EmodinNaturally occurring anthraquinone,antiproliferative CAS# 518-82-1 |
- Celastrol
Catalog No.:BCN5986
CAS No.:34157-83-0
- BMS-345541
Catalog No.:BCC1423
CAS No.:547757-23-3
- Bay 65-1942 free base
Catalog No.:BCC1408
CAS No.:600734-02-9
- Bay 65-1942 HCl salt
Catalog No.:BCC1409
CAS No.:600734-06-3
- Bay 65-1942 R form
Catalog No.:BCC1410
CAS No.:758683-21-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 518-82-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3220 | Appearance | Orange powder |
| Formula | C15H10O5 | M.Wt | 270.2 |
| Type of Compound | Anthraquinones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Frangula emodin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 9.4 mg/mL (34.78 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
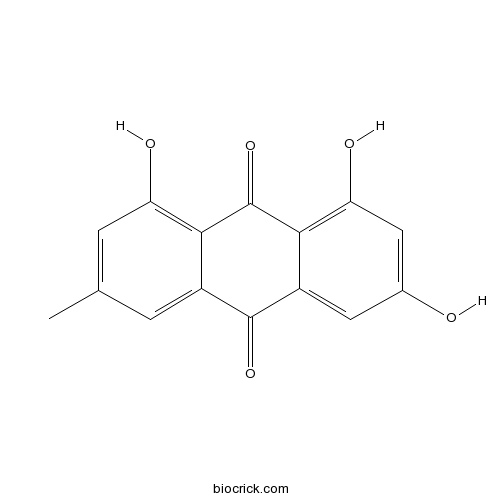
| Chemical Name | 1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methylanthracene-9,10-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=C2C(=C1)C(=O)C3=CC(=CC(=C3C2=O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RHMXXJGYXNZAPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H10O5/c1-6-2-8-12(10(17)3-6)15(20)13-9(14(8)19)4-7(16)5-11(13)18/h2-5,16-18H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Emodin has neuroprotective and antidepressant activity, can up-regulate GR and BDNF levels in hippocampus; it also has significant anti-neoplastic activity against bladder cancer cells and myeloid leukemia, by suppressing tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), iNOS and COX-2 expression. Emodin has protective effects, may be related to the inhibition of CCL5 expression and subsequent cell stress/inflammatory events possibly mediated by activation of MAPK signaling pathways. |
| Targets | p38MAPK | ERK | PARP | Caspase | PI3K | Akt | Bcl-2/Bax | mTOR | NF-kB | IkB | JNK | PPAR | NOS | COX | IL Receptor | TNF-α | IKK |
| In vitro | Protection of vascular endothelial cells from high glucose-induced cytotoxicity by emodin.[Pubmed: 25619422]Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Mar 1;94(1):39-45.Induction of endothelial cytotoxicity by hyperglycemia in diabetes has been widely accepted. Emodin is a natural anthraquinone in rhubarb used for treatment of diabetes, but its mechanism of action is not fully understood. This study aimed to examine the potential beneficial effects of Emodin on endothelial cytotoxicity caused by high glucose milieu. Emodin enhances ATRA-induced differentiation and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells.[Pubmed: 25174432]Int J Oncol. 2014 Nov;45(5):2076-84.Emodin, an extracted natural compound from the root and rhizome of Rheum palmatum L, has been shown to have multiple biological activities including anticancer functions in previous studies. |
| In vivo | Emodin opposes chronic unpredictable mild stress induced depressive-like behavior in mice by upregulating the levels of hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor.[Pubmed: 24932776]Fitoterapia. 2014 Oct;98:1-10.Emodin, the major active component of Rhubarb, has shown neuroprotective activity. This study is attempted to investigate whether Emodin possesses beneficial effects on chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS)-induced behavioral deficits (depression-like behaviors) and explore the possible mechanisms. |
| Kinase Assay | Emodin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response by activating PPAR-γ in mouse mammary epithelial cells.[Pubmed: 24874440]Emodin modulates epigenetic modifications and suppresses bladder carcinoma cell growth.[Pubmed: 24115089]Mol Carcinog. 2015 Mar;54(3):167-77.We investigated whether a natural product, Emodin, has the ability to reverse these two epigenetic modifications and inhibit bladder cancer cell growth. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Aug;21(2):354-60.Emodin, an anthraquinone derivative isolated from the rhizomes of Rheum palmatum, has been reported to have a protective effect against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced mastitis. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are not well understood. |

Emodin Dilution Calculator

Emodin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.701 mL | 18.5048 mL | 37.0096 mL | 74.0192 mL | 92.5241 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7402 mL | 3.701 mL | 7.4019 mL | 14.8038 mL | 18.5048 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3701 mL | 1.8505 mL | 3.701 mL | 7.4019 mL | 9.2524 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.074 mL | 0.3701 mL | 0.7402 mL | 1.4804 mL | 1.8505 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.037 mL | 0.185 mL | 0.3701 mL | 0.7402 mL | 0.9252 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Description: IC50 Value: observed at 72 hr were as follows: 66.9 uM, Hep3B cells; 74.36 uM, HepG2 cells; and 101.5 uM, Huh7 cells [1]. Emodin (1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methylanthraquinone) is a naturally occurring anthraquinone present in the roots and barks of numerous plants, molds, and lichens, and an active ingredient of various Chinese herbs. Emodin exerts antiproliferative effects in cancer cells that are regulated by different signaling pathways. in vitro: At 6h after emodin treatment, the levels of GDF15, CYP1A1, CYP1B1, and CYR61 were upregulated [1]. Emodin increased the resting tension of gallbladder smooth muscle strips and inhibited voltage-dependent K(+) current in a dose-dependent manner. When 10 microM emodin was applied to gallbladder smooth muscle cells for 3-6 min., the amplitude of voltage-dependent K(+) current was decreased by 31.5 +/- 0.5% at +40 mV, and this inhibitory effect mostly recovered after washout [2]. in vivo: Emodin treatment significantly alleviated the severity of the disease, based on the reduced hind paw swelling and clinical scores, compared with untreated CIA mice. Comparing with untreated CIA mice, emodin treatment inhibited the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in the plasma, PGE2 production, and COX-2 protein expression in synovial tissues in a dose manner [3]. Clinical trial: N/A
- Corydaline
Catalog No.:BCN2342
CAS No.:518-69-4
- Tetrandrine
Catalog No.:BCN5955
CAS No.:518-34-3
- (-)-beta-Peltatin
Catalog No.:BCN3606
CAS No.:518-29-6
- Podophyllotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN5957
CAS No.:518-28-5
- Evodiamine
Catalog No.:BCN1092
CAS No.:518-17-2
- Dehydroglyasperin D
Catalog No.:BCN6829
CAS No.:517885-72-2
- Rengynic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5644
CAS No.:517883-38-4
- Carteolol HCl
Catalog No.:BCC6466
CAS No.:51781-21-6
- Mefloquine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1737
CAS No.:51773-92-3
- Valechlorine
Catalog No.:BCN2763
CAS No.:51771-49-4
- Estra-4,9-diene-3,17-dione
Catalog No.:BCC8959
CAS No.:5173-46-6
- Uncarine E
Catalog No.:BCC8263
CAS No.:5171-37-9
- Xanthopurpurin
Catalog No.:BCN6723
CAS No.:518-83-2
- Cycleanine
Catalog No.:BCN8445
CAS No.:518-94-5
- Isomaculosidine
Catalog No.:BCN7069
CAS No.:518-96-7
- 3,3'-Di-O-methylellagic acid 4'-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1431
CAS No.:51803-68-0
- Nimesulide
Catalog No.:BCC4435
CAS No.:51803-78-2
- Oxoepistephamiersine
Catalog No.:BCN5645
CAS No.:51804-68-3
- Dihydrooxoepistephamiersine
Catalog No.:BCN5646
CAS No.:51804-69-4
- Raltegravir (MK-0518)
Catalog No.:BCC2137
CAS No.:518048-05-0
- KX1-004
Catalog No.:BCC5440
CAS No.:518058-84-9
- 2',4'-Dihydroxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN5647
CAS No.:1776-30-3
- UMI-77
Catalog No.:BCC5567
CAS No.:518303-20-3
- Angiotensin 1/2 + A (2 - 8)
Catalog No.:BCC1037
CAS No.:51833-76-2
Emodin modulates epigenetic modifications and suppresses bladder carcinoma cell growth.[Pubmed:24115089]
Mol Carcinog. 2015 Mar;54(3):167-77.
The deregulation of epigenetics was involved in early and subsequent carcinogenic events. Reversing cancer epigenetics to restore a normal epigenetic condition could be a rational approach for cancer treatment and specialized prevention. In the present study, we found that the expression levels of two epigenetic markers, histone H3K27 trimethylation (H3K27me3), was low but histone H3S10 phosphorylation (pH3Ser10) was high in human bladder cancer tissues, which showed opposite expression patterns in their normal counterparts. Thus, we investigated whether a natural product, Emodin, has the ability to reverse these two epigenetic modifications and inhibit bladder cancer cell growth. Emodin significantly inhibited the cell growth of four bladder cancer cell lines in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Emodin treatment did not induce specific cell cycle arrest, but it altered epigenetic modifications. Emodin treatment resulted in the suppression of pH3Ser10 and increased H3K27me3, contributing to gene silencing in bladder cancer cells. Microarray analysis demonstrated that oncogenic genes including fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) and fibroblast growth factor binding protein 1 (HBP17), RGS4, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 (TIMP3), WNT5b, URB, and collagen, type VIII, alpha 1 (COL8A1) responsible for proliferation, survival, inflammation, and carcinogenesis were significantly repressed by Emodin. The ChIP assays also showed that Emodin increased H3K27me3 but decreased pH3Ser10 modifications on the promoters of repressed genes, which indicate that Emodin reverses the cancer epigenetics towards normal epigenetic situations. In conclusion, our work demonstrates the significant anti-neoplastic activity of Emodin on bladder cancer cells and elucidates the novel mechanisms of Emodin-mediated epigenetic modulation of target genes. Our study warrants further investigation of Emodin as an effective therapeutic or preventive agent for bladder cancer.
Emodin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response by activating PPAR-gamma in mouse mammary epithelial cells.[Pubmed:24874440]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Aug;21(2):354-60.
Emodin, an anthraquinone derivative isolated from the rhizomes of Rheum palmatum, has been reported to have a protective effect against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced mastitis. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are not well understood. The aim of this study was to investigate the molecular mechanisms of Emodin in modifying lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced signaling pathways in mouse mammary epithelial cells (MEC). The pro-inflammatory cytokines were determined by ELISA. Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB), inhibitory kappa B (IkappaBalpha) protein, p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and PPAR-gamma were determined by Western blotting. The results showed that Emodin suppressed tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-6 (IL-6), iNOS and COX-2 expression. We also found that Emodin inhibited LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation, IkappaBalpha degradation, phosphorylation of ERK, JNK and P38. Furthermore, Emodin could activate PPAR-gamma and the anti-inflammatory effects of Emodin can be reversed by GW9662, a specific antagonist for PPAR-gamma. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that Emodin activates PPAR-gamma, thereby attenuating LPS-induced inflammatory response.
Emodin enhances ATRA-induced differentiation and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells.[Pubmed:25174432]
Int J Oncol. 2014 Nov;45(5):2076-84.
Emodin, an extracted natural compound from the root and rhizome of Rheum palmatum L, has been shown to have multiple biological activities including anticancer functions in previous studies. In this study, we investigated the anti-leukemic activity of Emodin alone or Emodin in the presence all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and the potential signaling pathway involved. We demonstrated that Emodin could significantly enhance the sensitivity to ATRA and present additive differentiation-inducing effects in AML cell line NB4 cells and, especially, in NB4-derived ATRA-resistant MR2 cells. Further study showed that increasing dose of Emodin could effectively induce growth inhibition and apoptotic effects in both cell lines as well as in primary leukemic cells from AML patients. Moreover, the apoptotic induction in AML cells was associated with the activation of caspase cascades involving caspase-9, caspase-3, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage. In addition, leukemic cell response to Emodin stimuli in vitro was observed through the decreased expression levels of Bcl-2 and retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARalpha). Importantly, Emodin was demonstrated as a new inhibitor of PI3K/Akt in AML cells, even in primary AML cells. It inhibited Akt phosphoration (p-Akt) at Ser473 as efficiently as mTOR at Ser2448. Consistently, it exerted suppression effects on the phosphoration of mTOR downstream targets, 4E-BP1 and p70S6K. Taken together, these findings indicate that Emodin might be developed as a promising anti-leukemic agent to improve the patient outcome in AML.
Emodin opposes chronic unpredictable mild stress induced depressive-like behavior in mice by upregulating the levels of hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor.[Pubmed:24932776]
Fitoterapia. 2014 Oct;98:1-10.
Emodin, the major active component of Rhubarb, has shown neuroprotective activity. This study is attempted to investigate whether Emodin possesses beneficial effects on chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS)-induced behavioral deficits (depression-like behaviors) and explore the possible mechanisms. ICR mice were subjected to chronic unpredictable mild stress for 42 consecutive days. Then, Emodin and fluoxetine (positive control drug) were administered for 21 consecutive days at the last three weeks of CUMS procedure. The classical behavioral tests: open field test (OFT), sucrose preference test (SPT), tail suspension test (TST) and forced swimming test (FST) were applied to evaluate the antidepressant effects of Emodin. Then plasma corticosterone concentration, hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels were tested to probe the mechanisms. Our results indicated that 6 weeks of CUMS exposure induced significant depression-like behavior, with high, plasma corticosterone concentration and low hippocampal GR and BDNF expression levels. Whereas, chronic Emodin (20, 40 and 80 mg/kg) treatments reversed the behavioral deficiency induced by CUMS exposure. Treatment with Emodin normalized the change of plasma corticosterone level, which demonstrated that Emodin could partially restore CUMS-induced HPA axis impairments. Besides, hippocampal GR (mRNA and protein) and BDNF (mRNA) expressions were also up-regulated after Emodin treatments. In conclusion, Emodin remarkably improved depression-like behavior in CUMS mice and its antidepressant activity is mediated, at least in part, by the up-regulating GR and BDNF levels in hippocampus.
Protection of vascular endothelial cells from high glucose-induced cytotoxicity by emodin.[Pubmed:25619422]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Mar 1;94(1):39-45.
Induction of endothelial cytotoxicity by hyperglycemia in diabetes has been widely accepted. Emodin is a natural anthraquinone in rhubarb used for treatment of diabetes, but its mechanism of action is not fully understood. This study aimed to examine the potential beneficial effects of Emodin on endothelial cytotoxicity caused by high glucose milieu. Culture of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with high concentrations of glucose resulted in damage to the cells, leading to decreased formazan products by 14-27%, reduced DNA contents by 12-19%, and increased hypodiploid apoptosis by 40-109%. These adverse effects of high glucose could be prevented to a large extent by co-culture with 3 muM of Emodin which per se did not affect HUVECs viability. In addition, CCL5 expression of HUVECs cultured in high glucose medium was significantly elevated at both mRNA and protein levels, an effect abolished after treatment with Emodin. Moreover, the enhanced adhesion of monocytes to HUVECs (2.1-2.2 fold over control) and elevated chemotaxis activities (2.3-2.4 fold over control) in HUVECs cultured in high glucose medium were completely reversed by Emodin. Emodin also suppressed activation of p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 due to high glucose. Our data demonstrated that endothelial cytotoxicity occurred clearly when HUVECs were exposed to high glucose milieu and Emodin was able to alleviate the impairments. The protective effects of Emodin might be related to the inhibition of CCL5 expression and subsequent cell stress/inflammatory events possibly mediated by activation of MAPK signaling pathways.
Anti-tumor activity of emodin against human chronic myelocytic leukemia K562 cell lines in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:19857484]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Feb 10;627(1-3):33-41.
Emodin (1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methyl-anthraquinone), a natural anthraquinone derivative isolated from Rheum palmatum L, has been reported to exhibit anti-cancer effect on several human cancers such as liver cancers and lung cancers. However, the molecular mechanisms of Emodin-mediated tumor regression have not been fully defined. Our preliminary study showed that Emodin had highly cytotoxic effect on human chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cell lines. This study was performed to investigate the anti-tumor effect of Emodin in human K562 cell line in vitro and in vivo. The MTT data showed the inhibition on growth of K562 cells following Emodin treatment. Flow cytometry showed that the cell cycle of K562 cells was arrested in G(0)/G(1) phase. Through Western blot analysis, we found that the apoptosis-related protein Bcl-2 was decreased in a dose-dependent manner and the Bax was increased after Emodin treatment. Moreover, activations of caspase-3, -8 and -9 were demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. The increased Bax concurrent with the decreased of Bcl-2 indicated that Emodin treatment might result in apoptosis of K562 cells. The cell apoptosis was also directly demonstrated by Annexin V-FITC, and DNA fragmentation assay. Additionally, the tumoricidal effect of Emodin was measured using a xenograft nude mice model. We found that, after inoculated with the K562 cells, the nude mice treated with Emodin showed a significant decrease of tumor volume and tumor weight in comparison to the control. Emodin could cause the regression of tumor. Both in vitro and in vivo studies suggest that Emodin can be developed as a promising anti-chronic myeloid leukemia drug.
Neuroprotective effects of emodin in rat cortical neurons against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity.[Pubmed:20573598]
Brain Res. 2010 Aug 6;1347:149-60.
Accumulation of beta-amyloid protein (Abeta) in the brain plays an important role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this study, the neuroprotective effect of Emodin extracted from the traditional Chinese medicinal herb Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc against Abeta(25-35)-induced cell death in cultured cortical neurons was investigated. We found that pre-treatment with Emodin prevented the cultured cortical neurons from beta-amyloid-induced toxicity. The preventive effect of Emodin was blocked by pre-treatment with a phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway inhibitor LY294002 or an estrogen receptor (ER) specific antagonist ICI182780, but not by pre-treatment with an extracellular signal-related kinases (ERK) inhibitor U0126. Furthermore, we found that Emodin exposure induced the activation of the Akt serine/threonine kinase and increased the level of Bcl-2 expression. Moreover, the application of Emodin for 24h was able to induce the activation of Abeta(25-35)-suppressed Akt and decrease the activation of the Jun-N-terminal kinases (JNK), but not of ERK. Interestingly, the up-regulation of Akt and Bcl-2 did not occur in the presence of LY294002 or ICI182780, suggesting that Emodin-up-regulated Bcl-2 is mediated via the ER and PI3K/Akt pathway. Taken together, our results suggest that Emodin is an effective neuroprotective drug and is a viable candidate for treating AD.
Emodin-mediated protection from acute myocardial infarction via inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis in local ischemic myocardium.[Pubmed:17939930]
Life Sci. 2007 Oct 13;81(17-18):1332-8.
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is associated with inflammation and apoptosis. Emodin plays an anti-inflammatory role in several inflammatory diseases. Recent studies have demonstrated that Emodin protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. However, its mechanism underlying its effects remains unknown. In a murine model of AMI, based on ligation of the left coronary artery, administration of Emodin reduced myocardial infarct size (MIS) in a dose-dependent manner. Emodin significantly suppressed TNF-alpha expression and NF-kappaB activation in the local myocardial infarction area. Treatment with Emodin inhibited myocardial cell apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3 activation. Therefore, these studies demonstrate that Emodin protects against myocardial cell injury via suppression of local inflammation and apoptosis.


