Desmodium heterocarpon
Desmodium heterocarpon
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Desmodium heterocarpon
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
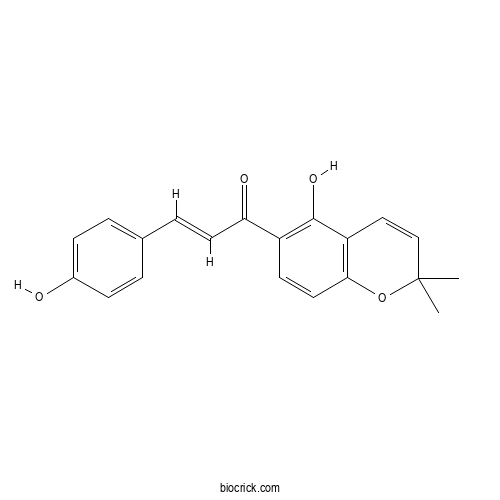
BCN5423
Vitexin3681-93-4
Instructions

-
BCX1469
4-Hydroxylonchocarpin56083-03-5
Instructions
Bradyrhizobium tropiciagri sp. nov. and Bradyrhizobium embrapense sp. nov., nitrogen-fixing symbionts of tropical forage legumes.[Pubmed: 26362866]
Biological nitrogen fixation is a key process for agricultural production and environmental sustainability, but there are comparatively few studies of symbionts of tropical pasture legumes, as well as few described species of the genus Bradyrhizobium, although it is the predominant rhizobial genus in the tropics. A detailed polyphasic study was conducted with two strains of the genus Bradyrhizobium used in commercial inoculants for tropical pastures in Brazil, CNPSo 1112T, isolated from perennial soybean (Neonotonia wightii), and CNPSo 2833T, from desmodium (Desmodium heterocarpon). Based on 16S-rRNA gene phylogeny, both strains were grouped in the Bradyrhizobium elkanii superclade, but were not clearly clustered with any known species. Multilocus sequence analysis of three (glnII, gyrB and recA) and five (plus atpD and dnaK) housekeeping genes confirmed that the strains are positioned in two distinct clades. Comparison with intergenic transcribed spacer sequences of type strains of described species of the genus Bradyrhizobium showed similarity lower than 93.1 %, and differences were confirmed by BOX-PCR analysis. Nucleotide identity of three housekeeping genes with type strains of described species ranged from 88.1 to 96.2 %. Average nucleotide identity of genome sequences showed values below the threshold for distinct species of the genus Bradyrhizobium ( < 90.6 %), and the value between the two strains was also below this threshold (91.2 %). Analysis of nifH and nodC gene sequences positioned the two strains in a clade distinct from other species of the genus Bradyrhizobium. Morphophysiological, genotypic and genomic data supported the description of two novel species in the genus Bradyrhizobium, Bradyrhizobium tropiciagri sp. nov. (type strain CNPSo 1112T = SMS 303T = BR 1009T = SEMIA 6148T = LMG 28867T) and Bradyrhizobium embrapense sp. nov. (type strain CNPSo 2833T = CIAT 2372T = BR 2212T = SEMIA 6208T = U674T = LMG 2987).
Responses of yearling steers to different stocking rates on a subtropical grass-legume pasture.[Pubmed: 1894572]
Despite potential benefits, limitations of individual tropical legumes have restricted development of sustainable grass-legume pastures in tropical and subtropical regions. Sowing mixtures of complementary legumes may overcome limitations of individual species. Responses of yearling steers grazing a mixture of three tropical legumes with bahiagrass (Paspalum notatum Flugge) were evaluated at three stocking rates under continuous grazing. Carpon desmodium (Desmodium heterocarpon [L.] DC.), which is persistent under grazing but often difficult to establish, was combined with the short-lived legumes aeschynomene (Aeschynomene americana L.) and phasey bean (Macroptilium lathyroides [L.] Urb.). Diet composition, as determined by microhistological analysis of fecal samples, and animal performance were evaluated in three grazing periods: summer 1987 and spring 1988 (2.0, 3.5, and 5.0 steers/ha) and summer 1988 (3.0, 5.3, and 7.5 steers/ha). Stocking rate did not affect percentage of the selectively grazed legumes, aeschynomene and phasey bean, in the diet. Average daily gain decreased linearly (P less than .05) with increased stocking rate, as is typical for grass pastures. Aeschynomene and phasey bean contributed to diets during the first summer, and carpon desmodium contribution was greater in the second summer. These results indicate that this pasture mixture can provide legume herbage from aeschynomene and phasey bean in the year of sowing and from carpon desmodium thereafter. Over the range of grazing pressures obtained, legume responses were generally consistent; thus, optimizing stocking rate for gain per hectare or for economic returns can be targeted without additional constraints to maintain the contribution of these legumes to grazing livestock.


