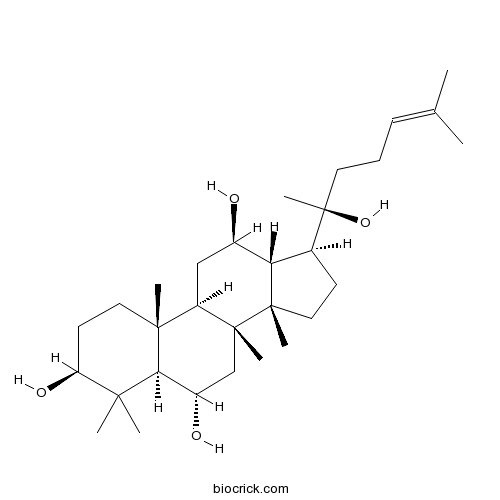
(20S)-ProtopanaxatriolCAS# 34080-08-5 |
- 20(R)-Protopanaxatriol
Catalog No.:BCN1079
CAS No.:1453-93-6
- Protopanaxatriol
Catalog No.:BCC9245
CAS No.:32773-56-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 34080-08-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 161798 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C30H52O4 | M.Wt | 476.7 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 20(S)-APPT; g-PPT | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 47 mg/mL (98.59 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (3S,5R,6S,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14S,17S)-17-[(2S)-2-hydroxy-6-methylhept-5-en-2-yl]-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,7,9,11,12,13,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6,12-triol | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCCC(C)(C1CCC2(C1C(CC3C2(CC(C4C3(CCC(C4(C)C)O)C)O)C)O)C)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SHCBCKBYTHZQGZ-PHFGEWBZSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | (20S)-Protopanaxatriol is a metabolite of ginsenoside, works through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and oestrogen receptor (ER), and is also a LXRα inhibitor. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol shows strong and selective antimicrobial activity, it also has anti-oxidant activity. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol exerts cardioprotective effects against myocardial ischemic injury, by enhancing the anti-free-radical actions of heart tissues. |
| Targets | Antifection | Glucocorticoid receptor | Oestrogen receptor | LXRα |
| In vivo | Effect of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol and its epimeric derivatives on myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol.[Pubmed: 21528638]Arzneimittelforschung. 2011;61(3):148-52.It was reported Panax ginseng had diverse components and multifaceted pharmacological functions. This study aims to investigate the effect of (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (PT, CAS 179799-20-3) and its epimeric derivatives (20S, 24R-epoxy-dammarane-3beta, 6alpha, 12beta, 25-tetraol, PTD1 and 20S, 24S-epoxy-dammarane-3beta, 6alpha, 12beta, 25-tetraol, PTD2) on myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol in rats.
|
| Structure Identification | J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;88:497-508.Identification of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol metabolites in rats by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.[Pubmed: 24184656](20S)-Protopanaxatriol (PPT), one of the aglycones of ginsenosides, has been shown to exert cardioprotective effects against myocardial ischemic injury. However, studies on PPT metabolism have rarely been reported. |

(20S)-Protopanaxatriol Dilution Calculator

(20S)-Protopanaxatriol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0978 mL | 10.4888 mL | 20.9776 mL | 41.9551 mL | 52.4439 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4196 mL | 2.0978 mL | 4.1955 mL | 8.391 mL | 10.4888 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2098 mL | 1.0489 mL | 2.0978 mL | 4.1955 mL | 5.2444 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.042 mL | 0.2098 mL | 0.4196 mL | 0.8391 mL | 1.0489 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.021 mL | 0.1049 mL | 0.2098 mL | 0.4196 mL | 0.5244 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
(20S)-Protopanaxatriol is a metabolite of ginsenoside, works through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and oestrogen receptor (ER), and is also a LXRα inhibitor and a PPARγ activator.
In Vitro:(20S)-Protopanaxatriol works through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and oestrogen receptor (ER) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (g-PPT) increases [Ca2+]i with an EC50 of 482 nM in HUVECs. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (1 µM) elevates NO production via ERβ[1]. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (PPT) inhibits the autonomous transactivation of Gal4-LXRα LBD, the T0901317-dependent transcription of SREBP-1c and its promoter. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (10 μg/mL) blocks the recruitment of RNA polymerase II to the LXRE region of SREBP-1c. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol also inhibits T0901317-dependent transcription of LXRα target genes related to lipogenesis, and reduces T0901317-induced cellular triglyceride (TG) accumulation in primary hepatocytes, but does not alter transcription of ABCA1, also an LXRα target gene[2]. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (1, 5, 10, 25 μM) increases GAL4/PPARγ transactivating activitys in COS-7 cells. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (10 μM) induces adipogenesis via expression of aP2, LPL, and PEPCK via PPARγ activation. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (10, 25 μM) also upregulates GLUT4 expression[3].
References:
[1]. Leung KW, et al. Protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol bind to glucocorticoid and oestrogen receptors in endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;156(4):626-37.
[2]. Oh GS, et al. 20(S)-protopanaxatriol inhibits liver X receptor α-mediated expression of lipogenic genes in hepatocytes. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Jun;128(2):71-7.
[3]. Han KL, et al. Ginsenoside 20S-protopanaxatriol (PPT) activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006 Jan;29(1):110-3.
- Z-Pro-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC2753
CAS No.:34079-31-7
- 2-2'-(Hydroxytetracosanoylamino)-octadecane-1,3,4-triol tetraacetate
Catalog No.:BCN1454
CAS No.:340702-68-3
- 1,3-Bis(4,5-dihydro-2-oxazolyl)benzene
Catalog No.:BCC8417
CAS No.:34052-90-9
- Diclofensine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5541
CAS No.:34041-84-4
- SMIFH2
Catalog No.:BCC6162
CAS No.:340316-62-3
- Auranofin
Catalog No.:BCC7952
CAS No.:34031-32-8
- H-D-Phe-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3014
CAS No.:3403-25-6
- 1-BCP
Catalog No.:BCC6909
CAS No.:34023-62-6
- Vinorine
Catalog No.:BCN4649
CAS No.:34020-07-0
- Z-Ala-OSu
Catalog No.:BCC3057
CAS No.:3401-36-3
- 7-Oxodehydroabietinol
Catalog No.:BCN5265
CAS No.:33980-71-1
- Clivorine
Catalog No.:BCN2067
CAS No.:33979-15-6
- Alpinumisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5266
CAS No.:34086-50-5
- 7-O-Methylbiochanin A
Catalog No.:BCN8212
CAS No.:34086-51-6
- Glycyrrhetic acid 3-O-mono-beta-D-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCN1453
CAS No.:34096-83-8
- Araloside V
Catalog No.:BCN2466
CAS No.:340963-86-2
- Fmoc-D-Asp-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC3470
CAS No.:34098-70-7
- Araloside VII
Catalog No.:BCN8129
CAS No.:340982-22-1
- Nucleozin
Catalog No.:BCC1811
CAS No.:341001-38-5
- Sunitinib malate
Catalog No.:BCC3664
CAS No.:341031-54-7
- (+)-Sophoranol
Catalog No.:BCN3743
CAS No.:3411-37-8
- Paludosine
Catalog No.:BCN2010
CAS No.:34137-24-1
- Celastrol
Catalog No.:BCN5986
CAS No.:34157-83-0
- Catalponol
Catalog No.:BCN5267
CAS No.:34168-56-4
Identification of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol metabolites in rats by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.[Pubmed:24184656]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;88:497-508.
20(S)-Protopanaxatriol (PPT), one of the aglycones of ginsenosides, has been shown to exert cardioprotective effects against myocardial ischemic injury. However, studies on PPT metabolism have rarely been reported. This study is the first to investigate the in vivo metabolism of PPT following oral administration by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q/TOF-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The structures of the metabolites were identified based on the characteristics of their MS data, MS(2) data, and chromatographic retention times. A total of 22 metabolites, including 17 phase I and 5 phase II metabolites, were found and tentatively identified by comparing their mass spectrometry profiles with those of PPT. Two new monooxygenation metabolites, (20S,24S)-epoxy-dammarane-3,6,12,25-tetraol and (20S,24R)-epoxy-dammarane-3,6,12,25-tetraol, were chemicallly synthesized and unambiguously characterized according to the NMR spectroscopic data. The metabolic pathways of PPT were proposed accordingly for the first time. Results revealed that oxidation of (1) double bonds at Delta((24,25)) to form 24,25-epoxides, followed by rearrangement to yield 20,24-oxide forms; and (2) vinyl-methyl at C-26/27 to form corresponding carboxylic acid were the predominant metabolic pathways. Phase II metabolic pathways were proven for the first time to consist of glucuronidation and cysteine conjugation. This study provides valuable and new information on the metabolism of PPT, which is indispensable for understanding the safety and efficacy of PPT, as well as its corresponding ginsenosides.
Effect of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol and its epimeric derivatives on myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol.[Pubmed:21528638]
Arzneimittelforschung. 2011;61(3):148-52.
OBJECTIVE: It was reported Panax ginseng had diverse components and multifaceted pharmacological functions. This study aims to investigate the effect of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol (PT, CAS 179799-20-3) and its epimeric derivatives (20S, 24R-epoxy-dammarane-3beta, 6alpha, 12beta, 25-tetraol, PTD1 and 20S, 24S-epoxy-dammarane-3beta, 6alpha, 12beta, 25-tetraol, PTD2) on myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol in rats. METHODS: Male Wistar rats were administered orally 20(S)-protopanaxatriol or its epimeric derivatives for 7 days. Four days after treatment, all rats, except those in the control group, were subcutaneously injected with isoproterenol (20 mg/kg) for 3 consecutive days. Two hours after the last isoproterenol injection, the rats were anaesthetized and sacrificed. The biochemical parameters were assayed and pathological examination of the heart tissues was performed. RESULTS: Administration of PT and PTD1 resulted in a reduction in creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase. PT and PTD1 Inhibited not only the elevation of malondialdehyde content, but also the reduction of superoxide dismutase activity, glutathione peroxidase and total antioxIdant capacity. The pathohistological changes induced by isoproterenol were also ameliorated by PT and PTD1. CONCLUSION: The present findings suggest that PT and PTD1 exerted cardioprotective effects against myocardial ischemic injury by enhancing the anti-free-radical actions of heart tissues. Furthermore the results indicated that the configuration of C-24 of the funan ring was involved in the phannacological action of the epimeric derivatives of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol.


