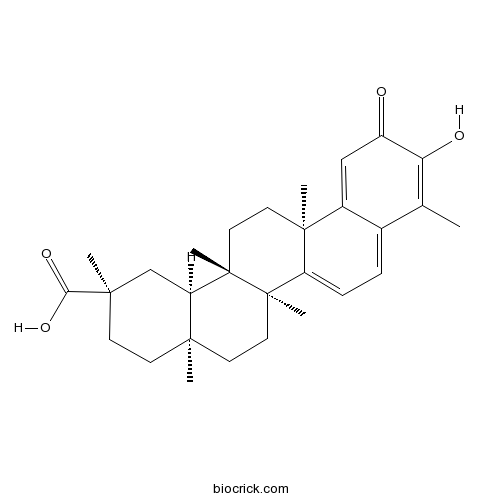
CelastrolAntioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent CAS# 34157-83-0 |
- Pefloxacin Mesylate Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5089
CAS No.:149676-40-4
- Besifloxacin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4764
CAS No.:405165-61-9
- Norfloxacin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4230
CAS No.:68077-27-0
- Pefloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4231
CAS No.:70458-92-3
- Pefloxacin Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4821
CAS No.:70458-95-6
- Norfloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4688
CAS No.:70458-96-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 34157-83-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 122724 | Appearance | Red crystalline |
| Formula | C29H38O4 | M.Wt | 450.61 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Tripterin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (110.96 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R,4aS,6aR,6aS,14aS,14bR)-10-hydroxy-2,4a,6a,6a,9,14a-hexamethyl-11-oxo-1,3,4,5,6,13,14,14b-octahydropicene-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=O)C=C2C1=CC=C3C2(CCC4(C3(CCC5(C4CC(CC5)(C)C(=O)O)C)C)C)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KQJSQWZMSAGSHN-JJWQIEBTSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C29H38O4/c1-17-18-7-8-21-27(4,19(18)15-20(30)23(17)31)12-14-29(6)22-16-26(3,24(32)33)10-9-25(22,2)11-13-28(21,29)5/h7-8,15,22,31H,9-14,16H2,1-6H3,(H,32,33)/t22-,25-,26-,27+,28-,29+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Celastrol is a potent proteasome inhibitor for the chymotrypsin-like activity of a purified 20S proteasome with IC50 of 2.5 μM. Celastrol is also a novel HSP90 inhibitor, it has anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor , antiangiogenesis, and antioxidant activities. Celastrol inhibits Plasmodium falciparum enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase and inhibits VEGF receptors expression. |
| Targets | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | VEGFR | HIF | NF-kB | Akt | HSP (e.g. HSP90) | ROS | JNK | Bcr-Abl | HIV | MAPK | TNF-α | IL Receptor | AP-1 | GLUT | HO-1 | NO |
| In vitro | Celastrol induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma bel-7402 cells.[Pubmed: 25657108]Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(1):137-48.Celastrol is a natural terpenoid isolated from Tripterygium wilfordii, a well-known Chinese medicinal herb that presents anti-proliferative activities in several cancer cell lines. Celastrol stimulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activity in tumor cells by initiating the ROS/Akt/p70S6K signaling pathway and enhancing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α protein synthesis.[Pubmed: 25383959]PLoS One. 2014 Nov 10;9(11):e112470.Celastrol, a tripterine derived from the traditional Chinese medicine plant Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. ("Thunder of God Vine"), has been reported to have multiple effects, such as anti-inflammation, suppression of tumor angiogenesis, inhibition of tumor growth, induction of apoptosis and protection of cells against human neurodegenerative diseases. However, the mechanisms that underlie these functions are not well defined. Celastrol inhibits Plasmodium falciparum enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase.[Pubmed: 25284249]Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 Nov 1;22(21):6053-61.Enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (ENR), a critical enzyme in type II fatty acid biosynthesis, is a promising target for drug discovery against hepatocyte-stage Plasmodium falciparum. |
| Kinase Assay | Celastrol ameliorates HIV-1 Tat-induced inflammatory responses via NF-kappaB and AP-1 inhibition and heme oxygenase-1 induction in astrocytes.[Pubmed: 25064159]Celastrol inhibits the growth of human glioma xenografts in nude mice through suppressing VEGFR expression.[Pubmed: 18343027 ]Cancer Lett. 2008 Jun 8;264(1):101-6.Celastrol, a compound purified from Tripterygium wilfordii whose preparations have been used for clinical treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, has been demonstrated to have antiangiogenic activity, and be inhibitory against mice tumor growth by a few recent studies. However, whether its antiangiogenic activity plays a role in the Celastrol-mediated suppression of tumor growth and the molecular basis of anti-tumor activity are poorly understood. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 1;280(1):42-52.HIV-1 Tat causes extensive neuroinflammation that may progress to AIDS-related encephalitis and dementia. Celastrol possesses various biological activities such as anti-oxidant, anti-tumor, and anti-inflammatory activities. |
| Cell Research | Celastrol, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory drug, as a possible treatment for Alzheimer's disease.[Pubmed: 11513350]Celastrol, a novel HSP90 inhibitor, depletes Bcr-Abl and induces apoptosis in imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells harboring T315I mutation.[Pubmed: 19819619 ]Cancer Lett. 2010 Apr 28;290(2):182-91.T315I Bcr-Abl in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is the most notorious point mutations to elicit acquired resistance to imatinib. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2001 Oct;25(7):1341-57.In the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) signs of neuronal degeneration are accompanied by markers of microglial activation, inflammation, and oxidant damage. The presence of nitrotyrosine in the cell bodies of neurons in AD suggests that peroxynitrite contributes to the pathogenesis of the disease. A drug with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity may prevent neuronal degeneration in AD. |

Celastrol Dilution Calculator

Celastrol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2192 mL | 11.0961 mL | 22.1921 mL | 44.3843 mL | 55.4803 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4438 mL | 2.2192 mL | 4.4384 mL | 8.8769 mL | 11.0961 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2219 mL | 1.1096 mL | 2.2192 mL | 4.4384 mL | 5.548 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0444 mL | 0.2219 mL | 0.4438 mL | 0.8877 mL | 1.1096 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0222 mL | 0.111 mL | 0.2219 mL | 0.4438 mL | 0.5548 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Celastrol is a potent proteasome inhibitor [1].Proteasomes are protein complexes that degrading unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis.
Celastrol is a potent proteasome inhibitor and an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent. In a cell-free proteasome activity assay, Celastrol inhibits the chymotrypsin-like activity of a purified rabbit 20S proteasome at 2.5umol and human prostate cancer cellular 26S proteasome at 1-5 μmol. In PC-3 and LNCaP (AR-positive) cells, Celastrol results in the accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins and proteasome substrates (IKB-A, Bax, and p27), and induction of apoptosis [1]. In KBM-5 cells, Celastrol enhances TNF-induced apoptosis by 2% to 92%. In the tumor cells, Celastrol inhibited TNF-induced tumor-cell invasion by 12-fold [2]. In human PBMCs, Celastrol inhibited LPS-induced TNF-α production with IC50 value of 70 nM and LPS-induced IL 113 production with IC50 value of 30nM in a dose-dependent way [3].
In PC-3 tumor–bearing nude mice, Celastrol (1-3 mg/kg/d,1-31 days) inhibited the tumor growth by 65-93% [1].
References:
[1]. Yang H, Chen D, Cui QC, et al. Celastrol, a triterpene extracted from the Chinese "Thunder of God Vine," is a potent proteasome inhibitor and suppresses human prostate cancer growth in nude mice. Cancer Res, 2006, 66(9): 4758-4765.
[2]. Allison AC, Cacabelos R, Lombardi VR, et al. Celastrol, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory drug, as a possible treatment for Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 2001, 25(7):,1341-1357.
[3]. Sethi G, Ahn KS, Pandey MK, et al. Celastrol, a novel triterpene, potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis and suppresses invasion of tumor cells by inhibiting NF-kappaB-regulated gene products and TAK1-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Blood, 2007, 109(7): 2727-2735.
- Paludosine
Catalog No.:BCN2010
CAS No.:34137-24-1
- (+)-Sophoranol
Catalog No.:BCN3743
CAS No.:3411-37-8
- Sunitinib malate
Catalog No.:BCC3664
CAS No.:341031-54-7
- Nucleozin
Catalog No.:BCC1811
CAS No.:341001-38-5
- Araloside VII
Catalog No.:BCN8129
CAS No.:340982-22-1
- Fmoc-D-Asp-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC3470
CAS No.:34098-70-7
- Araloside V
Catalog No.:BCN2466
CAS No.:340963-86-2
- Glycyrrhetic acid 3-O-mono-beta-D-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCN1453
CAS No.:34096-83-8
- 7-O-Methylbiochanin A
Catalog No.:BCN8212
CAS No.:34086-51-6
- Alpinumisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5266
CAS No.:34086-50-5
- (20S)-Protopanaxatriol
Catalog No.:BCN2705
CAS No.:34080-08-5
- Z-Pro-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC2753
CAS No.:34079-31-7
- Catalponol
Catalog No.:BCN5267
CAS No.:34168-56-4
- Pterosin Z
Catalog No.:BCN5268
CAS No.:34169-69-2
- Pterosin D
Catalog No.:BCN5269
CAS No.:34169-70-5
- H-Tyr-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3127
CAS No.:3417-91-2
- Pterosin B
Catalog No.:BCN7100
CAS No.:34175-96-7
- Propafenone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5079
CAS No.:34183-22-7
- Actinidic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5270
CAS No.:341971-45-7
- Lys-Bradykinin
Catalog No.:BCC5993
CAS No.:342-10-9
- 3-Methoxyfuran
Catalog No.:BCN5271
CAS No.:3420-57-3
- Dihydroflavokawin B
Catalog No.:BCN5272
CAS No.:3791-76-2
- 7-beta-Hydroxylathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN3413
CAS No.:34208-98-5
- Trachelogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2739
CAS No.:34209-69-3
Celastrol induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma Bel-7402 cells.[Pubmed:25657108]
Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(1):137-48.
Celastrol is a natural terpenoid isolated from Tripterygium wilfordii, a well-known Chinese medicinal herb that presents anti-proliferative activities in several cancer cell lines. Here, we investigated whether Celastrol induces apoptosis on hepatocellular carcinoma Bel-7402 cells and further explored the underlying molecular mechanisms. Celastrol caused a dose- and time-dependent growth inhibition and apoptosis of Bel-7402 cells. It increased apoptosis through the up-regulation of Bax and the down-regulation of Bcl-2 in Bel-7402 cells. Moreover, Celastrol induced the release of cytochrome c and increased the activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9, suggesting that Celastrol-induced apoptosis was related to the mitochondrial pathway. These results indicated that Celastrol could induce apoptosis in Bel-7402 cells, which may be associated with the activation of the mitochondria-mediated pathway.
Celastrol stimulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activity in tumor cells by initiating the ROS/Akt/p70S6K signaling pathway and enhancing hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein synthesis.[Pubmed:25383959]
PLoS One. 2014 Nov 10;9(11):e112470.
Celastrol, a tripterine derived from the traditional Chinese medicine plant Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. ("Thunder of God Vine"), has been reported to have multiple effects, such as anti-inflammation, suppression of tumor angiogenesis, inhibition of tumor growth, induction of apoptosis and protection of cells against human neurodegenerative diseases. However, the mechanisms that underlie these functions are not well defined. In this study, we reported for the first time that Celastrol could induce HIF-1alpha protein accumulation in multiple cancer cell lines in an oxygen-independent manner and that the enhanced HIF-1alpha protein entered the nucleus and promoted the transcription of the HIF-1 target genes VEGF and Glut-1. Celastrol did not influence HIF-1alpha transcription. Instead, Celastrol induced the accumulation of the HIF-1alpha protein by inducing ROS and activating Akt/p70S6K signaling to promote HIF-1alpha translation. In addition, we found that the activation of Akt by Celastrol was transient. With increased exposure time, inhibition of Hsp90 chaperone function by Celastrol led to the subsequent depletion of the Akt protein and thus to the suppression of Akt activity. Moreover, in HepG2 cells, the accumulation of HIF-1alpha increased the expression of BNIP3, which induced autophagy. However, HIF-1alpha and BNIP3 did not influence the cytotoxicity of Celastrol because the main mechanism by which Celastrol kills cancer cells is through stimulating ROS-mediated JNK activation and inducing apoptosis. Furthermore, our data showed that the dose required for Celastrol to induce HIF-1alpha protein accumulation and enhance HIF-1alpha transcriptional activation was below its cytotoxic threshold. A cytotoxic dose of Celastrol for cancer cells did not display cytotoxicity in LO2 normal human liver cells, which indicated that the novel functions of Celastrol in regulating HIF-1 signaling and inducing autophagy might be used in new applications, such as in anti-inflammation and protection of cells against human neurodegenerative diseases. Future studies regarding these applications are required.
Celastrol, a novel HSP90 inhibitor, depletes Bcr-Abl and induces apoptosis in imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells harboring T315I mutation.[Pubmed:19819619]
Cancer Lett. 2010 Apr 28;290(2):182-91.
T315I Bcr-Abl in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is the most notorious point mutations to elicit acquired resistance to imatinib. In the present study, we investigated the effect of Celastrol on CML cells bearing wild-type Bcr-Abl or T315I-mutant. The results revealed that Celastrol potently downregulated the protein levels of Bcr-Abl, and inhibited the growth in CML cells in vitro and in nude mouse xenografts regardless of Bcr-Abl mutation status. Celastrol induced mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. In conclusion, Celastrol exhibits potent activity against CML cells bearing wild-type Bcr-Abl or -the T315I-mutant.
Celastrol ameliorates HIV-1 Tat-induced inflammatory responses via NF-kappaB and AP-1 inhibition and heme oxygenase-1 induction in astrocytes.[Pubmed:25064159]
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 1;280(1):42-52.
HIV-1 Tat causes extensive neuroinflammation that may progress to AIDS-related encephalitis and dementia. Celastrol possesses various biological activities such as anti-oxidant, anti-tumor, and anti-inflammatory activities. In this study, we investigated the modulatory effects of Celastrol on HIV-1 Tat-induced inflammatory responses and the molecular mechanisms underlying its action in astrocytes. Pre-treatment of CRT-MG human astroglioma cells with Celastrol significantly inhibited HIV-1 Tat-induced expression of ICAM-1/VCAM-1 and subsequent monocyte adhesiveness in CRT-MG cells. In addition, Celastrol suppressed HIV-1 Tat-induced expression of pro-inflammatory chemokines, such as CXCL10, IL-8, and MCP-1. Celastrol decreased HIV-1 Tat-induced activation of JNK MAPK, AP-1, and NF-kappaB. Furthermore, Celastrol induced mRNA and protein expression of HO-1 as well as Nrf2 activation. Blockage of HO-1 expression using siRNA reversed the inhibitory effect of Celastrol on HIV-1 Tat-induced inflammatory responses. These results suggest that Celastrol has regulatory effects on HIV-1 Tat-induced inflammatory responses by blocking the JNK MAPK-AP-1/NF-kappaB signaling pathways and inducing HO-1 expression in astrocytes.
Celastrol inhibits Plasmodium falciparum enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase.[Pubmed:25284249]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 Nov 1;22(21):6053-6061.
Enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (ENR), a critical enzyme in type II fatty acid biosynthesis, is a promising target for drug discovery against hepatocyte-stage Plasmodium falciparum. In order to identify PfENR-specific inhibitors, we docked 70 FDA-approved, bioactive, and/or natural product small molecules known to inhibit the growth of whole-cell blood-stage P. falciparum into several PfENR crystallographic structures. Subsequent in vitro activity assays identified a noncompetitive low-micromolar PfENR inhibitor, Celastrol, from this set of compounds.
Celastrol inhibits the growth of human glioma xenografts in nude mice through suppressing VEGFR expression.[Pubmed:18343027]
Cancer Lett. 2008 Jun 8;264(1):101-6.
Celastrol, a compound purified from Tripterygium wilfordii whose preparations have been used for clinical treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, has been demonstrated to have antiangiogenic activity, and be inhibitory against mice tumor growth by a few recent studies. However, whether its antiangiogenic activity plays a role in the Celastrol-mediated suppression of tumor growth and the molecular basis of anti-tumor activity are poorly understood. In this study, we found that Celastrol inhibited the growth of human glioma xenografts in mice, which concurred with the suppression of angiogenesis. Interestingly, while Celastrol had no effect on either the expression of VEGF or its mRNA levels, Celastrol treatment lowered the expression levels of its receptors (VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2) and their mRNA levels. These findings suggest that Celastrol have potential to be used as an antiangiogenesis drug through its role in suppressing VEGF receptors expression that might consequently reduce the signal transduction between VEGF and VEGFR.
Celastrol, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory drug, as a possible treatment for Alzheimer's disease.[Pubmed:11513350]
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2001 Oct;25(7):1341-57.
In the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) signs of neuronal degeneration are accompanied by markers of microglial activation, inflammation, and oxidant damage. The presence of nitrotyrosine in the cell bodies of neurons in AD suggests that peroxynitrite contributes to the pathogenesis of the disease. A drug with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity may prevent neuronal degeneration in AD. Celastrol, a plant-derived triterpene, has these effects. In low nanomolar concentrations Celastrol was found to suppress the production by human monocytes and macrophages of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. Celastrol also decreased the induced expression of class II MHC molecules by microglia. In macrophage lineage cells and endothelial cells Celastrol decreased induced but not constitutive NO production. Celastrol suppressed adjuvant arthritis in the rat, demonstrating in vivo anti-inflammatory activity. Low doses of Celastrol administered to rats significantly improved their performance in memory, learning and psychomotor activity tests. The potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Celastrol, and its effects on cognitive functions, suggest that the drug may be useful to treat neurodegenerative diseases accompanied by inflammation, such as AD.
Celastrol, a novel triterpene, potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis and suppresses invasion of tumor cells by inhibiting NF-kappaB-regulated gene products and TAK1-mediated NF-kappaB activation.[Pubmed:17110449]
Blood. 2007 Apr 1;109(7):2727-35.
Celastrol, a quinone methide triterpene derived from the medicinal plant Tripterygium wilfordii, has been used to treat chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, but its mechanism is not well understood. Therefore, we investigated the effects of Celastrol on cellular responses activated by TNF, a potent proinflammatory cytokine. Celastrol potentiated the apoptosis induced by TNF and chemotherapeutic agents and inhibited invasion, both regulated by NF-kappaB activation. We found that TNF induced the expression of gene products involved in antiapoptosis (IAP1, IAP2, Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, c-FLIP, and survivin), proliferation (cyclin D1 and COX-2), invasion (MMP-9), and angiogenesis (VEGF) and that Celastrol treatment suppressed their expression. Because these gene products are regulated by NF-kappaB, we postulated that Celastrol mediates its effects by modulating the NF-kappaB pathway. We found that Celastrol suppressed both inducible and constitutive NF-kappaB activation. Celastrol was found to inhibit the TNF-induced activation of IkappaBalpha kinase, IkappaBalpha phosphorylation, IkappaBalpha degradation, p65 nuclear translocation and phosphorylation, and NF-kappaB-mediated reporter gene expression. Recent studies indicate that TNF-induced IKK activation requires activation of TAK1, and we indeed found that Celastrol inhibited the TAK1-induced NF-kappaB activation. Overall, our results suggest that Celastrol potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis and inhibits invasion through suppression of the NF-kappaB pathway.
Apoptosis induction in HL-60 cells and inhibition of topoisomerase II by triterpene celastrol.[Pubmed:14519971]
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2003 Sep;67(9):1883-7.
Celastrol, which is a triterpene purified from Celastraceae plants, has anticancer and anti-inflammatory activities. In this study we investigated to clarify whether Celastrol can induce apoptosis in a human leukemia HL-60 model system. Celastrol was found to induce apoptosis, and the rank order of the potency of Celastrol and its derivatives to induce internucleosomal DNA fragmentation was found to be Celastrol>cela-H>>the other derivatives=vehicle control. Many anticancer agents are known to possess the ability to inhibit topoisomerase II, so the inhibitory activities of Celastrol and its derivatives on topoisomerase II were also explored. The rank order of the inhibitory activity was found to be Celastrol>etoposide>cela-H, indicating that the apoptosis-inducing activities of cela derivatives correspond to their inhibitory activities on topoisomerase II. These data suggested that Celastrol may cause its effects such as anticancer activity by the mechanism of apoptosis along with topoisomerase II inhibition.


