Pterosin BCAS# 34175-96-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 34175-96-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 115049 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H18O2 | M.Wt | 218.29 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 250 mg/mL (1145.27 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
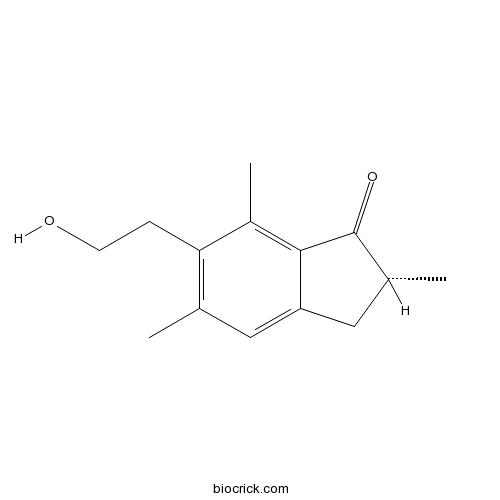
| Chemical Name | (2R)-6-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,5,7-trimethyl-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1CC2=CC(=C(C(=C2C1=O)C)CCO)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SJNCSXMTBXDZQA-SECBINFHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H18O2/c1-8-6-11-7-9(2)14(16)13(11)10(3)12(8)4-5-15/h6,9,15H,4-5,7H2,1-3H3/t9-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Pterosin B is a salt-inducible kinase 3 (Sik3) pathway inhibitor, it prevents chondrocyte hypertrophy and osteoarthritis in mice by inhibiting Sik3. 2. Pterosin B has multiple targets in gluconeogenic programs, including coenzyme Q in RORα-SRC2 signaling. 3. Pterosin B shows cytotoxicity against HL 60 cells (human leukemia) with the IC(50) value of 8.7 microg/mL. |
| Targets | cAMP | AMPK |

Pterosin B Dilution Calculator

Pterosin B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.5811 mL | 22.9053 mL | 45.8106 mL | 91.6212 mL | 114.5265 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9162 mL | 4.5811 mL | 9.1621 mL | 18.3242 mL | 22.9053 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4581 mL | 2.2905 mL | 4.5811 mL | 9.1621 mL | 11.4527 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0916 mL | 0.4581 mL | 0.9162 mL | 1.8324 mL | 2.2905 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0458 mL | 0.2291 mL | 0.4581 mL | 0.9162 mL | 1.1453 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- H-Tyr-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3127
CAS No.:3417-91-2
- Pterosin D
Catalog No.:BCN5269
CAS No.:34169-70-5
- Pterosin Z
Catalog No.:BCN5268
CAS No.:34169-69-2
- Catalponol
Catalog No.:BCN5267
CAS No.:34168-56-4
- Celastrol
Catalog No.:BCN5986
CAS No.:34157-83-0
- Paludosine
Catalog No.:BCN2010
CAS No.:34137-24-1
- (+)-Sophoranol
Catalog No.:BCN3743
CAS No.:3411-37-8
- Sunitinib malate
Catalog No.:BCC3664
CAS No.:341031-54-7
- Nucleozin
Catalog No.:BCC1811
CAS No.:341001-38-5
- Araloside VII
Catalog No.:BCN8129
CAS No.:340982-22-1
- Fmoc-D-Asp-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC3470
CAS No.:34098-70-7
- Araloside V
Catalog No.:BCN2466
CAS No.:340963-86-2
- Propafenone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5079
CAS No.:34183-22-7
- Actinidic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5270
CAS No.:341971-45-7
- Lys-Bradykinin
Catalog No.:BCC5993
CAS No.:342-10-9
- 3-Methoxyfuran
Catalog No.:BCN5271
CAS No.:3420-57-3
- Dihydroflavokawin B
Catalog No.:BCN5272
CAS No.:3791-76-2
- 7-beta-Hydroxylathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN3413
CAS No.:34208-98-5
- Trachelogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2739
CAS No.:34209-69-3
- Tovopyrifolin C
Catalog No.:BCN6888
CAS No.:34211-53-5
- Echinatin
Catalog No.:BCN6277
CAS No.:34221-41-5
- 3-Acetoxytropane
Catalog No.:BCN1933
CAS No.:3423-26-5
- Tropine acetate
Catalog No.:BCN1922
CAS No.:3423-27-6
- Clozapine N-oxide (CNO)
Catalog No.:BCC1487
CAS No.:34233-69-7
Isolation of 5-hydroxypyrrolidin-2-one and other constituents from the young fronds of Pteridium aquilinum.[Pubmed:18437503]
J Nat Med. 2008 Jul;62(3):358-9.
5-Hydroxypyrrolidin-2-one, along with (2R)-Pterosin B, shikimic acid, kaempferol-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, transtiliroside, beta-sitosterol, daucosterol, glycerol 1-stearate and benzoic acid, were isolated from the young fronds of the bracken fern Pteridium aquilinum. 5-Hydroxypyrrolidin-2-one, shikimic acid and glycerol 1-stearate were isolated from the plant for the first time.
Pterosin B prevents chondrocyte hypertrophy and osteoarthritis in mice by inhibiting Sik3.[Pubmed:27009967]
Nat Commun. 2016 Mar 24;7:10959.
Osteoarthritis is a common debilitating joint disorder. Risk factors for osteoarthritis include age, which is associated with thinning of articular cartilage. Here we generate chondrocyte-specific salt-inducible kinase 3 (Sik3) conditional knockout mice that are resistant to osteoarthritis with thickened articular cartilage owing to a larger chondrocyte population. We also identify an edible Pteridium aquilinum compound, Pterosin B, as a Sik3 pathway inhibitor. We show that either Sik3 deletion or intraarticular injection of mice with Pterosin B inhibits chondrocyte hypertrophy and protects cartilage from osteoarthritis. Collectively, our results suggest Sik3 regulates the homeostasis of articular cartilage and is a target for the treatment of osteoarthritis, with Pterosin B as a candidate therapeutic.
Pterosin B has multiple targets in gluconeogenic programs, including coenzyme Q in RORalpha-SRC2 signaling.[Pubmed:26970301]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Apr 29;473(2):415-20.
Hepatic gluconeogenic programs are regulated by a variety of signaling cascades. Glucagon-cAMP signaling is the main initiator of the gluconeogenic programs, including glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit (G6pc) gene expression. Pterosin B, an ingredient in Pteridium aquilinum, inhibits salt-inducible kinase 3 signaling that represses cAMP-response element-binding protein regulated transcription coactivator 2, an inducer of gluconeogenic programs. As the results, Pterosin B promotes G6pc expression even in the absence of cAMP. In this work, however, we noticed that once cAMP signaling was initiated, Pterosin B became a strong repressor of G6pc expression. The search for associated transcription factors for Pterosin B actions revealed that retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor alpha-steroid receptor coactivator 2 (RORalpha-SRC2) complex on the G6pc promoter was the target. Meanwhile, Pterosin B impaired the oxidation-reduction cycle of coenzyme Q in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS); and antimycin A, an inhibitor of coenzyme Q: cytochrome c-oxidoreductase (termed mitochondrial complex III), also mimicked Pterosin B actions on RORalpha-SRC2 signaling. Although other respiratory toxins (rotenone and oligomycin) also suppressed G6pc expression accompanied by lowered ATP levels following the activation of AMP-activated kinase, minimal or no effect of these other toxins on RORalpha-SRC2 activity was observed. These results suggested that individual components in OXPHOS differentially linked to different transcriptional machineries for hepatic gluconeogenic programs, and the RORalpha-SRC2 complex acted as a sensor for oxidation-reduction cycle of coenzyme Q and regulated G6Pc expression. This was a site disrupted by Pterosin B in gluconeogenic programs.
New benzoyl glucosides and cytotoxic pterosin sesquiterpenes from Pteris ensiformis Burm.[Pubmed:18305416]
Molecules. 2008 Feb 5;13(2):255-66.
Three new compounds: 2R,3R-pterosin L 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (1), beta-D-xylopyranosyl(1-->2)-7-O-benzoyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside (2) and 4-O-benzoyl-beta-D-xylo-pyranosyl(1-->2)-7-O-benzoyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), together with nine known compounds, were isolated from the ethyl acetate extract of Pteris ensiformis. 5-[2-Hydroxyethylidene]-2(5H)-furanone (4), which had been synthesized, was isolated from natural sources for the first time. The structures of all isolated compounds were determined on the basis of mass and spectroscopic evidence. Compound 1 and Pterosin B (5) show cytotoxicity against HL 60 cells (human leukemia) with the IC(50) values of 3.7 and 8.7 microg/mL, respectively.


