ButinCAS# 492-14-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 492-14-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 92775 | Appearance | Powder |
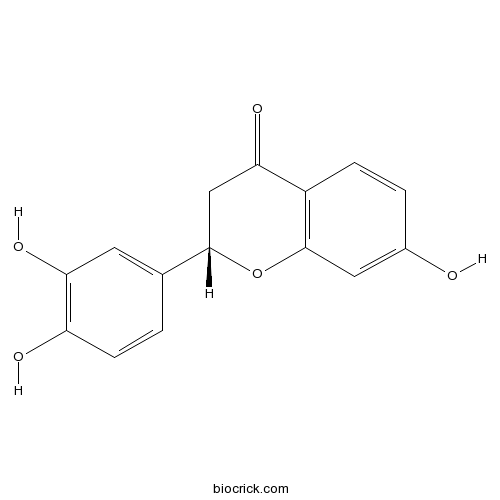
| Formula | C15H12O5 | M.Wt | 272.25 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-hydroxy-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1C(OC2=C(C1=O)C=CC(=C2)O)C3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MJBPUQUGJNAPAZ-AWEZNQCLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H12O5/c16-9-2-3-10-12(18)7-14(20-15(10)6-9)8-1-4-11(17)13(19)5-8/h1-6,14,16-17,19H,7H2/t14-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Butin has antioxidant activity, can protect cells against H2O2-induced apoptosis, oxidative DNA damage and oxidative mitochondrial dysfunction; it attenuates oxidative stress by activating Nrf2-mediated Mn SOD induction via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Butin against H2O2-induced apoptosis were exerted via blockade of membrane potential depolarization, inhibition of the JNK pathway and mitochondria-involved caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway, enhancing the expression of phosphorylated Akt (active form of Akt), a regulator of OGG1. |
| Targets | PI3K | Akt | Nrf2 | ROS | SOD | Calcium Channel | JNK | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | MAPK |
| In vitro | The cytoprotective effect of butin against oxidative stress is mediated by the up-regulation of manganese superoxide dismutase expression through a PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent pathway.[Pubmed: 22253095]J Cell Biochem. 2012 Jun;113(6):1987-97.Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone), a flavonoid with antioxidant activity, was recently reported to protect cells against H2O2-induced apoptosis, oxidative DNA damage and oxidative mitochondrial dysfunction. The objective of the present study was to elucidate the mechanism by which Butin protects mitochondria. Butin reduces oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction via scavenging of reactive oxygen species.[Pubmed: 20060874]Food Chem Toxicol. 2010 Mar;48(3):922-7.This study investigated the cytoprotective effect of Butin, a flavonoid, on hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2))-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Butin decreases oxidative stress-induced 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine levels via activation of oxoguanine glycosylase 1.[Pubmed: 19631197]Chem Biol Interact. 2009 Oct 30;181(3):338-42.In response to oxidative DNA base damage, oxoguanine glycosylase 1 (OGG1), in a base-excision repair (BER) pathway in mammals, plays a vital role in the repair of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), which is a reliable marker of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced DNA base modification and contributes to the pathologic process of cancer.Recently, we have shown that Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone) protects cells against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced damage of cellular components including DNA.
|
| Kinase Assay | Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone) reduces oxidative stress-induced cell death via inhibition of the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway.[Pubmed: 21747713]Inhibitory effect of Rhus verniciflua Stokes extract on human aromatase activity; butin is its major bioactive component.[Pubmed: 24630560]Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Apr 1;24(7):1730-3.Rhus verniciflua Stokes has been used as a traditional herbal medicine in Asia. In this study, the effect of R. verniciflua extract on human aromatase (cytochrome P450 19, CYP19) activity was investigated to elucidate the mechanism for the effect of R. verniciflua extract on androgen hormone levels.
Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(6):3871-87.Recently, we demonstrated that Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone) protected cells against hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2))-induced apoptosis by: (1) scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), activating antioxidant enzymes such superoxide dismutase and catalase; (2) decreasing oxidative stress-induced 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine levels via activation of oxoguanine glycosylase 1, and (3), reducing oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. The objective of this study was to determine the cytoprotective effects of Butin on oxidative stress-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis, and possible mechanisms involved. |

Butin Dilution Calculator

Butin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6731 mL | 18.3655 mL | 36.7309 mL | 73.4619 mL | 91.8274 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7346 mL | 3.6731 mL | 7.3462 mL | 14.6924 mL | 18.3655 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3673 mL | 1.8365 mL | 3.6731 mL | 7.3462 mL | 9.1827 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0735 mL | 0.3673 mL | 0.7346 mL | 1.4692 mL | 1.8365 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0367 mL | 0.1837 mL | 0.3673 mL | 0.7346 mL | 0.9183 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Plathymenin
Catalog No.:BCN6810
CAS No.:492-12-6
- (+)-Sparteine
Catalog No.:BCC9249
CAS No.:492-08-0
- Thermopsidine
Catalog No.:BCN7923
CAS No.:492-02-4
- TCS PIM-1 1
Catalog No.:BCC2447
CAS No.:491871-58-0
- Hemokinin 1 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5923
CAS No.:491851-53-7
- Biochanin A
Catalog No.:BCN1224
CAS No.:491-80-5
- Iridin
Catalog No.:BCN6868
CAS No.:491-74-7
- Chrysoeriol
Catalog No.:BCN5601
CAS No.:491-71-4
- Luteolin
Catalog No.:BCN5600
CAS No.:491-70-3
- Isosakuranin
Catalog No.:BCN3712
CAS No.:491-69-0
- Baicalein
Catalog No.:BCN5599
CAS No.:491-67-8
- Kaempferide
Catalog No.:BCN5598
CAS No.:491-54-3
- Kynurenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2228
CAS No.:492-27-3
- α-D-Glucose
Catalog No.:BCC9197
CAS No.:492-62-6
- Savinin
Catalog No.:BCN5602
CAS No.:493-95-8
- Methyl L-pyroglutamate
Catalog No.:BCN7060
CAS No.:4931-66-2
- Nifuratel
Catalog No.:BCC1800
CAS No.:4936-47-4
- Isoammodendrine
Catalog No.:BCN2146
CAS No.:494-15-5
- Nornicotine
Catalog No.:BCN8176
CAS No.:494-97-3
- TC-G 1001
Catalog No.:BCC6316
CAS No.:494191-73-0
- Ginsenoside Rk1
Catalog No.:BCN3552
CAS No.:494753-69-4
- Auraptene
Catalog No.:BCN5603
CAS No.:495-02-3
- Ammijin
Catalog No.:BCN3617
CAS No.:495-30-7
- Nodakenin
Catalog No.:BCN2378
CAS No.:495-31-8
Butin reduces oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction via scavenging of reactive oxygen species.[Pubmed:20060874]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2010 Mar;48(3):922-7.
This study investigated the cytoprotective effect of Butin, a flavonoid, on hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2))-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Electron spin resonance (ESR) spectrometry revealed Butin's significant scavenging effects on superoxide radicals and hydroxyl radicals. When H(2)O(2) was used to induce an increase in mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) in Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79-4) cells, Butin treatment decreased high level of ROS. Butin also attenuated intracellular Ca(2+) levels that have been induced by H(2)O(2). Furthermore, Butin recovered ATP levels and succinate dehydrogenase activity that had been decreased by H(2)O(2) treatment. We conclude these results suggest Butin decreased mitochondrial ROS accumulation, balanced intracellular Ca(2+) levels, and improved mitochondrial energy production, thus recovering mitochondrial function.
Butin decreases oxidative stress-induced 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine levels via activation of oxoguanine glycosylase 1.[Pubmed:19631197]
Chem Biol Interact. 2009 Oct 30;181(3):338-42.
In response to oxidative DNA base damage, oxoguanine glycosylase 1 (OGG1), in a base-excision repair (BER) pathway in mammals, plays a vital role in the repair of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), which is a reliable marker of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced DNA base modification and contributes to the pathologic process of cancer. Recently, we have shown that Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone) protects cells against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced damage of cellular components including DNA. In the present study, we examined the possible protective effect of Butin on oxidative stress-induced DNA base modification, especially 8-OHdG. Hydrogen peroxide significantly increased the level of 8-OHdG, which was detected by 8-OHdG ELISA and confocal microscopy, but Butin decreased this level. Suppression of 8-OHdG formation by Butin was related to the enhanced mRNA and protein expression of OGG1, which was detected by RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. Butin also increased the transcriptional activity of OGG1, which was suppressed by H2O2 treatment; this transcriptional activity was detected by OGG1 promoter luciferase assay. Butin enhanced the expression of phosphorylated Akt (active form of Akt), a regulator of OGG1, which was decreased by H2O2 treatment. A PI3K-specific inhibitor, LY294002, abolished the phosphorylated Akt and OGG1 expressions induced by Butin, suggesting that OGG1 induction by Butin involves the PI3K/Akt pathway.
The cytoprotective effect of butin against oxidative stress is mediated by the up-regulation of manganese superoxide dismutase expression through a PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent pathway.[Pubmed:22253095]
J Cell Biochem. 2012 Jun;113(6):1987-97.
Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone), a flavonoid with antioxidant activity, was recently reported to protect cells against H2O2-induced apoptosis, oxidative DNA damage and oxidative mitochondrial dysfunction. The objective of the present study was to elucidate the mechanism by which Butin protects mitochondria. The antioxidant function of manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn SOD) is important in preventing oxidative stress. While exposure to H2O2 reduced the expression of Mn SOD in Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79-4), the addition of Butin restored Mn SOD expression at both the mRNA and protein levels, resulting in increased Mn SOD activity. The transcription factor NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) regulates Mn SOD gene expression by binding to the antioxidant responsive element (ARE). Butin enhanced the nuclear translocation and ARE-binding activity of Nrf2, which was decreased by H2O2. The siRNA-mediated knockdown of Nrf2 attenuated Butin-induced Mn SOD expression and activity. Further, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB, Akt) contributed to the ARE-driven Mn SOD expression. Butin activated PI3K/Akt and exposure to either LY294002 (a PI3K inhibitor), Akt inhibitor IV (an Akt-specific inhibitor), or Akt siRNA suppressed the Butin-induced activation of Nrf2, resulting in decreased Mn SOD expression and activity. Finally, the cytoprotective effect of Butin against H2O2-induced cell damage was suppressed by the siRNA-mediated knockdown of Mn SOD. These studies demonstrate that Butin attenuates oxidative stress by activating Nrf2-mediated Mn SOD induction via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone) reduces oxidative stress-induced cell death via inhibition of the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway.[Pubmed:21747713]
Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(6):3871-87.
Recently, we demonstrated that Butin (7,3',4'-trihydroxydihydroflavone) protected cells against hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2))-induced apoptosis by: (1) scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), activating antioxidant enzymes such superoxide dismutase and catalase; (2) decreasing oxidative stress-induced 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine levels via activation of oxoguanine glycosylase 1, and (3), reducing oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. The objective of this study was to determine the cytoprotective effects of Butin on oxidative stress-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis, and possible mechanisms involved. Butin significantly reduced H(2)O(2)-induced loss of mitochondrial membrane potential as determined by confocal image analysis and flow cytometry, alterations in Bcl-2 family proteins such as decrease in Bcl-2 expression and increase in Bax and phospho Bcl-2 expression, release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into the cytosol and activation of caspases 9 and 3. Furthermore, the anti-apoptotic effect of Butin was exerted via inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-4, c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) and activator protein-1 cascades induced by H(2)O(2) treatment. Finally, Butin exhibited protective effects against H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis, as demonstrated by decreased apoptotic bodies, sub-G(1) hypodiploid cells and DNA fragmentation. Taken together, the protective effects of Butin against H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis were exerted via blockade of membrane potential depolarization, inhibition of the JNK pathway and mitochondria-involved caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway.
Inhibitory effect of Rhus verniciflua Stokes extract on human aromatase activity; butin is its major bioactive component.[Pubmed:24630560]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Apr 1;24(7):1730-3.
Rhus verniciflua Stokes has been used as a traditional herbal medicine in Asia. In this study, the effect of R. verniciflua extract on human aromatase (cytochrome P450 19, CYP19) activity was investigated to elucidate the mechanism for the effect of R. verniciflua extract on androgen hormone levels. Androstenedione was used as a substrate and incubated with R. verniciflua extract in cDNA-expressed CYP19 supersomes in the presence of NADPH, and estrone formation was measured using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. R. verniciflua extract was assessed at concentrations of 10-1000 mug/mL. The resulting data showed that R. verniciflua extract inhibited CYP19-mediated estrone formation in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 136 mug/mL. Subsequently, polyphenolic compounds from R. verniciflua extract were tested to identify the ingredients responsible for the aromatase inhibitory effects by R. verniciflua extract. As a result, Butin showed aromatase inhibitory effect in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 9.6 muM, whereas the inhibition by other compounds was negligible. These results suggest that R. verniciflua extract could modulate androgen hormone levels via the inhibition of CYP19 activity and Butin is a major ingredient responsible for this activity.


