IMD 0354IKKβ inhibitor CAS# 978-62-1 |
- DCC-2618
Catalog No.:BCC1520
CAS No.:1225278-16-9
- Imatinib Mesylate (STI571)
Catalog No.:BCC1115
CAS No.:220127-57-1
- Motesanib
Catalog No.:BCC1776
CAS No.:453562-69-1
- OSI-930
Catalog No.:BCC1253
CAS No.:728033-96-3
- Masitinib (AB1010)
Catalog No.:BCC1260
CAS No.:790299-79-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 978-62-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5081913 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H8ClF6NO2 | M.Wt | 383.67 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (260.64 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
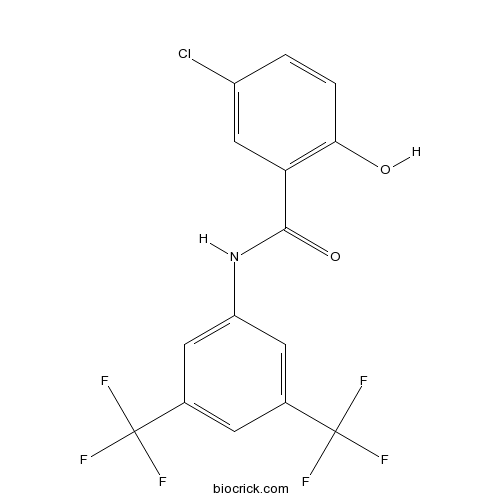
| Chemical Name | N-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1Cl)C(=O)NC2=CC(=CC(=C2)C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CHILCFMQWMQVAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H8ClF6NO2/c16-9-1-2-12(24)11(6-9)13(25)23-10-4-7(14(17,18)19)3-8(5-10)15(20,21)22/h1-6,24H,(H,23,25) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of IκB kinase-β (IKKβ) that blocks NF-κB nuclear translocation. Attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by decreasing expression of adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and P-selectin and inhibiting cytokine and chemokine production in cardiomyocytes. Induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HMC-1 and breast cancer cells. |

IMD 0354 Dilution Calculator

IMD 0354 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6064 mL | 13.032 mL | 26.0641 mL | 52.1281 mL | 65.1602 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5213 mL | 2.6064 mL | 5.2128 mL | 10.4256 mL | 13.032 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2606 mL | 1.3032 mL | 2.6064 mL | 5.2128 mL | 6.516 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0521 mL | 0.2606 mL | 0.5213 mL | 1.0426 mL | 1.3032 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0261 mL | 0.1303 mL | 0.2606 mL | 0.5213 mL | 0.6516 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: IMD-0354 showed anti-tumor effect on seven hematologic malignancy cells with IC50 ranged from 0.1M to 0.6 M.
IMD-0354, serving as an IKKβ inhibitor, inhibits IκBα phosphorylation in NF-κB pathway. [1]
In vitro: IMD-0354, at the concentration of less than 5 M, down-regulated the expression of NF-κB and blocked the translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus in HMC-1 cells. Study from HMC-1 cells also showed that IMD-0354 inhibited cell proliferation in a time and dose dependent manner. In addition, IMD-0354 at the concentration of 0.5 μM inhibited the proliferation of IC-2G559 cells and IC-2V814 cells. This agent was also reported to arrest the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase and decreased the ratio of cells in S and G2/M phases in HMC-1 cells. 1 μM IMD-0354 was reported to decrease Cyclin D3 expression and reduce pRb phosphorylation level in a time-dependent manner in HMC-1 cells. [1]
In vivo: A study from lungs of OVA-sensitized mice showed that 5 mg/kg IMD-0354 significantly inhibited NF-κB, although the magnitude of inhibition is lower than that caused by 20 mg/kg IMD-0354. 20 mg/kg IMD-0354 ameliorated airway hyper-responsiveness and decreased the numbers of bronchial eosinophils and mucus-producing cells in OVA-sensitized mice. In addition, the total numbers of cells and eosinophils was also reduced by IMD-0354 in OVA-sensitized mice. Moreover, IMD-0354 suppressed the production of Th2 cytokines inclusing IL-5, IL-13 and eotaxin in the airways and/or lungs of OVA-sensitized mice, whereas it did not alter the restoration of Th1 cytokines under the same experimental conditions. [2]
Clinical trial: So far, a phase I clinical trial of a topical formulation of IMD-0354 for treatment of atopic dermatitis had been successfully completed. [3]
References:
[1]Tanaka A, Konno M, Muto S, Kambe N, Morii E, Nakahata T, Itai A and Matsuda H. A novel NF-kappaB inhibitor, IMD-0354, suppresses neoplastic proliferation of human mast cells with constitutively activated c-kit receptors. Blood. 2005 Mar; 105(6): 2324-31.
[2]Sugita A, Ogawa H, Azuma M, Muto S, Honjo A, Yanagawa H, Nishioka Y, Tani K, Itai A and Sone S. Antiallergic and anti-inflammatory effects of a novel I kappaB kinase beta inhibitor, IMD-0354, in a mouse model of allergic inflammation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2009; 148(3): 186-98.
[3]Verstrepen L and Beyaert R. Receptor proximal kinases in NF-κB signaling as potential therapeutic targets in cancer and inflammation. Biochem Pharm. 2014; 92: 519-29.
- Lappaconitine Hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCN2505
CAS No.:97792-45-5
- Jasmoside
Catalog No.:BCN7552
CAS No.:97763-17-2
- 2,6-Dimethyl-3-O-methyl-4-(2-methylbutyryl)phloroglucinol
Catalog No.:BCN7356
CAS No.:97761-91-6
- 2,6-Dimethyl-3-O-methyl-4-isobutyrylphloroglucinol
Catalog No.:BCN7355
CAS No.:97761-90-5
- S186
Catalog No.:BCC5285
CAS No.:97759-16-5
- Chuanxiongzine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8147
CAS No.:97747-88-1
- Decynium 22
Catalog No.:BCC6271
CAS No.:977-96-8
- Boldenone propionate
Catalog No.:BCC8895
CAS No.:977-32-2
- Irinotecan
Catalog No.:BCC2490
CAS No.:97682-44-5
- Latrepirdine
Catalog No.:BCC4541
CAS No.:97657-92-6
- Ganoderic acid D2
Catalog No.:BCC8989
CAS No.:97653-94-6
- Lucidone B
Catalog No.:BCN8242
CAS No.:97653-93-5
- Penciclovir Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC5635
CAS No.:97845-62-0
- 8,9-Didehydro-7-hydroxydolichodial
Catalog No.:BCN6674
CAS No.:97856-19-4
- Norfloxacin lactate
Catalog No.:BCC9104
CAS No.:97867-34-0
- Estradiol valerate
Catalog No.:BCC4482
CAS No.:979-32-8
- 3,4'-Dihydroxy-3,5',7-trimethoxyflavan
Catalog No.:BCN4528
CAS No.:97914-19-7
- Methyl 3-carbazolecarboxylate
Catalog No.:BCN4529
CAS No.:97931-41-4
- Sophoraflavanone G
Catalog No.:BCN2987
CAS No.:97938-30-2
- Leachianone A
Catalog No.:BCN4530
CAS No.:97938-31-3
- Methyl (E)-3'-hydroxy-4'-methoxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN1294
CAS No.:97966-29-5
- Benzenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8846
CAS No.:98-11-3
- 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8688
CAS No.:98-50-0
- Terpineol
Catalog No.:BCN3595
CAS No.:98-55-5
IkappaB kinase-beta inhibitor IMD-0354 beneficially suppresses retinal vascular permeability in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.[Pubmed:25205865]
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Sep 9;55(10):6365-73.
PURPOSE: The purpose of the present study is to evaluate the effect of selective IKK-beta inhibition by IMD-0354 on inflammation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis in diabetic retinopathy (DR). METHODS: Six weeks after administration of a streptozotocin (STZ) injection, before diabetic retinopathy (DR) was evident, one group of STZ-induced diabetic mice was systemically administered with IMD-0354 (30 mg/kg) daily for another 6 weeks. Ten weeks after the STZ injection, with DR already present, another group of STZ-induced diabetic mice was administered IMD-0354 for 2 weeks. As controls, nondiabetic mice of the same age were treated with IMD-0354 for 6 weeks, and diabetic mice were treated with 10 muL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for 6 weeks. Using these groups of mice, the following effects of IMD-0354 were analyzed: (1) inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation, (2) retinal morphology, (3) apoptotic signaling by cleaved caspase-3, (4) retinal vascular permeability, (5) angiogenesis of the retina, and (6) retinal production of VEGF. RESULTS: Systemic administration of IMD-0354 for 6 weeks to week-6 diabetic mice caused significant reduction in the loss of retinal ganglion cells and apoptotic signaling, with preservation of retinal vascular integrity and suppression of retinal VEGF expression. When inhibition of NF-kappaB activation treatment started after the onset of STZ-induced DR (week 10), IMD-0354 was still effective in preventing further DR progression while the vascular integrity was preserved. CONCLUSIONS: The present data indicate that NF-kappaB activation is the key step in the development of DR. Its suppression by IMD-0354 may present a promising therapeutic strategy for DR, especially in the early stages of the disease.
IMD-0354 targets breast cancer stem cells: a novel approach for an adjuvant to chemotherapy to prevent multidrug resistance in a murine model.[Pubmed:24014113]
PLoS One. 2013 Aug 27;8(8):e73607.
Although early detection of breast cancer improved in recent years, prognosis of patients with late stage breast cancer remains poor, mostly due to development of multidrug resistance (MDR) followed by tumor recurrence. Cancer stem cells (CSCs), with higher drug efflux capability and other stem cell-like properties, are concentrated in a side population (SP) of cells, which were proposed to be responsible for MDR and tumor repopulation that cause patients to succumb to breast cancer. Therefore, targeting of CSCs as an adjuvant to chemotherapy should be able to provide a more effective treatment of this disease. Here, we used IMD-0354, an inhibitor of NF-kappaB, identified for targeting CSCs, in a combination therapy with doxorubicin encapsulated in targeted nanoparticles. IMD-0354 did target CSCs, evidenced by a decrease in the SP, demonstrated by the inhibition of the following: dye/drug efflux, reduction in ABC transporters as well as in colony formation in soft agar and low attachment plates. Decrease of stem-like gene expression of Oct4, Nanog and Sox2, and apoptosis resistance related to the Survivin gene also was observed after treatment with this compound. In addition, IMD-0354 targeted non-CSCs as indicated by reducing viability and increasing apoptosis. Targeted drug delivery, achieved with a legumain inhibitor, proved to enhance drug delivery under hypoxia, a hallmark of the tumor microenvironment, but not under normoxia. Together, this allowed a safe, non-toxic delivery of both anticancer agents to the tumor microenvironment of mice bearing syngeneic metastatic breast cancer. Targeting both bulk tumor cells with a chemotherapeutic agent and CSCs with IMD-0354 should be able to reduce MDR. This could eventually result in decreasing tumor recurrences and/or improve the outcome of metastatic disease.
IkappaB kinase beta inhibitor, IMD-0354, prevents allergic asthma in a mouse model through inhibition of CD4(+) effector T cell responses in the lung-draining mediastinal lymph nodes.[Pubmed:26868187]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Mar 15;775:78-85.
IkappaB kinase (IKK) is important for nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activation under inflammatory conditions. It has been demonstrated that IMD-0354, i.e. a selective inhibitor of IKKbeta, inhibited allergic inflammation in a mouse model of ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthma. The present study attempts to shed light on the involvement of CD4(+) effector (Teff) and regulatory (Treg) T cells in the anti-asthmatic action of IMD-0354. The animals were divided into three groups: vehicle treated, PBS-sensitized/challenged mice (PBS group); vehicle treated, OVA-sensitized/challenged mice (OVA group); and IMD-0354-treated, OVA-sensitized/challenged mice. The analyzed parameters included the absolute counts of Treg cells (Foxp3(+)CD25(+)CD4(+)), activated Teff cells (Foxp3(-)CD25(+)CD4(+)) and resting T cells (CD25(-)CD4(+)) in the mediastinal lymph nodes (MLNs), lungs and peripheral blood. Moreover, lung histopathology was performed to evaluate lung inflammation. It was found that the absolute number of cells in all studied subsets was considerably increased in the MLNs and lungs of mice from OVA group as compared to PBS group. All of these effects were fully prevented by treatment with IMD-0354. Histopathological examination showed that treatment with IMD-0354 protected the lungs from OVA-induced allergic airway inflammation. Our results indicate that IMD-0354 exerts anti-asthmatic action, at least partially, by blocking the activation and clonal expansion of CD4(+) Teff cells in the MLNs, which, consequently, prevents infiltration of the lungs with activated CD4(+) Teff cells. The beneficial effects of IMD-0354 in a mouse model of asthma are not mediated through increased recruitment of Treg cells into the MLNs and lungs and/or local generation of inducible Treg cells.
Activation of histamine H4 receptor inhibits TNFalpha/IMD-0354-induced apoptosis in human salivary NS-SV-AC cells.[Pubmed:25239604]
Apoptosis. 2014 Dec;19(12):1702-11.
Apoptosis is involved in the pathogenesis of Sjogren's syndrome (SS), an autoimmune disease affecting exocrine glands. Our recent studies revealed diminished histamine H4 receptor (H(4)R) expression and impaired histamine transport in the salivary gland epithelial cells in SS. The aim was now to test if nanomolar histamine and high-affinity H(4)R signaling affect apoptosis of human salivary gland epithelial cell. Simian virus 40-immortalized acinar NS-SV-AC cells were cultured in serum-free keratinocyte medium +/- histamine H(4)R agonist HST-10. Expression and internalization of H(4)R were studied by immunofluorescence staining +/- clathrin inhibitor methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (MbetaCD). Apoptosis induced using tumor necrosis factor-alpha with nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor IMD-0354 was studied using phase contrast microscopy, Western blot, flow cytometry and polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). HST-10-stimulated H(4)R internalization was inhibited by MbetaCD. Western blotting revealed diminished phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinase JNK, but unchanged levels of phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinase pERK1/2 in H(4)R-stimulated samples compared to controls. qRT-PCR showed up-regulated expression of anti-apoptotic B cell lymphoma-extra large/Bcl-xL mRNAs and proteins, whereas pro-apoptotic Bcl-2-associated X protein/BAX remained unchanged in H4R-stimulated samples. H(4)R stimulation diminished cleavage of PARP and flow cytometry showed significant dose-dependent inhibitory effect of H(4)R stimulation on apoptosis. As far as we know this is the first study showing inhibitory effect of H(4)R activation on apoptosis of human salivary gland cells. Diminished H(4)R-mediated activation may contribute to loss of immune tolerance in autoimmune diseases and in SS in particular.


