Dianthus superbus
Dianthus superbus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Dianthus superbus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5649
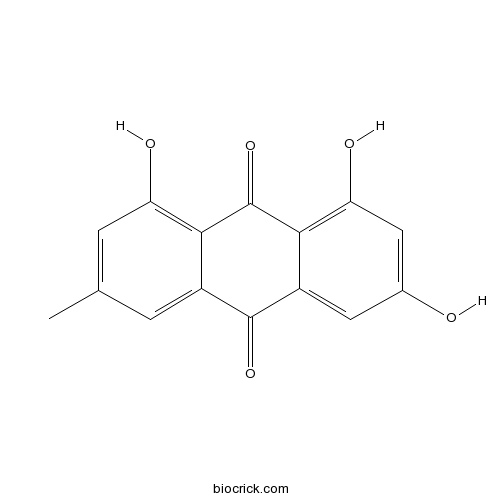
Emodin518-82-1
Instructions
[Effects of the additives and the combination of plants on Pb absorption, growth and quality of Dianthus superbus].[Pubmed: 29741311]
None
Effects of different soil remediation methods on inhibition of lead absorption and growth and quality of Dianthus superbus L.[Pubmed: 29019031]
Heavy metal pollution in soil poses a serious threat to the growth of plants used in traditional Chinese medicine. Therefore, a pot experiment was conducted to study the effects of various soil remediation methods on the performance of Herba Dianthi (Dianthus superbus L.) grown on Pb-contaminated soil. The results show that inoculation of Herba Dianthi with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) led to a significant reduction in Pb uptake (P< 0.05), and increased root development and root-to-shoot ratio compared to untreated control plants, along with the highest content of active components. When planting with Trifolium repens, the reduction effect of Pb absorption was insignificant. Herba Dianthi showed improved growth and active ingredients, and the lowest Pb content, with AMF inoculation. The addition of EDTA decreased the growth of Herba Dianthi, but promoted the absorption of Pb. The inhibition of tumor cells was highest in E2. In conclusion, inoculation with AMF can ensure that plant lead content meets testing standards, helping to improve the quality of medicinal herbs.
[Oligopeptides in plant medicines cited in Chinese Pharmacopoeia].[Pubmed: 28920330]
In total, 23 plant plant medicined containing oligopeptides were cited in Chinese Pharmacopoeia (1 part) of 2015 version including Rubia cordifolia, Linum usitatissimum, Aster tataricus, Psammosilene tunicoides, Pseudostellaria heterophylla, Stellaria dichotoma, Vaccaria segetalis, Dianthus superbus, Celosia argentea, Lycii Cortex, Citrus medica, C. aurantium, Panax ginseng, Parmx notoginseng, Schisandra chinensis, Sparganium stoloniferum, Euryale ferox, Ophiopogon japonicas, Pinellia ternate, Achyranthes bidentata, Physalis alkekengi, Polygonatum odoratum, and Leonuri Fructus. There were 187 oligopeptides in plant medicines above as reported. Oligopeptides consisted mainly of linear peptides and cyclic peptides. The linear peptides included dipeptides, tripeptides and pentapeptides, and cyclic peptides included cyclic, bicyclic and tricyclic peptides. The number of residues of single cyclic peptides ranged from two to twelve. Bicyclic peptides were isolated mainly from R. cordifolia and C. argentea. Modern pharmacological study showed that oligopeptides had many pharmacological effects, including antitumor, anticoagulant, antibacterial, immune suppression and so on.
Probing the impact of quercetin-7-O-glucoside on influenza virus replication influence.[Pubmed: 27387404]
Influenza virus is still at large and seriously affects social welfare and health. Dianthus superbus is a well-known medicinal plant widely used in Mongolian and Chinese traditional medicine for anti-inflammatory purposes.
Simultaneous Determination of Eight Bioactive Compounds in Dianthus superbus by High-performance Liquid Chromatography.[Pubmed: 27279718]
Dianthus superbus, one of traditional herbal medicine, is widely used to treat urethritis, carbuncles and carcinoma.
Cognitive-Enhancing Effect of Dianthus superbus var. Longicalycinus on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice.[Pubmed: 27133261]
Dianthus superbus (D. superbus) is a traditional crude drug used for the treatment of urethritis, carbuncles and carcinomas. The objective of this study was to confirm the cognitive enhancing effect of D. superbus in memory impairment induced mice and to elucidate the possible potential mechanism. Effect of D. superbus on scopolamine induced memory impairment on mice was evaluated using the Morris water maze and passive avoidance tests. We also investigated acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity and brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) expression in scopolamine-induced mice. HPLC-DAD analysis was performed to identify active compounds in D. superbus. The results revealed that D. superbus attenuated the learning and memory impairment induced by scopolamine. D. superbus also inhibited AChE levels in the hippocampi of the scopolamine-injected mice. Moreover, D. superbus increased BDNF expression in the hippocampus. Eight compounds were identified using HPLC-DAD analysis. The content of 4-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid was higher than contents of other compounds. These results indicated that D. superbus improved memory functioning accompanied by inhibition of AChE and upregulation of BDNF, suggesting that D. superbus may be a useful therapeutic agent for the prevention or treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Neuroprotective Properties of Compounds Extracted from Dianthus superbus L. against Glutamate-induced Cell Death in HT22 Cells.[Pubmed: 27076746]
Dianthus superbus L. has been used in Chinese herbal medicine as a diuretic and anti-inflammatory agent.
Analysis of the Complete Chloroplast Genome of a Medicinal Plant, Dianthus superbus var. longicalyncinus, from a Comparative Genomics Perspective.[Pubmed: 26513163]
Dianthus superbus var. longicalycinus is an economically important traditional Chinese medicinal plant that is also used for ornamental purposes. In this study, D. superbus was compared to its closely related family of Caryophyllaceae chloroplast (cp) genomes such as Lychnis chalcedonica and Spinacia oleracea. D. superbus had the longest large single copy (LSC) region (82,805 bp), with some variations in the inverted repeat region A (IRA)/LSC regions. The IRs underwent both expansion and constriction during evolution of the Caryophyllaceae family; however, intense variations were not identified. The pseudogene ribosomal protein subunit S19 (rps19) was identified at the IRA/LSC junction, but was not present in the cp genome of other Caryophyllaceae family members. The translation initiation factor IF-1 (infA) and ribosomal protein subunit L23 (rpl23) genes were absent from the Dianthus cp genome. When the cp genome of Dianthus was compared with 31 other angiosperm lineages, the infA gene was found to have been lost in most members of rosids, solanales of asterids and Lychnis of Caryophyllales, whereas rpl23 gene loss or pseudogization had occurred exclusively in Caryophyllales. Nevertheless, the cp genome of Dianthus and Spinacia has two introns in the proteolytic subunit of ATP-dependent protease (clpP) gene, but Lychnis has lost introns from the clpP gene. Furthermore, phylogenetic analysis of individual protein-coding genes infA and rpl23 revealed that gene loss or pseudogenization occurred independently in the cp genome of Dianthus. Molecular phylogenetic analysis also demonstrated a sister relationship between Dianthus and Lychnis based on 78 protein-coding sequences. The results presented herein will contribute to studies of the evolution, molecular biology and genetic engineering of the medicinal and ornamental plant, D. superbus var. longicalycinus.


