Dihydroflavokawin BCAS# 3791-76-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 3791-76-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 270058 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H18O4 | M.Wt | 286.32 |
| Type of Compound | Chalcones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
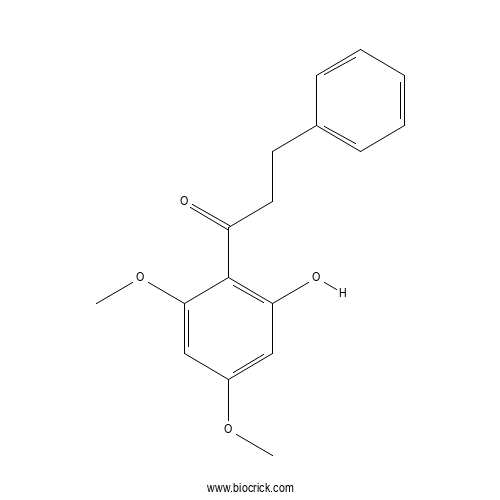
| Chemical Name | 1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-phenylpropan-1-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=C(C(=C1)OC)C(=O)CCC2=CC=CC=C2)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JAJFQMZJIQDRSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H18O4/c1-20-13-10-15(19)17(16(11-13)21-2)14(18)9-8-12-6-4-3-5-7-12/h3-7,10-11,19H,8-9H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Flavokawain A is an apoptotic inducer and immune- modulator ,it also shows anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor activities.Flavokawain A can significantly reduce the expression of CDK1-inhibitory kinases, Myt1 and Wee1, and cause cyclin B1 protein accumulation leading to CDK1 activation in T24 cells.Flavokawain A may suppress LPS-induced expression of pro-inflammatory mediators via blockage of NF-κB-AP-1-JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathways in the murine macrophages. |
| Targets | NF-kB | AP-1 | JNK | p38MAPK | TNF-α | CDK | NOS | COX | NO | PGE | IL Receptor | p53 | p21 |
| In vitro | Suppression of iNOS and COX-2 expression by flavokawain A via blockade of NF-κB and AP-1 activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.[Pubmed: 23727179 ]Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Aug;58:479-86.Flavokawain A, a major constituent of chalcones derived from kava extracts, exerts various biological activities such as anti-tumor activities. Flavokawain A induces apoptosis in MCF-7 and MDA-MB231 and inhibits the metastatic process in vitro.[Pubmed: 25286005]PLoS One. 2014 Oct 6;9(10):e105244.The kava-kava plant (Piper methsyticum) is traditionally known as the pacific elixir by the pacific islanders for its role in a wide range of biological activities. The extract of the roots of this plant contains a variety of interesting molecules including Flavokawain A and this molecule is known to have anti-cancer properties. Breast cancer is still one of the leading diagnosed cancers in women today. The metastatic process is also very pertinent in the progression of tumorigenesis.
Flavokawain A, a novel chalcone from kava extract, induces apoptosis in bladder cancer cells by involvement of Bax protein-dependent and mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway and suppresses tumor growth in mice.[Pubmed: 15833884]Cancer Res. 2005 Apr 15;65(8):3479-86.Consumption of the traditional kava preparation was reported to correlate with low and uncustomary gender ratios (more cancer in women than men) of cancer incidences in three kava-drinking countries: Fiji, Vanuatu, and Western Samoa. We have identified Flavokawain A, B, and C but not the major kavalactone, kawain, in kava extracts as causing strong antiproliferative and apoptotic effect in human bladder cancer cells. |
| In vivo | Kava chalcone, flavokawain A, inhibits urothelial tumorigenesis in the UPII-SV40T transgenic mouse model.[Pubmed: 24121102]Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013 Dec;6(12):1365-75.Flavokawain A (FKA) is the predominant chalcone identified from the kava plant. We have previously shown that FKA preferentially inhibits the growth of p53 defective bladder cancer cell lines. |
| Kinase Assay | Effects of the kava chalcone flavokawain A differ in bladder cancer cells with wild-type versus mutant p53.[Pubmed: 19138991]Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2008 Nov;1(6):439-51.Flavokawain A is the predominant chalcone from kava extract. We have assessed the mechanisms of Flavokawain A's action on cell cycle regulation. |
| Animal Research | In vitro Toxicity and in vivo Immunomodulatory Effects of Flavokawain A and Flavokawain B in Balb/C Mice.[Pubmed: 26411010]Nat Prod Commun. 2015 Jul;10(7):1199-202.Flavokawains are chalcones that can be found in the root extracts of the kava-kava (Piper methysticum) plant. Flavokawain A and flavokawain B are known to possess potential anti-inflammation and anti-cancer activities. Nevertheless, the effects of both these compounds on the normal function of the host have not been studied. There is a need to find agents that can enhance the functionality of the immune system without disturbing the homeostatic balance. This study aimed to determine the toxicity and immunomodulatory effects of Flavokawain A and flavokawain B on Balb/c mice. |

Dihydroflavokawin B Dilution Calculator

Dihydroflavokawin B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4926 mL | 17.463 mL | 34.926 mL | 69.8519 mL | 87.3149 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6985 mL | 3.4926 mL | 6.9852 mL | 13.9704 mL | 17.463 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3493 mL | 1.7463 mL | 3.4926 mL | 6.9852 mL | 8.7315 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0699 mL | 0.3493 mL | 0.6985 mL | 1.397 mL | 1.7463 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0349 mL | 0.1746 mL | 0.3493 mL | 0.6985 mL | 0.8731 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3-Methoxyfuran
Catalog No.:BCN5271
CAS No.:3420-57-3
- Lys-Bradykinin
Catalog No.:BCC5993
CAS No.:342-10-9
- Actinidic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5270
CAS No.:341971-45-7
- Propafenone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5079
CAS No.:34183-22-7
- Pterosin B
Catalog No.:BCN7100
CAS No.:34175-96-7
- H-Tyr-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3127
CAS No.:3417-91-2
- Pterosin D
Catalog No.:BCN5269
CAS No.:34169-70-5
- Pterosin Z
Catalog No.:BCN5268
CAS No.:34169-69-2
- Catalponol
Catalog No.:BCN5267
CAS No.:34168-56-4
- Celastrol
Catalog No.:BCN5986
CAS No.:34157-83-0
- Paludosine
Catalog No.:BCN2010
CAS No.:34137-24-1
- (+)-Sophoranol
Catalog No.:BCN3743
CAS No.:3411-37-8
- 7-beta-Hydroxylathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN3413
CAS No.:34208-98-5
- Trachelogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2739
CAS No.:34209-69-3
- Tovopyrifolin C
Catalog No.:BCN6888
CAS No.:34211-53-5
- Echinatin
Catalog No.:BCN6277
CAS No.:34221-41-5
- 3-Acetoxytropane
Catalog No.:BCN1933
CAS No.:3423-26-5
- Tropine acetate
Catalog No.:BCN1922
CAS No.:3423-27-6
- Clozapine N-oxide (CNO)
Catalog No.:BCC1487
CAS No.:34233-69-7
- Telbivudine
Catalog No.:BCC3862
CAS No.:3424-98-4
- Saralasin
Catalog No.:BCC5714
CAS No.:34273-10-4
- Angiotensin 1/2 (1-9)
Catalog No.:BCC1005
CAS No.:34273-12-6
- Gardneramine
Catalog No.:BCN5273
CAS No.:34274-91-4
- Urotensin II-related peptide
Catalog No.:BCC5884
CAS No.:342878-90-4


