SB 431542ALK inhibitor CAS# 301836-41-9 |
- SB-505124 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1930
CAS No.:356559-13-2
- SB525334
Catalog No.:BCC2531
CAS No.:356559-20-1
- GW788388
Catalog No.:BCC3666
CAS No.:452342-67-5
- A 77-01
Catalog No.:BCC1318
CAS No.:607737-87-1
- LY2109761
Catalog No.:BCC3806
CAS No.:700874-71-1
- LY2157299
Catalog No.:BCC3709
CAS No.:700874-72-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 301836-41-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4521392 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H16N4O3 | M.Wt | 384.39 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 40 mg/mL (104.06 mM) Ethanol : 11.17 mg/mL (29.06 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
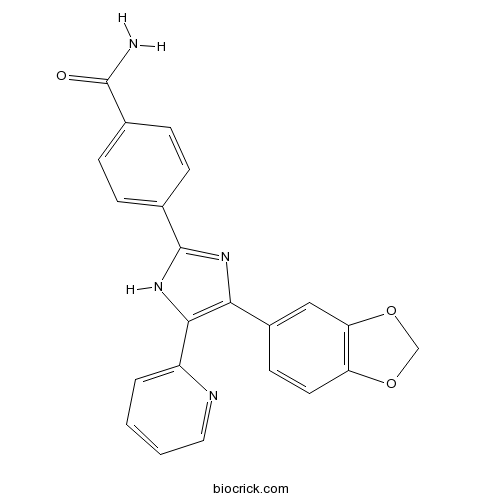
| Chemical Name | 4-[4-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-5-pyridin-2-yl-1H-imidazol-2-yl]benzamide | ||
| SMILES | C1OC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)C3=C(NC(=N3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)N)C5=CC=CC=N5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FHYUGAJXYORMHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H16N4O3/c23-21(27)13-4-6-14(7-5-13)22-25-19(20(26-22)16-3-1-2-10-24-16)15-8-9-17-18(11-15)29-12-28-17/h1-11H,12H2,(H2,23,27)(H,25,26) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective inhibitor of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) type I receptor activin receptor-like kinase ALK5 (IC50 = 94 nM), and its relatives ALK4 and ALK7. Suppresses TGF-β-induced proliferation of human osteosarcoma cells. Stimulates proliferation, differentiation and sheet formation of ESC-derived endothelial cells. Inhibits TGF-β-induced EMT, migration, invasion and VEGF secretion in several human cancer cell lines. |

SB 431542 Dilution Calculator

SB 431542 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6015 mL | 13.0076 mL | 26.0152 mL | 52.0305 mL | 65.0381 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5203 mL | 2.6015 mL | 5.203 mL | 10.4061 mL | 13.0076 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2602 mL | 1.3008 mL | 2.6015 mL | 5.203 mL | 6.5038 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.052 mL | 0.2602 mL | 0.5203 mL | 1.0406 mL | 1.3008 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.026 mL | 0.1301 mL | 0.2602 mL | 0.5203 mL | 0.6504 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SB431542 is a selective ATP-competitive inhibitor of ALK5 (activin receptor-like kinase 5) with an IC50 value of 94 nM [1].
SB431542 showed most potent efficacy among the series of hits screened out. It inhibited TGF-β1-induced mRNA formation in A498 cells with IC50 value of 50 nM. It also markedly reduced TGF-β-induced nuclear accumulation of Smad proteins with IC50 value of 40 nM. SB431542 was found to be a selective inhibitor for ALK4, ALK5 and ALK7, suppresses the phosphorylation of Smad2. It showed no significant inhibition of ALK1, ALK2, ALK6 and showed weak effect on ALK3 at concentration of 10 μM [1, 2].
References:
[1] Callahan J F, Burgess J L, Fornwald J A, et al. Identification of novel inhibitors of the transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) type 1 receptor (ALK5). Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2002, 45(5): 999-1001.
[2] Inman G J, Nicolás F J, Callahan J F, et al. SB-431542 is a potent and specific inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β superfamily type I activin receptor-like kinase (ALK) receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7. Molecular pharmacology, 2002, 62(1): 65-74.
- Jasminin
Catalog No.:BCN7468
CAS No.:30164-93-3
- Compstatin control peptide
Catalog No.:BCC6067
CAS No.:301544-78-5
- Seneganolide
Catalog No.:BCN5209
CAS No.:301530-12-1
- H-Val-NH2.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3144
CAS No.:3014-80-0
- P7C3
Catalog No.:BCC6524
CAS No.:301353-96-8
- CH 223191
Catalog No.:BCC3896
CAS No.:301326-22-7
- TCS 359
Catalog No.:BCC1183
CAS No.:301305-73-7
- Tianeptine sodium
Catalog No.:BCC2506
CAS No.:30123-17-2
- Malvidin-3-O-galactoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3030
CAS No.:30113-37-2
- Robinin
Catalog No.:BCN5208
CAS No.:301-19-9
- Oleamide
Catalog No.:BCC6827
CAS No.:301-02-0
- Methyl Linolenate
Catalog No.:BCN8318
CAS No.:301-00-8
- D4476
Catalog No.:BCC1508
CAS No.:301836-43-1
- Boc-Lys(Boc)-OSu
Catalog No.:BCC3415
CAS No.:30189-36-7
- Ro 5-3335
Catalog No.:BCC7962
CAS No.:30195-30-3
- Desoxyrhaponticin
Catalog No.:BCN2954
CAS No.:30197-14-9
- Hydroxyprogesterone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8997
CAS No.:302-23-8
- Aconitine
Catalog No.:BCN1014
CAS No.:302-27-2
- DL-Alanine
Catalog No.:BCN8539
CAS No.:302-72-7
- Retinoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2185
CAS No.:302-79-4
- Arenobufagin 3-hemisuberate
Catalog No.:BCN7837
CAS No.:30219-16-0
- Effusanin A
Catalog No.:BCN5210
CAS No.:30220-43-0
- Ingenol
Catalog No.:BCN2333
CAS No.:30220-46-3
- 1-Hydroxybaccatin I
Catalog No.:BCN5211
CAS No.:30244-37-2
Enhanced differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to mesenchymal progenitors by inhibition of TGF-beta/activin/nodal signaling using SB-431542.[Pubmed:20200949]
J Bone Miner Res. 2010 Jun;25(6):1216-33.
Directing differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) into specific cell types using an easy and reproducible protocol is a prerequisite for the clinical use of hESCs in regenerative-medicine procedures. Here, we report a protocol for directing the differentiation of hESCs into mesenchymal progenitor cells. We demonstrate that inhibition of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)/activin/nodal signaling during embryoid body (EB) formation using SB-431542 (SB) in serum-free medium markedly upregulated paraxial mesodermal markers (TBX6, TBX5) and several myogenic developmental markers, including early myogenic transcriptional factors (Myf5, Pax7), as well as myocyte-committed markers [NCAM, CD34, desmin, MHC (fast), alpha-smooth muscle actin, Nkx2.5, cTNT]. Continuous inhibition of TGF-beta signaling in EB outgrowth cultures (SB-OG) enriched for myocyte progenitor cells; markers were PAX7(+) (25%), MYOD1(+) (52%), and NCAM(+) (CD56) (73%). DNA microarray analysis revealed differential upregulation of 117 genes (>2-fold compared with control cells) annotated to myogenic development and function. Moreover, these cells showed the ability to contract (80% of the population) and formed myofibers when implanted intramuscularly in vivo. Interestingly, SB-OG cells cultured in 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) developed into a homogeneous population of mesenchymal progenitors that expressed CD markers characteristic of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): CD44(+) (100%), CD73(+) (98%), CD146(+) (96%), and CD166(+) (88%) with the ability to differentiate into osteoblasts, adipocytes, and chondrocytes in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, microarray analysis of these cells revealed downregulation of genes related to myogenesis: MYH3 (-167.9-fold), ACTA1 (-161-fold), MYBPH (-139-fold), ACTC (-100.3-fold), MYH8 (-45.5-fold), and MYOT (-41.8-fold) and marked upregulation of genes related to mesoderm-derived cell lineages. In conclusion, our data provides a simple and versatile protocol for directing the differentiation of hESCs into a myogenic lineage and then further into mesenchymal progenitors by blocking the TGF-beta signaling pathway.
SB-431542, a specific inhibitor of the TGF-beta type I receptor inhibits hypoxia-induced proliferation of pulmonary artery adventitial fibroblasts.[Pubmed:27004374]
Pharmazie. 2016 Feb;71(2):94-100.
The vascular remodeling process plays an important role in the pathology of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension, and it includes cell proliferation, cell motility, cell synthesis and collagen coagulation. Due to their proliferation and synthesis ability, the adventitial fibroblasts are thought to be critical in the vascular remodeling process initiated in response to hypoxia. However, the factors driving hypoxia-induced fibroblast proliferation and synthesis have yet to be elucidated, and the treatment regimens to treat hypoxia remain ineffective. As forthis study, its purpose was to examine the effects exerted by SB-431542, a small-molecule antagonist of transforming growth factor-beta-receptor, on the proliferation, synthesis and collagen coagulation in cultured adventitial fibroblasts. Another aim of this study was to assess the inhibitory ability of SB-431542 on pulmonary vascular remodeling in chronic hypoxia in vivo.The cell morphology and proliferation of cultured adventitial fibroblasts was assessed by laser confocal microscopy and the MTT assay, respectively. Additionally, collagen synthesis was determined by hydroxyproline chromatography, while the expression of cytokines in adventitial fibroblasts and lung tissues was evaluated by immunohistochemical and reverse transcription PCR analyses. The results indicated that the exposure of cultured fibroblasts to 1% oxygen led to the up regulation of cell proliferation, cell synthesis. In addition, increased expression of cytokines and collagen was detected in vivo in the pulmonary artery adventitia of rats exposed to chronic hypoxia. Conversely, SB-431542 inhibited fibroblast proliferation and synthesis in the process of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension (P < 0.01). Thus, the results suggested that by reducing cell proliferation, cell synthesis of vascular adventitia, small molecule inhibitors of the TGF-beta1 receptors may offer a novel therapy for pulmonary hypertension.
Transforming growth factor beta signaling inhibitor, SB-431542, induces maturation of dendritic cells and enhances anti-tumor activity.[Pubmed:21042762]
Oncol Rep. 2010 Dec;24(6):1637-43.
The transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) stimulates tumor progression and metastasis. Secretion of TGFbeta by tumor cells also suppresses an antitumor immune response in which dendritic cells (DCs) play an important role to activate cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Herein we report that the small molecule TGFbeta signaling inhibitor SB-431542, induces DC maturation in vitro and triggers antitumor activity in vivo. We added SB-431542 to cultures of murine bone-marrow derived DCs (BM-DCs) derived from BALB/c mice and human DCs generated from peripheral monocytes (human DCs) at different concentrations in triplicates and examined expression of co-stimulatory molecules by FACS and production of Interleukin-12 (IL-12) by ELISA. SB induced phenotypic maturation of BM-DCs and human DCs and improved their abilities to produce IL-12 in a dose-dependent manner. SB-431542 also augmented capacity of murine and human DCs to activate naive T cells in allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reaction. Interestingly, SB-431542 augmented the capacity of BM-DCs and human DCs to incorporate FITC-conjugated dextran. Intraperitoneal administration of SB-431542 initiated 3 and 7 days after the implantation of colon-26 cancer cells into the peritoneal cavity of BALB/c mice significantly induced CTL activity against colon-26. We incubated human DCs with SB-431542 and cell lysate of scirrhous gastric cancer cell line OCUM-8, and then examined CTL activities against OCUM-8. CD8 T cells activated by human DCs treated with SB-431542 showed modest augmentation CTL activity against cancer cells. Furthermore, pretreatment of human DCs with SB-431542 upregulated cytotoxic activity against K562 cells, suggesting SB should have potential to activate DCs to natural killer cells. In conclusion, TGFbeta receptor I kinase inhibitor such as SB-431542 might induce anti-tumor immune response in immuno-tolerant patients associated with TGFbeta activity.
SB-431542 inhibition of scar formation after filtration surgery and its potential mechanism.[Pubmed:19098325]
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Apr;50(4):1698-706.
PURPOSE: To explore the inhibitive effect of SB-431542 (an ALK5 inhibitor) on scar formation after glaucoma surgery and to identify the potential pharmacologic target(s). METHODS: Twenty-four New Zealand rabbits underwent filtration surgery on the right eye and were divided into a control group and three experimental groups (n=6). Human Tenon's fibroblast monolayer was scraped to generate a single gap, and then the control medium with SB-431542 only or containing 10 microg/L TGF-beta1 and SB-431542 (1-20 microM) was added. The cells were pretreated with SB-431542 or in control medium for 30 minutes before induction with 10 microg/L TGF-beta1 or 1 microg/L TGF-beta2. The expression of alpha-SM-actin, CTGF, and Col I, as well as changes in the Smad, ERK, P38, and AKT signaling pathways were detected. RESULTS: In comparison with the control rabbits, the IOPs in the experimental groups remained at lower levels until day 25 (P<0.05) after the surgery. Histologic profiles showed that there was only a mild deposition of collagen in the subconjunctival space in the experimental groups. The cell growth and migration were inhibited effectively by SB-431542, regardless of whether TGF-beta was present in the culture system. SB-431542 abrogated TGF-beta-induced upregulation of alpha-SM-actin, CTGF, and Col I. It effectively inhibited the phosphorylation of Smad2 stimulated by TGF-beta but not that of the components of the MAPK pathways. CONCLUSIONS: SB-431542 inhibits scar formation after glaucoma filtration surgery. The mechanism may be that SB-431542 interferes in the phosphorylation of Smad2, thus abrogating TGF-beta-induced fibroblast transdifferentiation and then decreasing Col I synthesis.
A specific inhibitor of TGF-beta receptor kinase, SB-431542, as a potent antitumor agent for human cancers.[Pubmed:15967103]
Neoplasia. 2005 May;7(5):509-21.
Small molecule inhibitors of signaling pathways have proven to be extremely useful for the development of therapeutic strategies for human cancers. Blocking the tumor-promoting effects of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) in advanced stage carcinogenesis provides a potentially interesting drug target for therapeutic intervention. Although very few TGF-beta receptor kinase inhibitors (TRKI) are now emerging in preclinical studies, nothing is known about how these inhibitors might regulate the tumor-suppressive or tumor-promoting effects of TGF-beta, or when these inhibitors might be useful for treatment during cancer progression. We have investigated the potential of TRKI in new therapeutic approaches in preclinical models. Here, we demonstrate that the TRKI, SB-431542, inhibits TGF-beta-induced transcription, gene expression, apoptosis, and growth suppression. We have observed that SB-431542 attenuates the tumor-promoting effects of TGF-beta, including TGF-beta-induced EMT, cell motility, migration and invasion, and vascular endothelial growth factor secretion in human cancer cell lines. Interestingly, SB-431542 induces anchorage independent growth of cells that are growth-inhibited by TGF-beta, whereas it reduces colony formation by cells that are growth-promoted by TGF-beta. However, SB-431542 has no effect on a cell line that failed to respond to TGF-beta. This represents a novel potential application of these inhibitors as therapeutic agents for human cancers with the goal of blocking tumor invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis, when tumors are refractory to TGF-beta-induced tumor-suppressor functions but responsive to tumor-promoting effects of TGF-beta.
SB-431542 and Gleevec inhibit transforming growth factor-beta-induced proliferation of human osteosarcoma cells.[Pubmed:14633705]
Cancer Res. 2003 Nov 15;63(22):7791-8.
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) has growth-stimulating effects on mesenchymal cells and several tumor cell lines. The signaling pathway for this effect is, however, not well understood. We examined how TGF-beta stimulates proliferation of MG63 human osteosarcoma cells. Two distinct type I receptors for TGF-beta, ALK-1 and ALK-5, were expressed and functional in MG63 cells. Of these two receptors, ALK-5 appears to be responsible for the growth stimulation because expression of constitutively active ALK-5, but not ALK-1, stimulated proliferation of MG63 cells. SB-431542 (0.3 microM), a novel inhibitor of ALK4/5/7 kinase, suppressed TGF-beta-induced growth stimulation. DNA microarray analysis as well as quantitative real-time PCR analysis of RNAs from TGF-beta-treated cells demonstrated that several growth factors, including platelet-derived growth factor AA, were induced in response to TGF-beta in MG63 cells. Gleevec (1 microM) as well as AG1296 (5 microM) inhibited TGF-beta-induced growth stimulation of MG63 cells, suggesting that platelet-derived growth factor AA was mainly responsible for the growth-stimulatory effect of TGF-beta. We also examined the mechanisms of perturbation of growth-suppressing signaling in MG63 cells. We found that expression of c-Myc, which is down-regulated by TGF-beta in many other cells, was up-regulated in MG63 cells, suggesting that up-regulation of c-Myc expression may be the mechanism canceling growth-suppressing signaling of TGF-beta in MG63 cells.
TGF-beta receptor kinase inhibitor enhances growth and integrity of embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells.[Pubmed:14676305]
J Cell Biol. 2003 Dec 22;163(6):1303-11.
Recent findings have shown that embryonic vascular progenitor cells are capable of differentiating into mural and endothelial cells. However, the molecular mechanisms that regulate their differentiation, proliferation, and endothelial sheet formation remain to be elucidated. Here, we show that members of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta superfamily play important roles during differentiation of vascular progenitor cells derived from mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and from 8.5-days postcoitum embryos. TGF-beta and activin inhibited proliferation and sheet formation of endothelial cells. Interestingly, SB-431542, a synthetic molecule that inhibits the kinases of receptors for TGF-beta and activin, facilitated proliferation and sheet formation of ESC-derived endothelial cells. Moreover, SB-431542 up-regulated the expression of claudin-5, an endothelial specific component of tight junctions. These results suggest that endogenous TGF-beta/activin signals play important roles in regulating vascular growth and permeability.
SB-431542 is a potent and specific inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta superfamily type I activin receptor-like kinase (ALK) receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7.[Pubmed:12065756]
Mol Pharmacol. 2002 Jul;62(1):65-74.
Small molecule inhibitors have proven extremely useful for investigating signal transduction pathways and have the potential for development into therapeutics for inhibiting signal transduction pathways whose activities contribute to human diseases. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) is a member of a large family of pleiotropic cytokines that are involved in many biological processes, including growth control, differentiation, migration, cell survival, adhesion, and specification of developmental fate, in both normal and diseased states. TGF-beta superfamily members signal through a receptor complex comprising a type II and type I receptor, both serine/threonine kinases. Here, we characterize a small molecule inhibitor (SB-431542) that was identified as an inhibitor of activin receptor-like kinase (ALK)5 (the TGF-beta type I receptor). We demonstrate that it inhibits ALK5 and also the activin type I receptor ALK4 and the nodal type I receptor ALK7, which are very highly related to ALK5 in their kinase domains. It has no effect on the other, more divergent ALK family members that recognize bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). Consistent with this, we demonstrate that SB-431542 is a selective inhibitor of endogenous activin and TGF-beta signaling but has no effect on BMP signaling. To demonstrate the specificity of SB-431542, we tested its effect on several other signal transduction pathways whose activities depend on the concerted activation of multiple kinases. SB-431542 has no effect on components of the ERK, JNK, or p38 MAP kinase pathways or on components of the signaling pathways activated in response to serum.
Inhibition of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1-induced extracellular matrix with a novel inhibitor of the TGF-beta type I receptor kinase activity: SB-431542.[Pubmed:12065755]
Mol Pharmacol. 2002 Jul;62(1):58-64.
Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) is a potent fibrotic factor responsible for the synthesis of extracellular matrix. TGF-beta1 acts through the TGF-beta type I and type II receptors to activate intracellular mediators, such as Smad proteins, the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. We expressed the kinase domain of the TGF-beta type I receptor [activin receptor-like kinase (ALK)5] and the substrate, Smad3, and determined that SB-431542 is a selective inhibitor of Smad3 phosphorylation with an IC50 of 94 nM. It inhibited TGF-beta1-induced nuclear Smad3 localization. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors SB-203580 and SB-202190 also inhibit phosphorylation of Smad3 by ALK5 with IC50 values of 6 and 3 microM, respectively. This suggests that these p38 MAPK inhibitors must be used at concentrations of less than 10 microM to selectively address p38 MAPK mechanisms. However, the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB-242235 did not inhibit ALK5. To evaluate the relative contribution of Smad signaling and p38 MAPK signaling in TGF-beta1-induced matrix production, the effect of SB-431542 was compared with that of SB-242235 in renal epithelial carcinoma A498 cells. All compounds inhibited TGF-beta1-induced fibronectin (FN) mRNA, indicating that FN synthesis is mediated in part via the p38 MAPK pathway. In contrast, SB-431542, but not the selective p38 MAPK inhibitor SB-242235, inhibited TGF-beta1-induced collagen Ialpha1 (col Ialpha1). These data indicate that some matrix markers that are stimulated by TGF-beta1 are mediated via the p38 MAPK pathway (i.e., FN), whereas others seem to be activated via ALK5 signaling independent of the p38 MAPK pathway (i.e., col Ialpha1).


