BMS-345541IKK inhibitor,highly selective CAS# 547757-23-3 |
- MRT67307
Catalog No.:BCC1779
CAS No.:1190378-57-4
- IKK-2 inhibitor VIII
Catalog No.:BCC1642
CAS No.:406209-26-5
- TPCA-1
Catalog No.:BCC2473
CAS No.:507475-17-4
- Bay 65-1942 HCl salt
Catalog No.:BCC1409
CAS No.:600734-06-3
- IKK-3 Inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1643
CAS No.:862812-98-4
- IMD 0354
Catalog No.:BCC4556
CAS No.:978-62-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 547757-23-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9926054 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H18ClN5 | M.Wt | 291.78 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | BMS-345541 hydrochloride | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 20 mg/mL (68.54 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
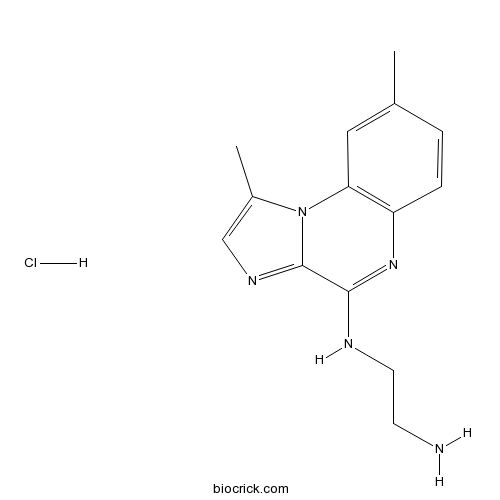
| Chemical Name | N'-(1,8-dimethylimidazo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-4-yl)ethane-1,2-diamine;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=C(C3=NC=C(N23)C)NCCN.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MIDKPVLYXNLFGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H17N5.ClH/c1-9-3-4-11-12(7-9)19-10(2)8-17-14(19)13(18-11)16-6-5-15;/h3-4,7-8H,5-6,15H2,1-2H3,(H,16,18);1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective allosteric inhibitor of IKK (IC50 values are 0.3 and 4.0 μM for IKKβ and IKKα respectively). Exhibits no effect against a panel of 15 other kinases. Attenuates LPS-induced cytokine production in vitro and blocks NFκB dependent transcription in mice. Also suppresses joint destruction in a mouse model of arthritis. |

BMS-345541 Dilution Calculator

BMS-345541 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4272 mL | 17.1362 mL | 34.2724 mL | 68.5448 mL | 85.681 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6854 mL | 3.4272 mL | 6.8545 mL | 13.709 mL | 17.1362 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3427 mL | 1.7136 mL | 3.4272 mL | 6.8545 mL | 8.5681 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0685 mL | 0.3427 mL | 0.6854 mL | 1.3709 mL | 1.7136 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0343 mL | 0.1714 mL | 0.3427 mL | 0.6854 mL | 0.8568 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
BMS-345541 is a highly selective inhibitor of IKK-1 and IKK-2 with IC50 values of 4μM and 0.3μM, respectively [1].
BMS-345541 is a highly selective inhibitor of IKK that inhibits NF-κB-dependent transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines both in vitro and in vivo. This specificity is proved in the assay measuring the IKK-2-catalyzed phosphorylation of GST-IκB. In this assay, BMS-345541 fails to inhibit other serine/threonine and tyrosine kinases. This selectivity is also evident in cells, only the stimulus-induced phosphorylation of IκB was inhibited by BMS-345541 whereas other signal transduction cascades were unaffected [1].
Since the IKK/ NFκB pathway is important for viability of leukemic cells and is a predictor of relapse in T-ALL, BMS-345541 is tested in some T-ALL cell lines. It is found that BMS-345541 can induce apoptosis and an accumulation of cells in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle. BMS-345541 can be used in combination with traditional therapies to overcome resistance to chemotherapeutic agents [2].
References:
[1] James R. Burke, Mark A. Pattoli, Kurt R. Gregor, Patrick J. Brassil, John F. MacMaster, Kim W. McIntyre, Xiaoxia Yang, Violetta S. Iotzova, Wendy Clarke, Joann Strnad, Yuping Qiu and F. Christopher Zusi. BMS-345541 Is a Highly Selective Inhibitor of IκB Kinase That Binds at an Allosteric Site of the Enzyme and Blocks NF-κB-dependent Transcription in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278:1450-1456.
[2] Francesca Buontempo, Francesca Chiarini, Daniela Bressanin, Giovanna tabellini, Fraia Melchionda, Andrea pession, Milena Fini, Luca M. Neri, James A. McCubrey and Alberto M. Martelli. Activity of the selective IκB kinase inhibitor BMS-345541 against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cell Cycle. 2012, 11 (13): 2467-2475.
- JTE 013
Catalog No.:BCC7348
CAS No.:547756-93-4
- Fluvoxamine
Catalog No.:BCC4214
CAS No.:54739-18-3
- 4-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone
Catalog No.:BCN6797
CAS No.:5471-51-2
- 20-Deoxyingenol
Catalog No.:BCN3770
CAS No.:54706-99-9
- Dodecanoic acid ingenol ester
Catalog No.:BCN8291
CAS No.:54706-70-6
- 8-Hydroxy-7-iodo-5-quinolinesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8788
CAS No.:547-91-1
- 4'-Benzyloxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8698
CAS No.:54696-05-8
- 2-(Acetylamino)-3-phenyl-2-propenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1420
CAS No.:5469-45-4
- 1-O-Methyljatamanin D
Catalog No.:BCN6671
CAS No.:54656-47-2
- ML 204
Catalog No.:BCC6272
CAS No.:5465-86-1
- 2-Amino-4-methoxybenzothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8532
CAS No.:5464-79-9
- Boc-Hyp(Bzl)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3253
CAS No.:54631-81-1
- Hypericin
Catalog No.:BCN5977
CAS No.:548-04-9
- Roemerine
Catalog No.:BCN8236
CAS No.:548-08-3
- Isoginkgetin
Catalog No.:BCN2320
CAS No.:548-19-6
- Isolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN5727
CAS No.:548-29-8
- Oxysanguinarine
Catalog No.:BCN8100
CAS No.:548-30-1
- Cornin
Catalog No.:BCN5008
CAS No.:548-37-8
- Crystal Violet
Catalog No.:BCC4772
CAS No.:548-62-9
- Quercetagetin-7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN6480
CAS No.:548-75-4
- Irigenin
Catalog No.:BCN3849
CAS No.:548-76-5
- Tectorigenin
Catalog No.:BCN1019
CAS No.:548-77-6
- Pinobanksin
Catalog No.:BCN5729
CAS No.:548-82-3
- Galangin
Catalog No.:BCN5730
CAS No.:548-83-4
BMS-345541 sensitizes MCF-7 breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation by selective inhibition of homologous recombinational repair of DNA double-strand breaks.[Pubmed:23259762]
Radiat Res. 2013 Feb;179(2):160-70.
Our study was to elucidate the mechanisms whereby BMS-345541 (BMS, a specific IkappaB kinase beta inhibitor) inhibits the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and evaluate whether BMS can sensitize MCF-7 breast cancer cells (MCF-7 cells) to ionizing radiation (IR) in an apoptosis-independent manner. In this study, MCF-7 cells were exposed to IR in vitro and in vivo with or without pretreatment of BMS. The effects of BMS on the repair of IR-induced DSBs by homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) were analyzed by the DR-GFP and EJ5-GFP reporter assays and IR-induced gamma-H2AX, 53BP1, Brca1 and Rad51 foci assays. The mechanisms by which BMS inhibits HR were examined by microarray analysis and quantitative reverse transcription PCR. The effects of BMS on the sensitivity of MCF-7 cells to IR were determined by MTT and clonogenic assays in vitro and tumor growth inhibition in vivo in a xenograft mouse model. The results showed that BMS selectively inhibited HR repair of DSBs in MCF-7 cells, most likely by down-regulation of several genes that participate in HR. This resulted in a significant increase in the DNA damage response that sensitizes MCF-7 cells to IR-induced cell death in an apoptosis-independent manner. Furthermore, BMS treatment sensitized MCF-7 xenograft tumors to radiation therapy in vivo in an association with a significant delay in the repair of IR-induced DSBs. These data suggest that BMS is a novel HR inhibitor that has the potential to be used as a radiosensitizer to increase the responsiveness of cancer to radiotherapy.
Activity of the selective IkappaB kinase inhibitor BMS-345541 against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: involvement of FOXO3a.[Pubmed:22713244]
Cell Cycle. 2012 Jul 1;11(13):2467-75.
Several lines of evidence suggest that the IkappaB kinase (IKK)/nuclear factor-kappaB (NFkappaB) axis is required for viability of leukemic cells and is a predictor of relapse in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). Moreover, many anticancer agents induce NFkappaB nuclear translocation and activation of its target genes, which counteract cellular resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. Therefore, the design and the study of IKK-specific drugs is crucial to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and to prevent cancer drug-resistance. Here, we report the anti-proliferative effects induced by BMS-345541 (a highly selective IKK inhibitor) in three Notch1-mutated T-ALL cell lines and in T-ALL primary cells from pediatric patients. BMS-345541 induced apoptosis and an accumulation of cells in the G 2/M phase of the cell cycle via inhibition of IKK/NFkappaB signaling. We also report that T-ALL cells treated with BMS-345541 displayed nuclear translocation of FOXO3a and restoration of its functions, including control of p21(Cip1) expression levels. We demonstrated that FOXO3a subcellular re-distribution is independent of AKT and ERK 1/2 signaling, speculating that in T-ALL the loss of FOXO3a tumor suppressor function could be due to deregulation of IKK, as has been previously demonstrated in other cancer types. It is well known that, differently from p53, FOXO3a mutations have not yet been found in human tumors, which makes therapeutics activating FOXO3a more appealing than others. For these features, BMS-345541 could be used alone or in combination with traditional therapies in the treatment of T-ALL.
Inhibition of type I interferon-mediated antiviral action in human glioma cells by the IKK inhibitors BMS-345541 and TPCA-1.[Pubmed:22509977]
J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012 Aug;32(8):368-77.
The nuclear factor-kappa B (NFkappaB) signal transduction pathway plays an important role in immunity, inflammation, cell growth, and survival. Since dysregulation of this pathway results in high, constitutive NFkappaB activation in various cancers and immune disorders, the development of specific drugs to target this pathway has become a focus for treating these diseases. NFkappaB regulates various aspects of the cellular response to interferon (IFN). However, the role of the upstream regulator of the NFkappaB signaling pathway, the inhibitor of kappaB kinase (IKK) complex, on IFN function has not been examined. In the present study, we examined the effects of 2 IKK inhibitors, N-(1,8-Dimethylimidazo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-4-yl)-1,2-ethanediamine hydrochloride (BMS-345541) and 2-[(aminocarbonyl)amino]-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-thiophenecarboxamide (TPCA-1), on IFN action in several human glioma cell lines. IKK inhibitors inhibit glioma cell proliferation, as well as TNF-induced RelA (p65) nuclear translocation and NFkappaB-dependent IL8 gene expression. Importantly, BMS-345541 and TPCA-1 differentially inhibit IFN-induced gene expression, completely suppressing MX1 and GBP1 gene expression, while having only a minor effect on ISG15 expression. Furthermore, these IKK inhibitors displayed marked differences in blocking IFN-induced antiviral action against cytopathic effects and replication of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV). Our results show that the IKK complex plays an important function in IFN-induced gene expression and antiviral activity. Since VSV and EMCV are oncolytic viruses used in cancer therapy, our results indicate the potential synergy in combining IKK inhibitors with oncolytic viruses.
Sensitization of melanoma cells for TRAIL-induced apoptosis by BMS-345541 correlates with altered phosphorylation and activation of Bax.[Pubmed:23348591]
Cell Death Dis. 2013 Jan 24;4:e477.
Resistance to TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand)- induced apoptosis limits its therapeutic use. Different strategies of TRAIL sensitization and a dependency on Bax have been reported, but common principles of TRAIL resistance and the way of Bax activation remained poorly understood. Applying a melanoma model of TRAIL-sensitive and -resistant cell lines, efficient sensitization for TRAIL-induced apoptosis is demonstrated by the kinase inhibitor BMS-345541 (N-(1,8-dimethylimidazo(1,2-a)quinoxalin-4-yl)-1,2-ethanediamine hydrochloride), which targets IkappaB (inhibitor of kappaB proteins) kinase beta (IKKbeta). This effect was completely abrogated by Bax knockout as well as by Bcl-2 overexpression, in accordance with a Bax dependency. Early loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome c and Smac (second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases) clearly indicated the activation of mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. Of note, BMS-345541 alone resulted in an early Bax activation, seen by conformational changes and by Bax translocation. The synergistic effects can be explained by Bid activation through TRAIL, which inhibits Bcl-2, and the activation of Bax through BMS-345541. The critical roles of XIAP (X-chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein), Smac and Bid were clearly proven by overexpression and siRNA knockdown, respectively. The way of Bax activation by BMS-345541 was unraveled by establishing new assays for Bax activation. These showed reduction of the inactivating Bax phosphorylation at serine-184, while the activating Bax phosphorylation at threonine-167 was enhanced. Thus, modulation of Bax phosphorylation appeared as tightly related to TRAIL sensitivity/resistance in melanoma cells, and therapeutic strategies may be considered.
Inhibition of choriodecidual cytokine production and inflammatory gene expression by selective I-kappaB kinase (IKK) inhibitors.[Pubmed:20649582]
Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;160(7):1808-22.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Inflammation of the extraplacental membranes plays a key role in the pathogenesis of preterm labour. The aim of this study was to screen a number of commercially available small molecule nuclear factor-kappa B inhibitors to identify candidates suitable for clinical evaluation as anti-inflammatory agents for the prevention of preterm birth. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: Nine inhibitors were evaluated across a range of concentrations for their ability to inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated cytokine production in primary term choriodecidual cells in culture without affecting cell viability. Expression of 112 inflammation- and apoptosis-related genes was evaluated using boutique oligonucleotide arrays. KEY RESULTS: Two IKKbeta inhibitors were found to be highly effective and non-toxic inhibitors of choriodecidual cytokine production: parthenolide and [5-(p-fluorophenyl)-2-ureido] thiophene-3-carboxamide (TPCA-1). Both compounds also inhibited LPS-stimulated nuclear translocation of p65/RelA. Expression of 38 genes on the arrays (34%) was significantly (P < 0.05) inhibited by TPCA-1 or parthenolide. Of the 14 genes significantly stimulated by LPS, all were inhibited by TPCA-1 and 12 were inhibited by parthenolide. Overall, gene expression was more robustly inhibited by TPCA-1 than parthenolide; however, expression of two genes was only inhibited by parthenolide. Neither compound significantly altered the expression profile of anti-apoptosis genes on the arrays. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: These studies provide evidence that pharmacological inhibition of IKKbeta activity holds promise as a potential strategy for the prevention and/or treatment of inflammation-driven preterm birth. TPCA-1 appeared the most promising compound among those tested in this study. Different inhibitors may have subtly different effect profiles despite having similar modes of action.
Collagen and aggrecan degradation is blocked in interleukin-1-treated cartilage explants by an inhibitor of IkappaB kinase through suppression of metalloproteinase expression.[Pubmed:16009742]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Oct;315(1):382-8.
It has previously been shown that BMS-345541 [4(2'-aminoethyl)amino-1,8-dimethylimidazo(1,2-a)quinoxaline], a highly-selective inhibitor of IkappaB kinase (IKK), blocks both inflammation and joint destruction in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Although this agent has been shown to inhibit nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent cytokine expression in mice, we examined whether the inhibitor directly inhibits cytokine-driven metalloproteinase expression and cartilage degradation. In SW-1353 human chondrosarcoma cells, BMS-345541 inhibited interleukin-1 (IL-1)-dependent expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 in a concentration-dependent manner. IL-1 treatment failed to induce and BMS-345541 did not inhibit the expression of aggrecanases ADAMTS-4 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain with thrombospondin motif) and ADAMTS-5, as well as the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3. In bovine cartilage explant cultures stimulated with IL-1 to induce aggrecan and collagen degradation over 3 weeks of culture, BMS-345541 was effective in inhibiting the degradation of both aggrecan and collagen. Secreted ADAMTS-4 was not inhibited by BMS-345541 in these explants, whereas ADAMTS-5 secretion was blocked in the same concentration range that inhibited aggrecan degradation. The ability of the IKK inhibitor to block aggrecan and collagen degradation through suppression of metalloproteinase expression, coupled with its ability to block inflammatory cytokine production, shows IKK to be a promising target for the development of novel agents to treat arthritic diseases.
BMS-345541 is a highly selective inhibitor of I kappa B kinase that binds at an allosteric site of the enzyme and blocks NF-kappa B-dependent transcription in mice.[Pubmed:12403772]
J Biol Chem. 2003 Jan 17;278(3):1450-6.
The signal-inducible phosphorylation of serines 32 and 36 of I kappa B alpha is critical in regulating the subsequent ubiquitination and proteolysis of I kappa B alpha, which then releases NF-kappa B to promote gene transcription. The multisubunit I kappa B kinase responsible for this phosphorylation contains two catalytic subunits, termed I kappa B kinase (IKK)-1 and IKK-2. BMS-345541 (4(2'-aminoethyl)amino-1,8-dimethylimidazo(1,2-a)quinoxaline) was identified as a selective inhibitor of the catalytic subunits of IKK (IKK-2 IC(50) = 0.3 microm, IKK-1 IC(50) = 4 microm). The compound failed to inhibit a panel of 15 other kinases and selectively inhibited the stimulated phosphorylation of I kappa B alpha in cells (IC(50) = 4 microm) while failing to affect c-Jun and STAT3 phosphorylation, as well as mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 activation in cells. Consistent with the role of IKK/NF-kappa B in the regulation of cytokine transcription, BMS-345541 inhibited lipopolysaccharide-stimulated tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-8, and interleukin-6 in THP-1 cells with IC(50) values in the 1- to 5-microm range. Although a Dixon plot of the inhibition of IKK-2 by BMS-345541 showed a non-linear relationship indicating non-Michaelis-Menten kinetic binding, the use of multiple inhibition analyses indicated that BMS-345541 binds in a mutually exclusive manner with respect to a peptide inhibitor corresponding to amino acids 26-42 of I kappa B alpha with Ser-32 and Ser-36 changed to aspartates and in a non-mutually exclusive manner with respect to ADP. The opposite results were obtained when studying the binding to IKK-1. A binding model is proposed in which BMS-345541 binds to similar allosteric sites on IKK-1 and IKK-2, which then affects the active sites of the subunits differently. BMS-345541 was also shown to have excellent pharmacokinetics in mice, and peroral administration showed the compound to dose-dependently inhibit the production of serum tumor necrosis factor alpha following intraperitoneal challenge with lipopolysaccharide. Thus, the compound is effective against NF-kappa B activation in mice and represents an important tool for investigating the role of IKK in disease models.


