Dendrocalamus strictus
Dendrocalamus strictus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Dendrocalamus strictus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN6168
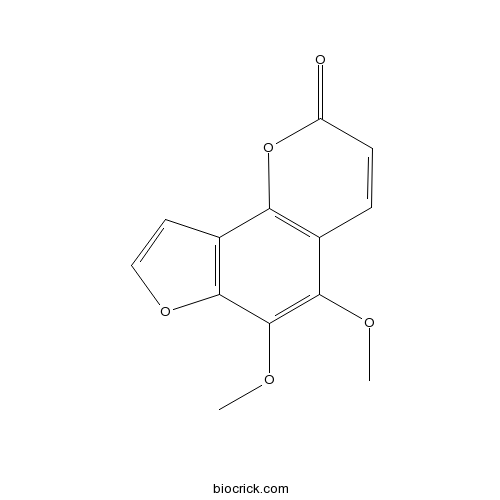
Pimpinellin131-12-4
Instructions
Measurement of microfibril angles in bamboo using Mueller matrix imaging.[Pubmed: 27857282]
The microfibril angle (MFA) giving the orientation of cellulose chains in hard sclerenchymatous bamboo fibers is one of the most important parameters determining the overall strength of the bamboo culm. In this work, Mueller matrix imaging polarimetry is implemented for determining MFA measured over a transverse section of group of fibers and parenchyma cells in bamboo of Dendrocalamus strictus species. The method, based on the Stokes-Mueller formalism, decouples the birefringence exhibited by crystalline cellulose from the clumped polarization parameters using 16 images taken with different polarization states at subcellular resolution. Retardance values, obtained from polar decomposition of the Mueller matrix, are extracted from different locations in the specimen, and distribution of MFA over the entire section is presented. The method permits simultaneous measurement of MFA in a transverse section of several fibers and parenchyma cells. The range of MFA obtained for bamboo fibers from Mueller matrix imaging is verified with the results obtained through x-ray diffraction using the pole figure method.
Micropropagation and assessment of genetic fidelity of Dendrocalamus strictus (Roxb.) nees using RAPD and ISSR markers.[Pubmed: 28324545]
Dendrocalamus strictus popularly known as 'Male bamboo' is a multipurpose bamboo which is extensively utilized in pharmaceutical, paper, agricultural and other industrial implements. In this study, in vitro regeneration of D. strictus through nodal culture has been attempted. Murashige and Skoog's medium supplemented with 4 mg/l BAP was found to be most effective in shoot regeneration with 3.68 ± 0.37 shoots per explant. The effect of Kn was found to be moderate. These hormones also had considerable effect on the shoot length. The highest shoot length after 6 weeks (3.11 ± 0.41 cm) was noted with 5 mg/l BAP followed by 3.07 ± 0.28 cm with 5 mg/l Kn, while decrease in the shoot length was noted with other treatments. The effect of IBA and NAA individually or in combination at different concentrations on rooting was evaluated. The highest number of root (1.36 ± 0.04) was regenerated on full-strength MS medium supplemented with 3 mg/l NAA, while maximum length of 1.64 ± 0.03 cm of roots was recorded with combination of 1 mg/l IBA and 3 mg/l NAA. Tissue-cultured plants thus obtained were successfully transferred to the soil. The clonal fidelity among the in vitro-regenerated plantlets was assessed by RAPD and ISSR markers. The ten RAPD decamers produced 58 amplicons, while nine ISSR primers generated a total of 66 bands. All the bands generated were monomorphic. These results confirmed the clonal fidelity of the tissue culture-raised D. strictus plantlets and corroborated the fact that nodal culture is perhaps the safest mode for multiplication of true to type plants.
Effects of high nutrient supply on the growth of seven bamboo species.[Pubmed: 24933901]
Over the last decade, bamboo has emerged as an interesting plant for the treatment of various polluted waters using plant-based wastewater treatment systems. In these systems, nitrogen and phosphorous concentrations in wastewater can exceed plant requirements and potentially limit plant growth. The effects of two nutrient rates on the growth of seven bamboo species were assessed in a one-year experiment: Dendrocalamus strictus, Thyrsostachys siamensis, Bambusa tuldoides, Gigantochloa wrayi, Bambusa oldhamii, Bambusa multiplex and Bambusa vulgaris. Nutrient rates were applied with a 20:20:20 NPK fertilizer as 2.6 and 13.2 t.ha.yr(-1) NPK to three-year-old bamboo planted in 70 L containers. Morphological characters, photosynthetic responses, and NPK content in bamboo tissues were investigated. Under high-nutrient supply rate, the main trend observed was an increase of culm production but the culms' diameters were reduced. For the seven species, the above ground biomass yield tended to increase with high-nutrient rate. Increasing in nutrient rates also improved the photosynthetic activity which is consistent with the increase of nitrogen and phosphorus contents measured in plant tissues. All the bamboo species tested appears suitable for wastewater treatment purposes, but the species Bambusa oldhamii and Gigantochloa wrayi showed the higher biomass yield and nutrient removaL.
Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculations on seedling growth and biomass productivity of two bamboo species.[Pubmed: 23729895]
A study was conducted to identify suitable arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi for inoculation of Bambusa bambos and Dendrocalamus strictus at nursery stage for increasing growth and productivity. Twelve AM species, isolated from bamboo and other common trees of Bundelkhand were used for inoculations. In B. bambos, total dry weight and phosphorus (P) uptake were significantly increased by all studied fungi and shoot length was increased by eight AM inoculants. Maximum mycorrhizal dependency (MD) was recorded for Acaulospora scrobiculata (44.2%), followed by Glomus cerebriforme (41.6%) and G. intraradix (41.0%). In D. strictus, all tested AM inoculants significantly increased shoot length, dry shoot weight and P uptake, except Glomus 1. Dry root weight was significantly increased by only two inoculants namely, G. cerebriforme and G. etunicatum. Total dry weight was significantly increased by eight AM fungi. Maximum MD was recorded for G. cerebriforme (62.9%), followed by G. diaphanum (55.0%) and G. etunicatum (51.3%). Thus, the results showed that utilization of effective AM fungi can enhance the productivity of bamboo in the region.
Optimization of processing conditions for cyanide content reduction in fresh bamboo shoot during NaCl treatment by response surface methodology.[Pubmed: 23572832]
NaCl treatment was optimized for maximum reduction of cyanide content in raw bamboo (Dendrocalamus strictus) shoot using response surface methodology with 4 independent variables like concentration of NaCl, thickness of bamboo shoot, amount of NaCl solution and duration of treatment at 3 levels of each variable. Box-Behnken design was used to select the levels of variables in experimental runs. Cyanide content ranged between 12.8 and 29.6 mg/kg in bamboo shoot after NaCl treatment. The effect of concentration of NaCl was higher in reducing the cyanide content followed by thickness of bamboo shoot and treatment time in decreasing order. Amount of NaCl solution did not affect the reduction of cyanide content significantly. Optimum condition was 2.4% NaCl concentration, 1.25 cm thickness of bamboo shoot, 216 ml of NaCl solution and 23 min treatment. Corresponding cyanide content was 11.2 mg/kg. Experimental verification at optimum condition gave average cyanide content of 11.3 mg/kg on fresh weight basis, which was in good agreement with predicted and was well below permissible limit (500 mg/kg). The reduction of cyanide content was of 98.3% at optimum level.
Growth responses and metal accumulation capabilities of woody plants during the phytoremediation of tannery sludge.[Pubmed: 20889325]
Five woody plants species (i.e. Terminalia arjuna, Prosopis juliflora, Populus alba, Eucalyptus tereticornis and Dendrocalamus strictus) were selected for phytoremediation and grow on tannery sludge dumps of Common Effluent Treatment Plant (CETP), Unnao (Uttar Pradesh), India. Concentration of toxic metals were observed high in the raw tannery sludge i.e. Fe-1667>Cr-628>Zn-592>Pb-427>Cu-354>Mn-210>Cd-125>Ni-76 mg kg(-1) dw, respectively. Besides, physico-chemical properties of the raw sludge represented the toxic nature to human health and may pose numerous risks to local environment. The growth performances of woody plants were assessed in terms of various growth parameters such as height, diameter at breast height (DBH) and canopy area of plants. All the plant species have the capabilities to accumulate substantial amount of toxic metals in their tissues during the remediation. The ratio of accumulated metals in the plants were found in the order Fe>Cr>Mn>Pb>Zn>Cu>Cd>Ni and significant changes in physico-chemical parameters of tannery sludge were observed after treatment. All the woody plants indicated high bioconcentration factor for different metals in the order Fe>Cr>Mn>Ni>Cd>Pb>Zn>Cu. After one year of phytoremediation, the level of toxic metals were removed from tannery sludge up to Cr (70.22)%, Ni (59.21)%, Cd (58.4)%, Fe (49.75)%, Mn (30.95)%, Zn (22.80)%, Cu (20.46)% and Pb (14.05)%, respectively.
Development of monolithic eco-composites from carbonized blocks of solid iron bamboo (Dendrocalamus strictus) by impregnation with furfuryl alcohol.[Pubmed: 18835773]
The purpose of this work was to manufacture the porous biomorphous composite using carbonized shapes cut from solid stem of solid iron bamboo, Dendrocalamus strictus, as a monolithic support. Bamboo carbonized at 800 degrees C was next infiltrated with liquid filler--furfuryl alcohol. After the polymerization and cross-linking of the filler, the shapes were carbonized again to obtain carbon/carbon composite. TGA method was used to investigate the thermal decomposition of the resulting composite as well as of the raw and carbonized bamboo. The ultrasonic measurements, optical microscopy observations, the adsorption of N(2) at -196 degrees C and mercury porosimetry were applied to characterize the structure of the investigated materials. The obtained composite was found to be highly porous (over 80%), thermo-resistant in inert atmosphere (up to 940 degrees C). It possessed stiff hierarchically ordered pore structure with elastic moduli >4 GPa along the stem, and >1 GPa perpendicularly to the stem. Furthermore, the layer of carbon from the polymer coated the support accurately and did not affect the shape of the monolithic pieces of carbonized bamboo. The resulting composite possessed also more uniform, mesoporous structure than the support.
Seasonal variation of leaf dust accumulation and pigment content in plant species exposed to urban particulates pollution.[Pubmed: 18453408]
To assess the dust interception efficiency of some selected tree species and impact of dust deposition on chlorophyll and ascorbic acid content of leaves the present study was undertaken. The plant species selected for the study were Ficus religiosa, Ficus benghalensis, Mangifera indica, Dalbergia sissoo, Psidium guajava, and Dendrocalamus strictus. It was found that all species have maximum dust deposition in the winter season followed by summer and rainy seasons. Chlorophyll content decreased and ascorbic acid content increased with the increase of dust deposition. There was significant negative and positive correlation between dust deposition and chlorophyll and ascorbic acid content, respectively. Maximum dust interception was done by Dalbergia sisso and least by Dendrocalamus strictus. Thus plants can be used to intercept dust particles which are of potential health hazards to humans.
The thermal decomposition studies of solid iron bamboo (Dendrocalamus strictus) - potential precursor for eco-materials.[Pubmed: 17977721]
Block samples of carbonized solid iron bamboo (Dendrocalamus strictus) - unique genus among bamboos, were prepared by means of slow pyrolysis. They are expected to be promising monolithic supports for various composites. The purpose of this study is to describe the thermal decomposition of rectangular shapes cut from solid stems of Dendrocalamus strictus, raw and pre-charred in a wide range of temperatures: 300, 350, 400, 500 and 600 degrees C. The DTG thermograms of carbonized solid iron bamboo (char), determined at temperatures up to 900 degrees C, exhibited minima even for samples previously pyrolysed at temperatures over 400 degrees C, at which decomposition of plant material have to be completed. For pre-charred samples, the temperature of the DTG peaks increased, while the weight loss registered in the temperature range up to 900 degrees C decreased, with increasing temperature of carbonization. It was found that extension of time of holding at final temperature of carbonization decreased a height of the DTG peaks to full reduction of it after heating along the time of 8h. It was suggested that bamboo tar remaining in vessels after carbonization reacts with the bamboo char creating new compounds that decompose in distinctly higher temperatures.
Applicability of high rate transpiration system for treatment of biologically treated distillery effluent.[Pubmed: 17882528]
The biologically treated distillery effluent (BTDE) contains intense colour, high total dissolved solids (TDS), chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). These properties even after primary, secondary and tertiary treatments contain high concentrations of TDS, COD and BOD. The paper highlights the safe disposal and treatment of BTDE on land through High Rate Transpiration System (HRTS). HRTS is a zero discharge, low cost, high-tech method for improving the quality of BTDE for potential reuse. The experiments conducted at bench and pilot scale showed that HRTS having coconut husk as a bedding material could successfully treat the BTDE with a hydraulic load of 200 m3 ha(-1) day(-1) having BOD of 100 mg l(-1) and 500 m3 ha(-1) day(-1) having BOD of 500 mg l(-1) with average COD load of 0.686 and 2.88 ton ha(-1) day(-1) during the post and pre monsoon periods respectively. There was no significant increase in the organic carbon of the soil irrigated with BTDE. The concentrations of various pollutants analyzed in the leachate were within the prescribed limit for the drinking water sources. The colour removal was 99 to 100% and BOD and COD were possible to treat with optimum hydraulic loading of BTDE through HRTS planted with Dendrocalamus strictus.


