4-HydroxylonchocarpinCAS# 56083-03-5 |
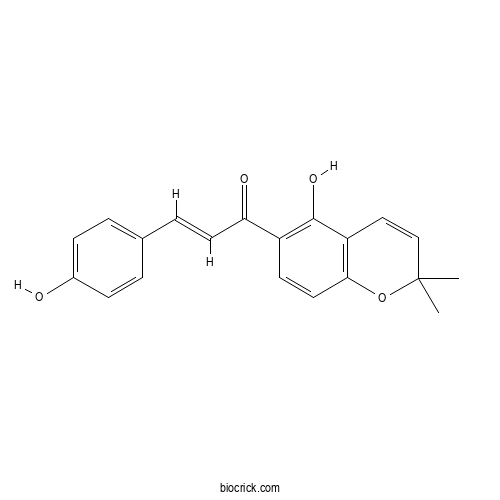
- Isobavachromene
Catalog No.:BCN3192
CAS No.:52801-22-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 56083-03-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5889042.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H18O4 | M.Wt | 322.36 |
| Type of Compound | Chalcones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-1-(5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylchromen-6-yl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C=CC2=C(O1)C=CC(=C2O)C(=O)C=CC3=CC=C(C=C3)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IQHPDUUSMBMDGN-WEVVVXLNSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H18O4/c1-20(2)12-11-16-18(24-20)10-8-15(19(16)23)17(22)9-5-13-3-6-14(21)7-4-13/h3-12,21,23H,1-2H3/b9-5+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

4-Hydroxylonchocarpin Dilution Calculator

4-Hydroxylonchocarpin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1021 mL | 15.5106 mL | 31.0212 mL | 62.0424 mL | 77.553 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6204 mL | 3.1021 mL | 6.2042 mL | 12.4085 mL | 15.5106 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3102 mL | 1.5511 mL | 3.1021 mL | 6.2042 mL | 7.7553 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.062 mL | 0.3102 mL | 0.6204 mL | 1.2408 mL | 1.5511 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.031 mL | 0.1551 mL | 0.3102 mL | 0.6204 mL | 0.7755 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Dehydroandrographolide Succinate Sodium Potasium Salt
Catalog No.:BCX1468
CAS No.:863319-40-8
- Nor-β-anhydroicaritin
Catalog No.:BCX1467
CAS No.:28610-34-6
- trans-Nerolidol
Catalog No.:BCX1466
CAS No.:40716-66-3
- Hordenine Chloride
Catalog No.:BCX1465
CAS No.:6027-23-2
- Zhebeirine
Catalog No.:BCX1464
CAS No.:143120-47-2
- Demethylwedelolactone sulfate
Catalog No.:BCX1463
CAS No.:1318240-80-0
- 6α-(3-methylvaleryloxy)-Britannilactone
Catalog No.:BCX1462
CAS No.:1260151-66-3
- 6α-isovaleryloxy-Britannilactone
Catalog No.:BCX1461
CAS No.:1259933-04-4
- 6α-isobutyryloxy-Britannilactone
Catalog No.:BCX1460
CAS No.:1259933-02-2
- Puerarin-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1459
CAS No.:117047-08-2
- 6α-(2-methybutyryloxy)-Britannilactone
Catalog No.:BCX1458
CAS No.:1260151-65-2
- Teprenone
Catalog No.:BCX1457
CAS No.:6809-52-5
- Salicortin
Catalog No.:BCX1470
CAS No.:1887055-63-1
- Iodixanol Impurity E
Catalog No.:BCX1471
CAS No.:255376-57-9
- Ganoderenic acid C2
Catalog No.:BCX1472
CAS No.:1961358-00-8
- Ganoderic acid Gama
Catalog No.:BCX1473
CAS No.:294674-00-3
- Oleuropein Aglycone
Catalog No.:BCX1474
CAS No.:31773-95-2
- (20S)-Panaxatriol
Catalog No.:BCX1475
CAS No.:848830-68-2
- (20S)-Panaxadiol
Catalog No.:BCX1476
CAS No.:112791-34-1
- 20(S)-25-Hydroxyprotopanaxatiol
Catalog No.:BCX1477
CAS No.:113566-83-9
- 20(S)-25-Methoxyprotopanaxadiol
Catalog No.:BCX1478
CAS No.:66007-93-0
- 20(S)-25-Hydroxyprotopanaxadiol
Catalog No.:BCX1479
CAS No.:66007-91-8
- Ganoderic acid Epsilon
Catalog No.:BCX1480
CAS No.:294674-05-8
- Purpurogallin carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1481
CAS No.:5146-12-3
4-hydroxylonchocarpin and corylifol A: The potential hepatotoxic components of Psoralea corylifolia L.[Pubmed:37598872]
Toxicol Lett. 2023 Aug 15;385:31-41.
Psoralea corylifolia L. (P. corylifolia) has attracted increasing attention because of its potential hepatotoxicity. In this study, we used network analysis (toxic component and hepatotoxic target prediction, proteinprotein interaction, GO enrichment analysis, KEGG pathway analysis, and molecular docking) to predict the components and mechanism of P. corylifolia-induced hepatotoxicity and then selected 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin and corylifol A for experimental verification. HepG2 cells were treated with low, medium, and high concentrations of 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin or corylifol A. The activities of ALT, AST, and LDH in cell culture media and the MDA level, SOD activity, and GSH level in cell extracts were measured. Moreover, apoptosis, ROS levels, and mitochondrial membrane potential were evaluated. The results showed that the activities of ALT, AST, and LDH in the culture medium increased, and hepatocyte apoptosis increased. The level of MDA increased, and the activity of SOD and level of GSH decreased, and the ROS level increased with 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin and corylifol A intervention. Furthermore, the mitochondrial membrane potential decreased in the 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin and corylifol A groups. This study suggests that 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin and corylifol A cause hepatocyte injury and apoptosis by inducing oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, suggesting that these compounds may be the potential hepatotoxic components of P. corylifolia.
Potent insecticidal activity of Eleocharis dulcis (Burm. f.) Trin peel extract and its main components against aphids.[Pubmed:36349434]
Pest Manag Sci. 2023 Apr;79(4):1295-1304.
BACKGROUND: Aphids are significant pests of cash crops and food farm crops. Botanical insecticides are safe for aphid control, especially for organic farming. In this study, Eleocharis dulcis (Burm. f.) Trin. peel extract (EDPE), a new botanical insecticide, was investigated for its active compositions against several agricultural aphids. RESULTS: The results showed that the EDPE had high insecticidal activity against Sitobion avenae Fabricius, Aphis gossypii Glover, Megoura crassicauda Mordvilko, and Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris, with half-lethal concentration (LC(50) ) values of 95.92, 81.04, 140.31, and 255.73 mg/L after 48 h of treatment. In the pot culture assay, the aphicidal effects of 25% EDPE soluble liquid (SL) at a concentration of 0.016% were 68.98 +/- 5.61%, 79.33 +/- 8.27%, and 88.82 +/- 3.91% after the first, third, and seventh days of treatment, respectively. Nine compounds were identified by bioactivity-directed fractionation: 4',5'-dimethoxy-6,6-dimethylpyranoisoflavone (1), 3-methoxy-4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (2), 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (3), 4-methoxylonchocarpin (4), barbigerone (5), lonchocarpusone (6), 6a,12a-dehydrodeguelin (7), 13-homo-13-oxa-6a, 12a-dehydrodeguelin (8) and deguelin (9). Among them, 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (3) showed the highest aphidicidal activity against M. crassicauda, S. avenae, and A. pisum, with LC(50) values of 97.24, 140.63, and 112.31 mg/L, respectively. CONCLUSION: These data contribute to a better understanding of the aphicidal activity of EDPE and its main component, 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin. This will help to develop new botanical insecticides to contro aphids. (c) 2022 Society of Chemical Industry.
Cytotoxic flavonoids from two Lonchocarpus species.[Pubmed:29656660]
Nat Prod Res. 2019 Sep;33(18):2609-2617.
A new isoflavone, 4'-prenyloxyvigvexin A (1) and a new pterocarpan, (6aR,11aR)-3,8-dimethoxybitucarpin B (2) were isolated from the leaves of Lonchocarpus bussei and the stem bark of Lonchocarpus eriocalyx, respectively. The extract of L. bussei also gave four known isoflavones, maximaisoflavone H, 7,2'-dimethoxy-3',4'-methylenedioxyisoflavone, 6,7,3'-trimethoxy-4',5'-methylenedioxyisoflavone, durmillone; a chalcone, 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin; a geranylated phenylpropanol, colenemol; and two known pterocarpans, (6aR,11aR)-maackiain and (6aR,11aR)-edunol. (6aR,11aR)-Edunol was also isolated from the stem bark of L. eriocalyx. The structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated by spectroscopy. The cytotoxicity of the compounds was tested by resazurin assay using drug-sensitive and multidrug-resistant cancer cell lines. Significant antiproliferative effects with IC(50) values below 10 muM were observed for the isoflavones 6,7,3'-trimethoxy-4',5'-methylenedioxyisoflavone and durmillone against leukemia CCRF-CEM cells; for the chalcone, 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin and durmillone against its resistant counterpart CEM/ADR5000 cells; as well as for durmillone against the resistant breast adenocarcinoma MDA-MB231/BCRP cells and resistant gliobastoma U87MG.DeltaEGFR cells.
Anti-inflammatory and anticholinesterase activity of six flavonoids isolated from Polygonum and Dorstenia species.[Pubmed:26048035]
Arch Pharm Res. 2017 Oct;40(10):1129-1134.
This study was aimed at investigating the anti-inflammatory and anticholinesterase activity of six naturally occurring flavonoids: (-) pinostrobin (1), 2',4'-dihydroxy-3',6'-dimethoxychalcone (2), 6-8-diprenyleriodictyol (3), isobavachalcone (4), 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (5) and 6-prenylapigenin (6). These compounds were isolated from Dorstenia and Polygonum species used traditionally to treat pain. The anti-inflammatory activity was determined by using the Griess assay and the 15-lipoxygenase inhibitory activity was determined with the ferrous oxidation-xylenol orange assay. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition was determined by the Ellman's method. At the lowest concentration tested (3.12 microg/ml), compounds 2, 3 and 4 had significant NO inhibitory activity with 90.71, 84.65 and 79.57 % inhibition respectively compared to the positive control quercetin (67.93 %). At this concentration there was no significant cytotoxicity against macrophages with 91.67, 72.86 and 70.86 % cell viability respectively, compared to 73.1 % for quercetin. Compound 4 had the most potent lipoxygenase inhibitory activity (IC(50) of 25.92 microg/ml). With the exception of (-) pinostrobin (1), all the flavonoids had selective anticholinesterase activity with IC(50) values ranging between 5.93 and 8.76 microg/ml compared to the IC(50) 4.94 microg/ml of eserine the positive control. These results indicate that the studied flavonoids especially isobavachalcone are potential anti-inflammatory natural products that may have the potential to be developed as therapeutic agents against inflammatory conditions and even Alzheimer's disease.
Millettia pachycarpa exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through the suppression of LPS-induced NO/iNOS expression.[Pubmed:25004885]
Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(4):949-65.
The present study was designed to investigate the in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoids isolated from Millettia pachycarpa Benth. The seeds of M. pachycarpa Benth were extracted with ethanol and subjected to chromatographic separation for the isolation of bioactive compounds. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods. The anti-inflammatory activity of the compounds was investigated by evaluating the inhibition ability of NO production, iNOS activity and iNOS protein expression induced by LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages in vitro and the carrageenan-induced hind paw edema model in vivo. Molecular docking simulation was also employed to obtain the binding parameters in the binding pocket of iNOS. Thirteen compounds (1-13) were isolated from Chinese herbal medicine M. pachycarpa Benth. Among them, 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (6) and deguelin (7) exhibited remarkable inhibitory rates of 66.5% and 57.7%, respectively, compared with that of 52.5% of indomethacin in LPS-induced macrophages cells. 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (6) with low toxicity (IC50 > 100 mum) exhibited better inhibitory effects to positive control of 1400W on iNOS activity at the concentration of 10 mum. Western blot assay revealed that 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (6) inhibited iNOS protein expression in RAW264.7 cells and molecular docking simulation showed that 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (6) fit well into the binding pocket of iNOS. In the carrageenan-induced paw edema model, our data revealed that the anti-inflammatory potential of 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (6) at 10 mg/kg showed comparable inhibitory ability to indomethacin at 5 h while a higher concentration of 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (6) at 50 mg/kg showed higher inhibitory activity than indomethacin, which was further confirmed by plasma levels of nitrite. The overall results suggest that 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (6) might be used as a potential therapeutic agent for inflammation-associated disorders.
Chemistry and pharmacology of 4-hydroxylonchocarpin: a review.[Pubmed:23784469]
Chin J Integr Med. 2013 Jun;19(6):475-80.
4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (LCP) or 2',4-dihydroxy-3',4'-(2,2-dimethylchromene) chalcone is a chalcone of the class flavonoid, with a molecular weight of 322 g/mol mostly isolated in the family Moraceae and Leguminosae. LCP was reported to have a variety of pharmacological activities such as antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, anti-reverse transcriptase, antitubercular, antimalarial, anti-inflammatory, ornitnine decarboxylase activity and antioxidant. The hemisynthesis of the compound has been described. The present review was undertaken to bring out together the knowledge on LCP, and can serve as the start point for future research and valorization accomplishments.
Antimicrobial action mechanism of flavonoids from Dorstenia species.[Pubmed:23715504]
Drug Discov Ther. 2013 Apr;7(2):66-72.
Naturally occurring flavonoids have been reported to possess antimicrobial activity against a wide range of pathogens. However, the antimicrobial action mechanism of these compounds has not yet been elucidated. This study investigated the mechanism underlying the antibacterial activity of four flavonoids: 6,8-diprenyleriodictyol (1), isobavachalcone (2), 6-prenylapigenin (3) and 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (4). In addition, the toxicity of these compounds was evaluated. Determination of the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) was performed by microbroth dilution method. Radiolabeled thymidine, uridine, and methionine were used to evaluate the effect of the compounds on the biosynthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins while the sensitive cyanine dye DiS-C3-(5) (3,3'-dipropylthiadicarbocyanine iodide) was used for the effect on membrane potential. Bactericidal/bacteriolysis activities were performed by time-kill kinetic method. In the toxicity study, the numbers of survivors was recorded after injection of compounds into the hemolymph of silkworm larvae. Compounds showed significant antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus including methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains with MICs values ranged between 0.5-128 mug/mL. Depolarization of membrane and inhibition of DNA, RNA, and proteins synthesis were observed in S. aureus when treated with those flavonoids. At 5-fold minimum inhibitory concentration, compounds reduced rapidly the bacterial cell density and caused lysis of S. aureus. Compounds 1, 2, and 4 did not show obvious toxic effects in silkworm larvae up to 625 mug/g of body weight. Flavonoids from Dorstenia species, 6,8-diprenyleriodictyol, isobavachalcone, and 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin are bactericidal compounds. They cause damage of cell membrane, leading to the inhibition of macromolecular synthesis. Taking into account the in vivo safety and their significant antimicrobial potency, these flavonoids are promising leads for further drug development.
Chemical profile and biological activities of Deguelia duckeana A.M.G. Azevedo (Fabaceae).[Pubmed:23092395]
Nat Prod Res. 2013 Mar;27(4-5):425-32.
Deguelia duckeana is popularly known as timbo and used by indigenous people as ictiotoxic. On account of there being no literature pertaining to the chemical profile or biological activity of this plant, the hexane, methanol and aqueous crude extracts from leaves, stems and roots were assayed that presented very high cytotoxic potential against Artemia salina, achieving 100% mortality in up to 5.0 microg mL(-1) concentration, but lower antioxidant potential on 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl and Fe(3+)/Phenanthroline assays. The phytochemical analysis of crude extracts showed the presence of flavonoids and related compounds as major constituents as well as steroids in all of them, and tannins in polar extracts. All the extracts were assayed for antibacterial activity but only the hexane extract of stems showed moderate activity on Staphylococcus aureus, which was fractionated and yielded a mixture of 3,5,4'-trimethoxy-4-prenylstilbene, lonchocarpine, 4-Hydroxylonchocarpine and derricidine, reported for the first time in D. duckeana and other fraction with beta-sitosterol and stigmasterol mixture.
Cytotoxicity and mode of action of four naturally occuring flavonoids from the genus Dorstenia: gancaonin Q, 4-hydroxylonchocarpin, 6-prenylapigenin, and 6,8-diprenyleriodictyol.[Pubmed:21800276]
Planta Med. 2011 Dec;77(18):1984-9.
Several flavonoid-like compounds were found to possess good antiproliferative properties. Herein, we examined the ability of four naturally occuring and biologically active flavonoids from the genus Dorstenia, gancaonin Q (1), 6-prenylapigenin (2), 6,8-diprenyleriodictyol (3), and 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin ( 4), to inhibit the proliferation of a panel of fourteen cancer cell lines including leukemia and solid cancer cells, as well as AML12 normal hepatocytes. The study was extended to the analysis of cell cycle distribution, apoptosis induction, and caspase 3/7 activity and the antiangiogenic properties of the four compounds. The results of the cytotoxicity assays showed that more than 50 % inhibition of proliferation was obtained with compound 1 on all the fourteen studied cancer cell lines, with IC (50) values below 20 microg/mL. Compounds 2, 4, and 3 showed selective activity, with IC (50) values below 20 microg/mL being noted on 57.15 %, 71.42 %, and 85.71 % of the fourteen cancer cell lines, respectively. None of the compounds exhibited more than 50 % inhibition against AML12 normal hepatocytes cells at 20 microg/mL. IC (50) values below or around 4 microg/mL were recorded on 28.57 % of the tested cell lines for both compound 1 and 4 and 21.43 % for compound 3, which appeared to be the best cytotoxic compounds. This study indicates that caspase 3/7 activation is one of the modes of induction of apoptosis for compounds 1, 3, and 4 in CCRF-CEM cells. The results of the antiangiogenic assay indicated that compounds 1, 3, and 4 were also able to inhibit the growth of blood capillaries on the chorioallantoic membrane of quail eggs, the best effect being noted for compound 4 (54.1 % inhibition). The results of the present work provide evidence of the cytotoxic potential of the four studied flavonoids and supportive data for further investigations.
Antibacterial activity of some natural products against bacteria expressing a multidrug-resistant phenotype.[Pubmed:21163632]
Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011 Feb;37(2):156-61.
The present study assessed the antimicrobial activities of various natural products belonging to the terpenoids, alkaloids and phenolics against a collection of Gram-negative multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. The results demonstrated that most of the compounds were extruded by bacterial efflux pumps. In the presence of the efflux pump inhibitor phenylalanine arginine beta-naphthylamide (PAbetaN), the activities of laurentixanthone B (xanthone), plumbagin (naphthoquinone), 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (flavonoid) and MAB3 (coumarin) increased significantly against all studied MDR bacteria. Laurentixanthone B, 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin and MAB3 contained the same pharmacophoric moiety as plumbagin. This study indicates that the AcrAB-TolC (Enterobacteriaceae) and MexAB-OprM (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) efflux pumps are involved in resistance of Gram-negative bacteria to most of the natural products.
Evaluation of flavonoids from Dorstenia barteri for their antimycobacterial, antigonorrheal and anti-reverse transcriptase activities.[Pubmed:20599632]
Acta Trop. 2010 Oct;116(1):100-4.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the antimycobacterial, antigonorrheal and reverse transcriptase activities of five flavonoids: isobachalcone (IBC); kanzanol C (KAN); 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (4-LCP); stipulin (SPL) and amentoflavone (AMF) from Dortenia barteri, together with the crude extract from this plant. The Agar disc diffusion, broth microdilution, microplate alamar blue assay (MABA), radiometric respiratory technique using BACTEC 460 system and the reverse transcriptase (RT) assay were used for the investigations. The results of the antimycobacterial assay showed that the crude extract and compounds were able to prevent the growth of Mycobacteria with MIC<10 microg/ml being recorded with IBC on M. tuberculosis. Results of the killing rate experiment revealed that total inhibition effect on M. tuberculosis H37Rv strain was noted with IBC and SPL at day 9 when tested at 4x MIC. The results of the antigonorrheal assay indicated that MIC values below 10 microg/ml were also recorded with IBC on all the tested N. gonorrhoeae strains, meanwhile good activities (MIC<10 microg/ml) were also noted with the extract, KAN, 4-LCP and SPL on some of these strains. The anti-reverse transcriptase activities of extract and compounds also demonstrated that all samples were able to inhibit at various extents the reverse transcriptase activity, with IBC and 4-LCP showing the best effects. The overall results of this work provided evidence that the crude extract as well as some flavonoids from D. barteri could be potential sources of new antimicrobial drug against tuberculosis (TB), gonorrhea and probably the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
Antimicrobial activity of the crude extracts and five flavonoids from the twigs of Dorstenia barteri (Moraceae).[Pubmed:18280679]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Mar 28;116(3):483-9.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the antimicrobial activity of the crude extract of the twigs of Dorstenia barteri (DBT) as well as that of four of the five flavonoids isolated from this extract. Gram-positive bacteria (six species), Gram-negative bacteria (12 species) and fungi (four species) were used. The agar disc diffusion test was used to determine the sensitivity of the tested samples while the well micro-dilution was used to determine the minimal inhibition concentrations (MIC) and the minimal microbicidal concentration (MMC) of the active samples. The results of the disc diffusion assay showed that DBT, isobavachalcone (1), and kanzonol C (4) prevented the growth of all the 22 tested microbial species. Other compounds showed selective activity. The inhibitory activity of the most active compounds namely compounds 1 and 4 was noted on 86.4% of the tested microorganisms and that of 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (3) was observed on 72.7%. This lowest MIC value of 19.06microg/ml was observed with the crude extract on seven microorganisms namely Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter aerogens, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus stearothermophilus and Candida albicans. For the tested compounds, the lowest MIC value of 0.3microg/ml (on six of the 22 organisms tested) was obtained only with compound 1, which appeared as the most active compound. This lowest MIC value (0.3microg/ml) is about 4-fold lower than that of the RA, indicating the powerful and very interesting antimicrobial potential of isobavachalcone (1). The antimicrobial activities of DBT, as well as that of compounds 1, 3, 4, amentoflavone (5) are being reported for the first time. The overall results provide promising baseline information for the potential use of the crude extracts from DBT as well as some of the isolated compounds in the treatment of bacterial and fungal infections.
Inhibition of MMP-2 secretion from brain tumor cells suggests chemopreventive properties of a furanocoumarin glycoside and of chalcones isolated from the twigs of Dorstenia turbinata.[Pubmed:17070879]
Phytochemistry. 2006 Dec;67(23):2573-9.
A furanocoumarin glycoside new named turbinatocoumarin (1) was isolated from the twigs of Dorstenia turbinata. The structure of turbinatocoumarin (1) was assigned as 5-methoxy-3-[3-(beta-glucopyranosyloxy)-2-hydroxy-3-methylbutyl]psoralen by means of spectroscopic analysis. Known compounds have also been isolated from this genus and identified as (2'S, 3'R)-3'-hydroxymarmesin (2), 5-methoxy-3-(3-methyl-2,3-dihydroxybutyl)psoralen (3), psoralen (4), kanzonol C (5) which was isolated for the first time from this genus, 4-Hydroxylonchocarpin (6), umbelliferone, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde and 4-methoxyphenol. As part of our continuing search for potential naturally-occurring antitumor drug candidates, the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 secretion from brain tumor-derived glioblastoma cells by the isolated compounds 1, 3, 5, and 6 was evaluated by zymography and compared to the documented naturally-occurring MMP secretion inhibitors chlorogenic acid (CHL) and epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCg). Among the compounds tested, the inhibiting MMP secretion concentrations ranged from 0.025 to 250 microM with up to 80% inhibition. The inhibitory activities of compounds 5 and 6 were found comparable to the common reference compounds CHL and EGCg. This suggests that alternate sources can be explored and exploited for the availability of chemopreventive molecules.


