Desmodium styracifolium
Desmodium styracifolium
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Desmodium styracifolium
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
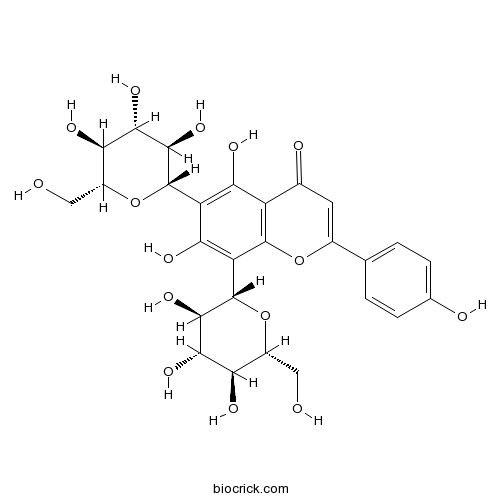
BCN3013
Vicenin -223666-13-9
Instructions
-
BCN2343
Schaftoside51938-32-0
Instructions

-
BCN3011
Isoschaftoside52012-29-0
Instructions

Total flavone of Desmodium styracifolium relieved apoptosis and autophagy of COM-induced HK-2 cells by regulating KIM-1 via p38/MAPK pathway.[Pubmed: 29071538]
The purpose of the study was to investigate the mechanism of total flavone of Desmodium styracifolium (TFDS) in regulating the formation of urinary calculi. Protein levels of KIM-1, LC3-II, p-p38 were measured by Western blot. The effect of different COM concentrations, different TFDS concentrations, SB203580 (specific inhibitor of p38/MAPK), and overexpression of KIM-1 on cell viability were detected by WST-1 assay. The apoptotic cells and FITC positive cells were detected by flow cytometry. HK-2 cell viability decreased with the increase of COM concentration, and the protein levels of KIM-1, LC3-II, and p-p38 increased with the time. Blocking the p38/MAPK pathway or co-cultured with TFDS inhibited the effects of COM on apoptosis and autophagy of HK-2 cells. In addition, blocking the p38/MAPK pathway inhibited the expression of KIM-1. In COM-induced cells, after treated with SB203580, overexpression of KIM-1 could reverse the protection effect of SB203580 on COM-induced cell damage and the inhibition of SB203580 on COM-induced excessive autophagy, suggesting p38/MAPK regulated KIM-1 to regulate COM-induced cell apoptosis and autophagy. Finally, we proved that TFDS inhibited p38/MAPK pathway. And the protection effect of COM-induced cell injury increased with the increase of TFDS concentration, and the adhesion between COM and cells decreased with the increase of TFDS concentration. With the increase of the concentration of TFDS, p38/MAPK pathway was gradually inhibited, and KIM-1 and autophagy related proteins were decreased. TFDS inhibited HK-2 cell apoptosis and autophagy by regulating KIM-1 via p38/MAPK pathway.
[Research on distribution and quality suitability division of Desmodium styracifolium].[Pubmed: 28959832]
The research on distribution and quality suitability division of Desmodium styracifolium were formulated by Maxent and ArcGIS model based on the content of schaftoside and polysaccharide of D. styracifolium and its field research in the south and southwest areas of China (Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan and Yunnan), and the most suitable habitats of distribution suitability and quality suitability were screened. The distribution suitability results indicated that average air temperature in April,mean temperature of coldest quarter, soil type, coldness index were found as the four dominant factors contributing to the plant distribution. The quality suitability results indicated that: ①Polysaccharide content and precipitation in April show significant positive correlation;Schaftoside content and mean temperature of April, mean temperature of coldest quarter show significant negative correlation. Schaftoside content shows significant negative correlation with the precipitation in October and November and the sunshine duration in April and May, while there is a significant positive correlation between schaftoside content and precipitation in April and temperature seasonality standard deviation, and a highly significant positive correlation was found between schaftoside content and precipitation in February and March. ②The quality zoning map was drawn depend on general content of polysaccharide and schaftoside as the index of quality. And this research provides scientific location basis for the production regionalization, cultivation bases selection and directive breeding of D. styracifolium.
Total flavonoids of Desmodium styracifolium attenuates the formation of hydroxy-L-proline-induced calcium oxalate urolithiasis in rats.[Pubmed: 28567512]
Desmosium styracifolium (D. styracifolium), which is considered as a Chinese herbal medicine, has been reported to treat the kidney stone diseases. However, the potential phytochemically active components and the underlying mechanisms associated with its efficacy in targeting urolithiasis remain to be elucidated. This study aims to investigate the anti-urolithiatic effect of total flavonoids of D. styracifolium (TFDS) on calcium oxalate (CaOx) renal stones in Sprague-Dawley rats. Animal models of CaOx urolithiasis were established in male Sprague-Dawley rats by adding 5% w/w hydroxy-L-proline (HLP) in regular rat chow. The TFDS orally at 100, 400 mg/kg, respectively, were administered along with HLP for 28 days. At the end of 28 days of treatment, urine and serum samples were collected for crystalluria determination and various biochemical analysis. Kidney tissues were isolated and processed for antioxidant parameters measurement and histopathological examinations. HLP-induced hyperoxaluria alone reliably caused CaOx nephrolithiasis in rats. We showed that TFDS significantly reduced crystalluria and CaOx crystal deposits in the kidney sections as compared to untreated HLP group. Also, TFDS was observed to decrease urinary oxalate excretion, alleviate the pro-acidosis condition, improve the impaired renal functions and renal epithelial cell injury. Moreover, TFDS protected against the oxidative stress changes via reducing MDA content, increasing CAT and GSH-Px activities in renal homogenate, as well as attenuating the expression of MCP-1, OPN and TGF-β proteins. These results indicated that TFDS had beneficial effect on inhibition of CaOx formation in the rat kidney probably through a combination of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, urine alkalinizing activities, and lowering the concentration of urinary stone-forming constituents. Thus, TFDS might have clinical implications in preventing oxidative renal cell injury and, ultimately, kidney stone formation. The data provide a rationale for the medicinal use of TFDS in nephrolithiasis and identify this agent as a potential source of new antiurolithic drugs.
[Effects of storage time on quality of Desmodium styracifolium seeds].[Pubmed: 27062808]
The dynamic changes of germination percentage, germination potential, thousand-seed weight, antioxidase activity in Desmodium styracifolium seeds with different storage time were tested, and electrical conductivity, contents of soluble sugar, soluble protein, starch in seed leach liquor were also determined in order to reveal the mechanism of seed deterioration. The results as the following. (1) The germination percentage, germination potential and thousand-seed weight of D. styracifolium seeds declined, while the seed coat color darkened with the extension of storage time. (2) The activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) decreased with the prolongation of storage period. The SOD activity declined fastest in 1,095-1,185 d of storage, while the POD activity declined significantly in 365-395 d of storage. (3) The electrical conductivity and the contents of soluble sugar, starch in seed leach liquor increased, while the content of soluble protein declined with the extension of storage time. (4) Correlation analysis indicated that the germination percentage, germination potential and thousand-seed weight of D. styracifolium seeds have a significantly positive correlation with SOD and POD activity, while have a significantly negative correlation with the electrical conductivity, contents of soluble sugar and starch. It can be concluded that during the storage of D. styracifolium seeds, physiological and biochemical changes including decrease in antioxidase activity, rise in electrical conductivity, degradation effluent of soluble sugar and starch, degradation of soluble protein were the main factors leading to the seed deterioration.
Antilithic effects of extracts from different polarity fractions of Desmodium styracifolium on experimentally induced urolithiasis in rats.[Pubmed: 26123751]
Desmodium styracifolium (D. styracifolium) has been widely used in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of urolithiasis. This work was undertaken to investigate extracts from different polarity fractions of D. styracifolium for possible antilithic effects as well as antioxidant potential to explore the underlying phytochemically active constituents of this plant. The extracts of D. styracifolium were divided into four different polarity fractions by petroleum ether (Fr. PE), chloroform (Fr. CH), ethyl acetate (Fr. EA), and n-butyl alcohol (Fr. NB). The antilithic and antioxidant effects were evaluated and compared in vivo on an animal model of calcium oxalate (CaOx) urolithiasis, which was established by administration of 1 % ethylene glycol along with 2 % ammonium chloride in drinking water for 28 days. A total of 60 male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into six groups: normal control group, lithogenic group, and four different polarity fractions of D. styracifolium-treated groups. At the end of the study, urine, blood, and kidney tissue samples were all collected for evaluation. Among the four polarity fractions of D. styracifolium extracts, the Fr. PE and Fr. NB treatment significantly reduced the CaOx crystal deposition in kidneys, prevented the renal toxic changes like pH, Cr, and BUN. In addition, Fr. PE and Fr. NB treatment significantly decreased urinary excretion of oxalate along with a increase of citrate excretion. The increased amounts of malondialdehyde and decreased activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase were detected in lithogenic group, D. styracifolium extracts treatment prevented the oxidative stress changes especially for the Fr. PE and Fr. NB extracts. In conclusion, our data suggest that the extracts from D. styracifolium possess the antiurolithic activity, possibly mediated through the inhibition of CaOx crystal aggregation as well as the alleviation of oxidative injury in the kidney, and the Fr. PE and Fr. NB extracts are the active fractions of D. styracifolium extract.
Bioassay-guided preparative separation of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory C-flavone glycosides from Desmodium styracifolium by recycling complexation high-speed counter-current chromatography.[Pubmed: 25459924]
A new strategy of the convergence of high-speed counter-current chromatography (HSCCC) and bioactive assay technique was developed for rapidly screening and separating the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors from the aerial parts of Desmodium styracifolium. Bioactivity-guided fractionation of the crude extract was first established to target the bioactive fractions based on HSCCC coupled with in vitro ACE inhibitory assay. Subsequently, the bioactive fractions were further separated by the recycling complexation HSCCC respectively, using 0.10 mol/L copper sulfate in the lower phase of two-phase solvent system composed of n-butanol/water (1:1, v/v). Five C-glycosylflavones, vicenin 2 (1), carlinoside (2), vicenin 1 (3), schaftoside (4) and vicenin 3 (5), were successfully obtained. Their chemical structures were identified using ESI-MS and NMR. All the isolates showed in vitro ACE inhibitory activity with the IC50 values between 33.62 and 58.37 μM. The results demonstrated that the established method was proposed as an excellent strategy to systematically screen and purify active compounds from traditional Chinese medicines.
Herbal preparations affect the kinetic factors of calcium oxalate crystallization in synthetic urine: implications for kidney stone therapy.[Pubmed: 24648109]
Herbal remedies are increasingly being considered as suitable long-term treatments for renal dysfunction. The objective of the present study was to investigate the effect of some herbal extracts, all previously identified in published studies as influencing kidney stone formation, on the crystallization characteristics of calcium oxalate (CaOx) in synthetic urine (SU). Five herbal extracts were selected for the study: Folium pyrrosiae, Desmodium styracifolium, Phyllanthus niruri, Orthosiphon stamineus and Cystone(®). Concentrated stock solutions of each herbal extract were prepared and were tested at their recommended dosages in in vitro crystallization studies in SU. CaOx crystallization experiments were performed in which the metastable limit (MSL), average particle size, and nucleation and growth rates were determined. The CaOx MSL of SU was unaltered by the five herbal extracts. Three of the herbs (Desmodium styracifolium, Orthosiphon stamineus and Cystone(®)) significantly reduced the average particle size of precipitated crystals relative to undosed SU. All of the extracts increased the rate of nucleation and decreased the rate of growth significantly in SU. Cystone(®) showed the greatest effect on the measured risk factors. It is concluded that all of the herbs have the potential to serve as inhibitors of calcium oxalate stone formation and warrant investigation in clinical trials.
[Analysis of quality variation and genetic diversity of Desmodium styracifolium from different provenances].[Pubmed: 23944066]
To explore the quality variation and genetic diversity of Desmodium styracifolium from different provenances, and lay a foundation for rational exploitation on germplasm resources and fine variety breeding of D. styracifolium.


