EchinatinCAS# 34221-41-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 34221-41-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6442675 | Appearance | Orange powder |
| Formula | C16H14O4 | M.Wt | 270.28 |
| Type of Compound | Chalcones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 4,4'-Dihydroxy 2-methoxychalcone; Retrochalcone | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 250 mg/mL (924.97 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
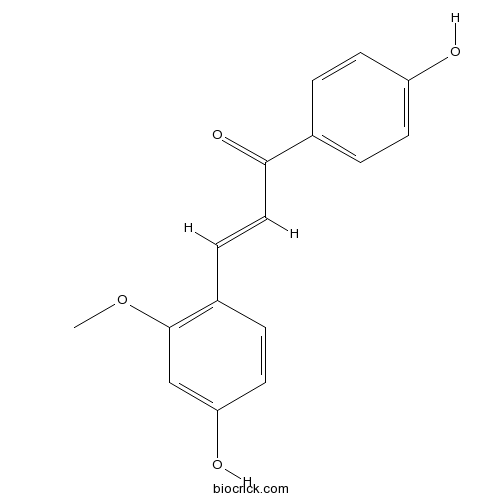
| Chemical Name | (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)O)C=CC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QJKMIJNRNRLQSS-WEVVVXLNSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H14O4/c1-20-16-10-14(18)8-4-12(16)5-9-15(19)11-2-6-13(17)7-3-11/h2-10,17-18H,1H3/b9-5+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Echinatin has significant antioxidant and anti-inflammary activities, it shows strong scavenging activity toward the ABTS + radical, it also inhibits the production of nitric oxide (NO), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in LPS-induced macrophage cells. Echinatin disturbs the mitochondrial energy transfer reactions and membrane permeability, at a low concentration cause deterioration of respiratory control and oxidative phosphorylation of isolated rat liver mitochondria, inhibits DNP-ATPase activity while stimulating range latent ATPase activity. |
| Targets | ATPase | ROS | NO | PGE | IL Receptor |
| In vitro | The effects of echinatin and its related compounds on the mitochondrial energy transfer reaction.[Pubmed: 6221118]J Toxicol Sci. 1982 Nov;7(4):245-54.
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of six flavonoids separated from licorice.[Pubmed: 23790887]Food Chem. 2013 Nov 15;141(2):1063-71.Licorice, the roots and rhizomes of several Glycyrrhiza species (Leguminosae), is an important natural sweetening agent and a widely used herbal medicine. Determination of antioxidant activity in licorice vitro metabolites by DPPH spiking coupled with HPLC-Q-TOF MS/MS[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 2013, 22(21):2547-52. To investigate the antioxidant activity of liver microsomal metabolites from six flavonoids in licorice by 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) spiking coupled with HPLC-Q-TOF MS/MS. |

Echinatin Dilution Calculator

Echinatin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6999 mL | 18.4993 mL | 36.9987 mL | 73.9973 mL | 92.4967 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.74 mL | 3.6999 mL | 7.3997 mL | 14.7995 mL | 18.4993 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.37 mL | 1.8499 mL | 3.6999 mL | 7.3997 mL | 9.2497 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.074 mL | 0.37 mL | 0.74 mL | 1.4799 mL | 1.8499 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.037 mL | 0.185 mL | 0.37 mL | 0.74 mL | 0.925 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tovopyrifolin C
Catalog No.:BCN6888
CAS No.:34211-53-5
- Trachelogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2739
CAS No.:34209-69-3
- 7-beta-Hydroxylathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN3413
CAS No.:34208-98-5
- Dihydroflavokawin B
Catalog No.:BCN5272
CAS No.:3791-76-2
- 3-Methoxyfuran
Catalog No.:BCN5271
CAS No.:3420-57-3
- Lys-Bradykinin
Catalog No.:BCC5993
CAS No.:342-10-9
- Actinidic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5270
CAS No.:341971-45-7
- Propafenone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5079
CAS No.:34183-22-7
- Pterosin B
Catalog No.:BCN7100
CAS No.:34175-96-7
- H-Tyr-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3127
CAS No.:3417-91-2
- Pterosin D
Catalog No.:BCN5269
CAS No.:34169-70-5
- Pterosin Z
Catalog No.:BCN5268
CAS No.:34169-69-2
- 3-Acetoxytropane
Catalog No.:BCN1933
CAS No.:3423-26-5
- Tropine acetate
Catalog No.:BCN1922
CAS No.:3423-27-6
- Clozapine N-oxide (CNO)
Catalog No.:BCC1487
CAS No.:34233-69-7
- Telbivudine
Catalog No.:BCC3862
CAS No.:3424-98-4
- Saralasin
Catalog No.:BCC5714
CAS No.:34273-10-4
- Angiotensin 1/2 (1-9)
Catalog No.:BCC1005
CAS No.:34273-12-6
- Gardneramine
Catalog No.:BCN5273
CAS No.:34274-91-4
- Urotensin II-related peptide
Catalog No.:BCC5884
CAS No.:342878-90-4
- SDM25N hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7054
CAS No.:342884-71-3
- Chikusetsusaponin V methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN3472
CAS No.:34291-22-0
- 2,3-Dihydrohinokiflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6680
CAS No.:34292-87-0
- 5,6-Dimethoxy-2-isopropenylbenzofuran
Catalog No.:BCN7195
CAS No.:34293-09-9
The effects of echinatin and its related compounds on the mitochondrial energy transfer reaction.[Pubmed:6221118]
J Toxicol Sci. 1982 Nov;7(4):245-54.
To investigate the mechanism by which various biological action of licorice root are brought about, the effects of Echinatin as a small constituent of Glycyrrhiza echinata and several related compounds on mitochondrial energy transfer reactions were examined. The results obtained were as follows: 1) Echinatin, 4'-hydroxychalcone, chalcone and 3,4'-dihydroxychalcone at a low concentration cause deterioration of respiratory control and oxidative phosphorylation of isolated rat liver mitochondria. 2) Chalcone and 4'-hydroxychalcone stimulate both latent and DNP-ATPase activity of mitochondria. Echinatin inhibits DNP-ATPase activity while stimulating range latent ATPase activity in the low concentration. 3) Chalcone and 4'-hydroxychalcone induce a rapid potassium release from mitochondrial vesicles, while Echinatin and 3,4'-dihydroxychalcone have lesser effect than the former two substances. From these results, it can be concluded that Echinatin and several related compounds disturb the mitochondrial energy transfer reactions and membrane permeability.
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of six flavonoids separated from licorice.[Pubmed:23790887]
Food Chem. 2013 Nov 15;141(2):1063-71.
Licorice, the roots and rhizomes of several Glycyrrhiza species (Leguminosae), is an important natural sweetening agent and a widely used herbal medicine. In this work, six flavonoids, 5-(1,1-dimethylallyl)-3,4,4'-trihydroxy-2-methoxychalcone (1), licochalcone B (2), licochalcone A (3), Echinatin (4), glycycoumarin (5) and glyurallin B (6), were isolated from the extracts of licorice (Glycyrrhiza inflata and Glycyrrhiza uralensis). Their structures were elucidated using various spectroscopic methods. To our knowledge, compound 1 was isolated from natural plants for the first time. All the isolates were tested by antioxidant and anti-inflammatory assays. Compounds 2, 4 and 5 showed strong scavenging activity toward the ABTS(+) radical, and compounds 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6 exhibited potent inhibition of lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes compared with the reference controls. Compounds 1-4 dose-dependently inhibited LPS induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in RAW 264.7 cells. Furthermore, compounds 1-5 were demonstrated to inhibit the production of nitric oxide (NO), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in LPS-induced macrophage cells. Moreover, the contents of the six compounds, in different Glycyrrhiza species, were quantified by HPLC-MS.


