti-tumor activity in preclinical studies. Deregulation of TGF-β signaling pathway is correlated with various malignant. LY2109761 suppressed proliferation, migration and invasion, and induced apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells [1]. When combined with gemcitabine, it inhibited tumor growth and metastasis in a mouse model of metastatic pancreatic cancer [1]. It also inhibited the anti-apoptotic effects of TGF-beta1 in myelo-monocytic leukaemic cells [3]. Results in GBM cell lines and an orthotopic intracranial model indicated that LY2109761 increased radiosensitivity and resulted in prolonged survival in glioblastoma [4]. In addition, LY2109761 reduced radiation-induced pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis in a murine model [5].
References:
[1]Melisi D, Ishiyama S, Sclabas GM et al. LY2109761, a novel transforming growth factor beta receptor type I and type II dual inhibitor, as a therapeutic approach to suppressing pancreatic cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 829-840.[2]Li HY, McMillen WT, Heap CR et al. Optimization of a dihydropyrrolopyrazole series of transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor kinase domain inhibitors: discovery of an orally bioavailable transforming growth factor-beta receptor type I inhibitor as antitumor agent. J Med Chem 2008; 51: 2302-2306.[3]Xu Y, Tabe Y, Jin L et al. TGF-beta receptor kinase inhibitor LY2109761 reverses the anti-apoptotic effects of TGF-beta1 in myelo-monocytic leukaemic cells co-cultured with stromal cells. Br J Haematol 2008; 142: 192-201.[4]Zhang M, Kleber S, Rohrich M et al. Blockade of TGF-beta signaling by the TGFbetaR-I kinase inhibitor LY2109761 enhances radiation response and prolongs survival in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 7155-7167.[5]Flechsig P, Dadrich M, Bickelhaupt S et al. LY2109761 attenuates radiation-induced pulmonary murine fibrosis via reversal of TGF-beta and BMP-associated proinflammatory and proangiogenic signals. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 3616-3627.
- Acronycine
Catalog No.:BCC8114
CAS No.:7008-42-6
- 4,10-Aromadendranediol
Catalog No.:BCN4261
CAS No.:70051-38-6
- LPYFD-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC6113
CAS No.:700361-48-4
- Rivularin
Catalog No.:BCN3189
CAS No.:70028-59-0
- Terazosin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4354
CAS No.:70024-40-7
- 2-Adamantanone
Catalog No.:BCN8473
CAS No.:700-58-3
- 2-Adamantanol
Catalog No.:BCN8479
CAS No.:700-57-2
- Indole-3-carbinol
Catalog No.:BCC5318
CAS No.:700-06-1
- H-Tyr(3-I)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3265
CAS No.:70-78-0
- 1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN4597
CAS No.:70-70-2
- H-Asn-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2875
CAS No.:70-47-3
- L-Glutathione Reduced
Catalog No.:BCC8030
CAS No.:70-18-8
- LY2157299
Catalog No.:BCC3709
CAS No.:700874-72-2
- TCN 237 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6111
CAS No.:700878-19-9
- 5-Heneicosylresorcinol
Catalog No.:BCN7630
CAS No.:70110-59-7
- 5-Tricosyl-1,3-benzenediol
Catalog No.:BCN4262
CAS No.:70110-60-0
- 5-Pentacosylresorcinol
Catalog No.:BCN4263
CAS No.:70110-61-1
- BMS-626529
Catalog No.:BCC1427
CAS No.:701213-36-7
- DGAT-1 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1529
CAS No.:701232-20-4
- Talopram hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7579
CAS No.:7013-41-4
- Liquiritic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8332
CAS No.:10379-72-3
- Isotetrandrine N-2'-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN4264
CAS No.:70191-83-2
- Papain Inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1024
CAS No.:70195-20-9
- Taranabant
Catalog No.:BCC1985
CAS No.:701977-09-5
LY2109761 attenuates radiation-induced pulmonary murine fibrosis via reversal of TGF-beta and BMP-associated proinflammatory and proangiogenic signals.[Pubmed:22547771]
Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jul 1;18(13):3616-27.
PURPOSE: Radiotherapy is used for the treatment of lung cancer, but at the same time induces acute pneumonitis and subsequent pulmonary fibrosis, where TGF-beta signaling is considered to play an important role. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: We irradiated thoraces of C57BL/6 mice (single dose, 20 Gy) and administered them a novel small-molecule TGF-beta receptor I serine/threonine kinase inhibitor (LY2109761) orally for 4 weeks before, during, or after radiation. Noninvasive lung imaging including volume computed tomography (VCT) and MRI was conducted 6, 16, and 20 weeks after irradiation and was correlated to histologic findings. Expression profiling analysis and protein analysis was conducted in human primary fibroblasts. RESULTS: Radiation alone induced acute pulmonary inflammation and lung fibrosis after 16 weeks associated with reduced life span. VCT, MRI, and histology showed that LY2109761 markedly reduced inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis resulting in prolonged survival. Mechanistically, we found that LY2109761 reduced p-SMAD2 and p-SMAD1 expression, and transcriptomics revealed that LY2109761 suppressed expression of genes involved in canonical and noncanonical TGF-beta signaling and downstream signaling of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP). LY2109761 also suppressed radiation-induced inflammatory [e.g., interleukin (IL)-6, IL-7R, IL-8] and proangiogenic genes (e.g., ID1) indicating that LY2109761 achieves its antifibrotic effect by suppressing radiation-induced proinflammatory, proangiogenic, and profibrotic signals. CONCLUSION: Small-molecule inhibitors of the TGF-beta receptor I kinase may offer a promising approach to treat or attenuate radiation-induced lung toxicity or other diseases associated with fibrosis.
LY2109761 enhances cisplatin antitumor activity in ovarian cancer cells.[Pubmed:26191185]
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):4923-32. eCollection 2015.
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVE: Ovarian cancer is among the most lethal of all malignancies in women. While chemotherapy is the preferred treatment modality, chemoresistance severely limits treatment success. Because transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) could increase survival of ovarian cancer cells in the presence of cisplatin, we conducted a preclinical study of the antitumor effects of the TGF-beta type I (TbetaRI) and type II (TbetaRII) kinase inhibitor LY2109761 in combination with cisplatin. METHODS: SKOV3, OV-90 and SKOV3(DDP) cells were treated with LY2109761, and/or cisplatin, and cell viability, apoptosis mRNA and protein expression levels were then evaluated. Furthermore, the efficacy of LY2109761 combined with cisplatin was further examined in established xenograft models. RESULTS: LY2109761 was sufficient to induce spontaneous apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells. Combination with LY2109761 significantly augmented the cytotoxicity of cisplatin in both parental and cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer cells. LY2109761 significantly increased apoptotic cell death in cisplatin-resistant cells. Combination treatment of LY2109761 and cisplatin showed antiproliferative effects and induced a greater rate of apoptosis than the sum of the single-treatment rates and promoted tumor regression in established parental and cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer xenograft models. CONCLUSIONS: Chemotherapeutic approaches using LY2109761 might enhance the treatment benefit of the cisplatin in the treatment of ovarian cancer patients.
Blockade of TGF-beta signaling by the TGFbetaR-I kinase inhibitor LY2109761 enhances radiation response and prolongs survival in glioblastoma.[Pubmed:22006998]
Cancer Res. 2011 Dec 1;71(23):7155-67.
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a highly aggressive primary brain tumor that tends to be resistant to the ionizing radiotherapy used to treat it. Because TGF-beta is a modifier of radiation responses, we conducted a preclinical study of the antitumor effects of the TGF-beta receptor (TGFbetaR) I kinase inhibitor LY2109761 in combination with radiotherapy. LY2109761 reduced clonogenicity and increased radiosensitivity in GBM cell lines and cancer stem-like cells, augmenting the tumor growth delay produced by fractionated radiotherapy in a supra-additive manner in vivo. In an orthotopic intracranial model, LY2109761 significantly reduced tumor growth, prolonged survival, and extended the prolongation of survival induced by radiation treatment. Histologic analyses showed that LY2109761 inhibited tumor invasion promoted by radiation, reduced tumor microvessel density, and attenuated mesenchymal transition. Microarray-based gene expression analysis revealed signaling effects of the combinatorial treatments that supported an interpretation of their basis. Together, these results show that a selective inhibitor of the TGFbetaR-I kinase can potentiate radiation responses in glioblastoma by coordinately increasing apoptosis and cancer stem-like cells targeting while blocking DNA damage repair, invasion, mesenchymal transition, and angiogenesis. Our findings offer a sound rationale for positioning TGFbetaR kinase inhibitors as radiosensitizers to improve the treatment of glioblastoma.
LY2109761 inhibits metastasis and enhances chemosensitivity in osteosarcoma MG-63 cells.[Pubmed:25912577]
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Apr;19(7):1182-90.
OBJECTIVE: Studies have shown that transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) is associated with metastasis and chemoresistance of osteosarcoma. The TGF-beta kinase inhibitor LY2109761 could inhibits metastasis and enhances chemosensitivity in several cancers, but its role and mechanisms in osteosarcoma (OS) is unclear. Here, we investigated the role and mechanism of LY2109761 on metastasis and chemosensitivity of OS MG-63 cells. MATERIALS AND METHODS: MG-63 cells were treated with LY2109761 or/and cisplatin. The cell viability and apoptosis of MG-63 cells were detected by MTT and ELISA. Matrigel invasion assay was used to detect cell invasion in vitro. pSMAD2 and S100A4 was detected by western blot assay. Furthermore, the efficacy of LY2109761 combined with S100A4 cDNA plaismid transfection on cell viability, apoptosis and chemosensitivity to cisplatin in OS MG-63 cells was further examined. RESULTS: LY2109761 was sufficient to induce apoptosis and inhibited growth of MG-63 cells in vitro. Combination with LY2109761 significantly augmented the cytotoxicity of cisplatin in MG-63 cells. LY2109761 significantly inhibited invasion of MG-63 cells in vitro. The LY2109761-induced increase in cell apoptosis and the cytotoxicity of cisplatin, and decrease in cell invasion was blocked completely when S100A4 expression was restored in the MG-63 cells by S100A4 cDNA plasmid transfection. CONCLUSIONS: Our data indicate that LY2109761 suppresses OS metastasis and enhanced chemosensitivity by targeting S100A4. LY2109761 may have important implications for the development of strategies for inhibiting metastasis and overcoming OS cell resistance to chemotherapy.


