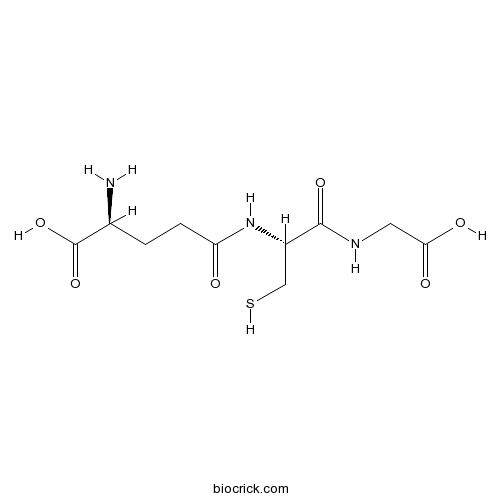
L-Glutathione ReducedEndogenous antioxidant CAS# 70-18-8 |
- mGlu2 agonist
Catalog No.:BCC1745
CAS No.:1311385-32-6
- LY341495
Catalog No.:BCC1724
CAS No.:201943-63-7
- MPEP Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1777
CAS No.:219911-35-0
- CPPHA
Catalog No.:BCC1501
CAS No.:693288-97-0
- Dipraglurant
Catalog No.:BCC1531
CAS No.:872363-17-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 70-18-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 124886 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H17N3O6S | M.Wt | 307.32 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | GSH | ||
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 60 mg/mL (195.24 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-amino-5-[[(2R)-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxo-3-sulfanylpropan-2-yl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C(CC(=O)NC(CS)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)C(C(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RWSXRVCMGQZWBV-WDSKDSINSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H17N3O6S/c11-5(10(18)19)1-2-7(14)13-6(4-20)9(17)12-3-8(15)16/h5-6,20H,1-4,11H2,(H,12,17)(H,13,14)(H,15,16)(H,18,19)/t5-,6-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Glutathione plays important roles in antioxidant defense, nutrient metabolism, and regulation of cellular events (including gene expression, DNA and protein synthesis, cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, cytokine production and immune response, and protein glutathionylation); glutathione deficiency contributes to oxidative stress, which plays a key role in aging and the pathogenesis of many diseases (including kwashiorkor, seizure, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, liver disease, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, HIV, AIDS, cancer, heart attack, stroke, and diabetes). |
| Targets | DNA/RNA Synthesis | HIV | Immunology & Inflammation related |
| Kinase Assay | Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health[Pubmed: 14988435]J Nutr. 2004 Mar;134(3):489-92.Glutathione (gamma-glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine; GSH) is the most abundant low-molecular-weight thiol, and GSH/Glutathione disulfide is the major redox couple in animal cells. The synthesis of GSH from glutamate, cysteine, and glycine is catalyzed sequentially by two cytosolic enzymes, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and GSH synthetase. |
| Structure Identification | Food Chemistry,2000,68(4):475-80.Automated HPLC analysis of glutathione and thiol-containing compounds in grape juice and wine using pre-column derivatization with fluorescence detection.[Reference: WebLink]
|

L-Glutathione Reduced Dilution Calculator

L-Glutathione Reduced Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2539 mL | 16.2697 mL | 32.5394 mL | 65.0787 mL | 81.3484 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6508 mL | 3.2539 mL | 6.5079 mL | 13.0157 mL | 16.2697 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3254 mL | 1.627 mL | 3.2539 mL | 6.5079 mL | 8.1348 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0651 mL | 0.3254 mL | 0.6508 mL | 1.3016 mL | 1.627 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0325 mL | 0.1627 mL | 0.3254 mL | 0.6508 mL | 0.8135 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Triflurdine (Viroptic)
Catalog No.:BCC3873
CAS No.:70-00-8
- Isocostic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4260
CAS No.:69978-82-1
- 20(S),24(R)-Ocotillol
Catalog No.:BCN3891
CAS No.:69926-31-4
- Swertisin
Catalog No.:BCN2762
CAS No.:6991-10-2
- Cyanopindolol hemifumarate
Catalog No.:BCC6880
CAS No.:69906-86-1
- Cinalbicol
Catalog No.:BCN7464
CAS No.:69904-85-4
- Immethridine dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7328
CAS No.:699020-93-4
- Rhapontisterone B
Catalog No.:BCN2664
CAS No.:698975-64-3
- (+)-Isoajmaline
Catalog No.:BCN3425
CAS No.:6989-79-3
- Evodine
Catalog No.:BCN2630
CAS No.:6989-38-4
- Bayogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2458
CAS No.:6989-24-8
- Atractylone
Catalog No.:BCN3048
CAS No.:6989-21-5
- H-Asn-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2875
CAS No.:70-47-3
- 1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN4597
CAS No.:70-70-2
- H-Tyr(3-I)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3265
CAS No.:70-78-0
- Indole-3-carbinol
Catalog No.:BCC5318
CAS No.:700-06-1
- 2-Adamantanol
Catalog No.:BCN8479
CAS No.:700-57-2
- 2-Adamantanone
Catalog No.:BCN8473
CAS No.:700-58-3
- Terazosin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4354
CAS No.:70024-40-7
- Rivularin
Catalog No.:BCN3189
CAS No.:70028-59-0
- LPYFD-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC6113
CAS No.:700361-48-4
- 4,10-Aromadendranediol
Catalog No.:BCN4261
CAS No.:70051-38-6
- Acronycine
Catalog No.:BCC8114
CAS No.:7008-42-6
- LY2109761
Catalog No.:BCC3806
CAS No.:700874-71-1
Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health.[Pubmed:14988435]
J Nutr. 2004 Mar;134(3):489-92.
Glutathione (gamma-glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine; GSH) is the most abundant low-molecular-weight thiol, and GSH/glutathione disulfide is the major redox couple in animal cells. The synthesis of GSH from glutamate, cysteine, and glycine is catalyzed sequentially by two cytosolic enzymes, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and GSH synthetase. Compelling evidence shows that GSH synthesis is regulated primarily by gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase activity, cysteine availability, and GSH feedback inhibition. Animal and human studies demonstrate that adequate protein nutrition is crucial for the maintenance of GSH homeostasis. In addition, enteral or parenteral cystine, methionine, N-acetyl-cysteine, and L-2-oxothiazolidine-4-carboxylate are effective precursors of cysteine for tissue GSH synthesis. Glutathione plays important roles in antioxidant defense, nutrient metabolism, and regulation of cellular events (including gene expression, DNA and protein synthesis, cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, cytokine production and immune response, and protein glutathionylation). Glutathione deficiency contributes to oxidative stress, which plays a key role in aging and the pathogenesis of many diseases (including kwashiorkor, seizure, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, liver disease, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, HIV, AIDS, cancer, heart attack, stroke, and diabetes). New knowledge of the nutritional regulation of GSH metabolism is critical for the development of effective strategies to improve health and to treat these diseases.
The antioxidant role of glutathione and N-acetyl-cysteine supplements and exercise-induced oxidative stress.[Pubmed:18500954]
J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2005 Dec 9;2:38-44.
An increase in exercise intensity is one of the many ways in which oxidative stress and free radical production has been shown to increase inside our cells. Effective regulation of the cellular balance between oxidation and antioxidation is important when considering cellular function and DNA integrity as well as the signal transduction of gene expression. Many pathological states, such as cancer, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease have been shown to be related to the redox state of cells. In an attempt to minimize the onset of oxidative stress, supplementation with various known antioxidants has been suggested. Glutathione and N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) are antioxidants which are quite popular for their ability to minimize oxidative stress and the downstream negative effects thought to be associated with oxidative stress. Glutathione is largely known to minimize the lipid peroxidation of cellular membranes and other such targets that is known to occur with oxidative stress. N-acetyl-cysteine is a by-product of glutathione and is popular due to its cysteine residues and the role it has on glutathione maintenance and metabolism. The process of oxidative stress is a complicated, inter-twined series of events which quite possibly is related to many other cellular processes. Exercise enthusiasts and researchers have become interested in recent years to identify any means to help minimize the detrimental effects of oxidative stress that are commonly associated with intense and unaccustomed exercise. It is possible that a decrease in the amount of oxidative stress a cell is exposed to could increase health and performance.
Glutathione homeostasis in response to exercise training and nutritional supplements.[Pubmed:10448900]
Mol Cell Biochem. 1999 Jun;196(1-2):31-42.
Glutathione plays a central role in the maintenance of tissue antioxidant defenses and in the regulation of redox sensitive signal transduction. In muscle cells, the level and redox status of GSH regulates activity of the redox sensitive transcription factor NF-kappaB. Physical exercise may cause oxidation of GSH in tissues such as the blood, skeletal muscle and liver. Endurance training strengthened GSH dependent tissue antioxidant defenses in most studies. Although studies investigating the effect of sprint training are few, current results show that sprint training may also have a beneficial effect on tissue GSH homeostasis. Skeletal muscle GSH level appears to be tightly regulated by the state of physical activity. Regular exercise enhances and chronic inactivity decreases the level of GSH in this tissue. N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) and alpha-lipoic acid (LA) are two antioxidant dietary supplements that are able to enhance cellular GSH levels. Because LA can be recycled to its potent dithiol form, dihydrolipoate, by enzymes present in the human cell it has a clear advantage over NAC. Recently an improved form of LA, a positively charged analogue (LA-Plus), has been discovered. LA-Plus has more potent immuno-modulatory activity compared to LA. Both LA and NAC have been shown to have beneficial effects in protecting tissue GSH homeostasis against exercise induced oxidative stress.


