Urotensin II-related peptideCAS# 342878-90-4 |
- CX-5461
Catalog No.:BCC3700
CAS No.:1138549-36-6
- Gemcitabine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1076
CAS No.:122111-03-9
- Fludarabine Phosphate (Fludara)
Catalog No.:BCC3681
CAS No.:75607-67-9
- Bleomycin Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC3694
CAS No.:9041-93-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 342878-90-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 72793454 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C49H64N10O10S2 | M.Wt | 1017.23 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in 5% acetonitrile / sterile water | ||
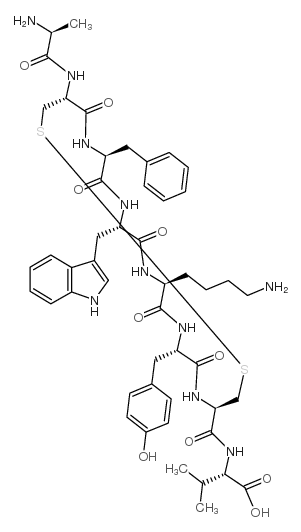
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[[(4R,7S,10S,13S,16S,19R)-10-(4-aminobutyl)-19-[[(2S)-2-aminopropanoyl]amino]-16-benzyl-7-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-13-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-6,9,12,15,18-pentaoxo-1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentazacycloicosane-4-carbonyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(C(=O)O)NC(=O)C1CSSCC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)N1)CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)CCCCN)CC3=CNC4=CC=CC=C43)CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)C(C)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WDZHTXUSYGCGPY-KOOAXUMWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C49H64N10O10S2/c1-27(2)41(49(68)69)59-48(67)40-26-71-70-25-39(57-42(61)28(3)51)47(66)55-36(21-29-11-5-4-6-12-29)44(63)56-38(23-31-24-52-34-14-8-7-13-33(31)34)46(65)53-35(15-9-10-20-50)43(62)54-37(45(64)58-40)22-30-16-18-32(60)19-17-30/h4-8,11-14,16-19,24,27-28,35-41,52,60H,9-10,15,20-23,25-26,50-51H2,1-3H3,(H,53,65)(H,54,62)(H,55,66)(H,56,63)(H,57,61)(H,58,64)(H,59,67)(H,68,69)/t28-,35-,36-,37-,38-,39-,40-,41-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent endogenous agonist for the urotensin-II (UT) receptor. Binds with high affinity and potently activates recombinant rat and human UT receptors (EC50 values are 0.55 and 4.8 nM respectively). Produces hypotensive effects following systemic administration in rats. |

Urotensin II-related peptide Dilution Calculator

Urotensin II-related peptide Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Gardneramine
Catalog No.:BCN5273
CAS No.:34274-91-4
- Angiotensin 1/2 (1-9)
Catalog No.:BCC1005
CAS No.:34273-12-6
- Saralasin
Catalog No.:BCC5714
CAS No.:34273-10-4
- Telbivudine
Catalog No.:BCC3862
CAS No.:3424-98-4
- Clozapine N-oxide (CNO)
Catalog No.:BCC1487
CAS No.:34233-69-7
- Tropine acetate
Catalog No.:BCN1922
CAS No.:3423-27-6
- 3-Acetoxytropane
Catalog No.:BCN1933
CAS No.:3423-26-5
- Echinatin
Catalog No.:BCN6277
CAS No.:34221-41-5
- Tovopyrifolin C
Catalog No.:BCN6888
CAS No.:34211-53-5
- Trachelogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2739
CAS No.:34209-69-3
- 7-beta-Hydroxylathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN3413
CAS No.:34208-98-5
- Dihydroflavokawin B
Catalog No.:BCN5272
CAS No.:3791-76-2
- SDM25N hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7054
CAS No.:342884-71-3
- Chikusetsusaponin V methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN3472
CAS No.:34291-22-0
- 2,3-Dihydrohinokiflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6680
CAS No.:34292-87-0
- 5,6-Dimethoxy-2-isopropenylbenzofuran
Catalog No.:BCN7195
CAS No.:34293-09-9
- Harmine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN2485
CAS No.:343-27-1
- 2,16-Kauranediol
Catalog No.:BCN5274
CAS No.:34302-37-9
- Boc-Abu-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3200
CAS No.:27494-48-0
- Chelerythrine
Catalog No.:BCN5275
CAS No.:34316-15-9
- TCS PrP Inhibitor 13
Catalog No.:BCC5999
CAS No.:34320-83-7
- OXA (17-33)
Catalog No.:BCC6364
CAS No.:343268-91-7
- Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN3697
CAS No.:34328-54-6
- Cirsiliol
Catalog No.:BCN6822
CAS No.:34334-69-5
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCII. Urotensin II, urotensin II-related peptide, and their receptor: from structure to function.[Pubmed:25535277]
Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(1):214-58.
Urotensin II (UII) is a cyclic neuropeptide that was first isolated from the urophysis of teleost fish on the basis of its ability to contract the hindgut. Subsequently, UII was characterized in tetrapods including humans. Phylogenetic studies and synteny analysis indicate that UII and its paralogous peptide Urotensin II-related peptide (URP) belong to the somatostatin/cortistatin superfamily. In mammals, the UII and URP genes are primarily expressed in cholinergic neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord. UII and URP mRNAs are also present in various organs notably in the cardiovascular, renal, and endocrine systems. UII and URP activate a common G protein-coupled receptor, called UT, that exhibits relatively high sequence identity with somatostatin, opioid, and galanin receptors. The UT gene is widely expressed in the central nervous system (CNS) and in peripheral tissues including the retina, heart, vascular bed, lung, kidney, adrenal medulla, and skeletal muscle. Structure-activity relationship studies and NMR conformational analysis have led to the rational design of a number of peptidic and nonpeptidic UT agonists and antagonists. Consistent with the wide distribution of UT, UII has now been shown to exert a large array of biologic activities, in particular in the CNS, the cardiovascular system, and the kidney. Here, we review the current knowledge concerning the pleiotropic actions of UII and discusses the possible use of antagonists for future therapeutic applications.
Concordant localization of functional urotensin II and urotensin II-related peptide binding sites in the rat brain: Atypical occurrence close to the fourth ventricle.[Pubmed:24478001]
J Comp Neurol. 2014 Aug 1;522(11):2634-49.
Urotensin II (UII) and Urotensin II-related peptide (URP) are structurally related paralog peptides that exert peripheral and central effects. UII binding sites have been partly described in brain, and those of URP have never been reported. We exhaustively compared [(125)I]-UII and -URP binding site distributions in the adult rat brain, and found that they fully overlapped at the regional level. We observed UII/URP binding sites in structures lining ventricles, comprising the sphenoid nucleus and cell rafts scattered on a line joining the fourth ventricle and its lateral recess. After injection of UII and URP in the lateral ventricle, we observed c-Fos-positive cell nuclei in areas close to the fourth ventricle, indicating that these receptors are functional. Different c-Fos-containing cell populations were activated. They were all positive for vimentin and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), excluding the possibility of an ependymal nature. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that UII and URP binding sites are totally overlapping and that these sites were functional in regions bordering the fourth ventricle. These data support a role for UII/URP at the interface between brain parenchyma and cerebrospinal fluid.
Generation of BAC transgenic tadpoles enabling live imaging of motoneurons by using the urotensin II-related peptide (ust2b) gene as a driver.[Pubmed:25658845]
PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0117370.
Xenopus is an excellent tetrapod model for studying normal and pathological motoneuron ontogeny due to its developmental morpho-physiological advantages. In mammals, the Urotensin II-related peptide (UTS2B) gene is primarily expressed in motoneurons of the brainstem and the spinal cord. Here, we show that this expression pattern was conserved in Xenopus and established during the early embryonic development, starting at the early tailbud stage. In late tadpole stage, uts2b mRNA was detected both in the hindbrain and in the spinal cord. Spinal uts2b+ cells were identified as axial motoneurons. In adult, however, the uts2b expression was only detected in the hindbrain. We assessed the ability of the uts2b promoter to drive the expression of a fluorescent reporter in motoneurons by recombineering a green fluorescent protein (GFP) into a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone containing the entire X. tropicalis uts2b locus. After injection of this construction in one-cell stage embryos, a transient GFP expression was observed in the spinal cord of about a quarter of the resulting animals from the early tailbud stage and up to juveniles. The GFP expression pattern was globally consistent with that of the endogenous uts2b in the spinal cord but no fluorescence was observed in the brainstem. A combination of histological and electrophysiological approaches was employed to further characterize the GFP+ cells in the larvae. More than 98% of the GFP+ cells expressed choline acetyltransferase, while their projections were co-localized with alpha-bungarotoxin labeling. When tail myotomes were injected with rhodamine dextran amine crystals, numerous double-stained GFP+ cells were observed. In addition, intracellular electrophysiological recordings of GFP+ neurons revealed locomotion-related rhythmic discharge patterns during fictive swimming. Taken together our results provide evidence that uts2b is an appropriate driver to express reporter genes in larval motoneurons of the Xenopus spinal cord.
Development and pharmacological characterization of conformationally constrained urotensin II-related peptide agonists.[Pubmed:24251366]
J Med Chem. 2013 Dec 12;56(23):9612-22.
Urotensin II (UII) and its paralog peptide, Urotensin II-related peptide (URP), exert not only common but also divergent actions through the activation of UT, a specific membrane-bound receptor that belongs to the 1A G protein-coupled receptor subclass. In this study, we have designed and synthesized new URP analogues in which the intracyclic Trp residue was replaced with natural, unnatural, and constrained amino acids to determine important physicochemical features for receptor binding and activation. The biological data, highlighting the potent agonistic behavior of [Tiq(4)]URP and [Tpi(4)]URP, also suggest that the Trp residue, and more specifically the indole ring, is not critical for receptor interaction and could in fact be involved in the intramolecular stabilization of the bioactive conformation of URP. Finally, these analogues, which are intracyclic constrained URP-based agonists, could represent useful pharmacological tools for the study of the urotensinergic system.


