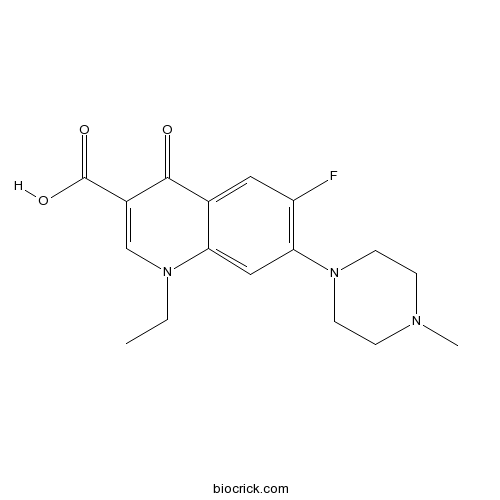
PefloxacinCAS# 70458-92-3 |
- GSK2334470
Catalog No.:BCC4982
CAS No.:1227911-45-6
- BX-912
Catalog No.:BCC1250
CAS No.:702674-56-4
- OSU-03012 (AR-12)
Catalog No.:BCC1255
CAS No.:742112-33-0
- NVP-BAG956
Catalog No.:BCC1813
CAS No.:853910-02-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 70458-92-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 51081 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H20FN3O3 | M.Wt | 333.36 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Pefloxacinium | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCN1C=C(C(=O)C2=CC(=C(C=C21)N3CCN(CC3)C)F)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FHFYDNQZQSQIAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H20FN3O3/c1-3-20-10-12(17(23)24)16(22)11-8-13(18)15(9-14(11)20)21-6-4-19(2)5-7-21/h8-10H,3-7H2,1-2H3,(H,23,24) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Pefloxacin is a an antibacterial agent and prevents bacterial DNA replication by inhibiting DNA gyrase (topoisomerse)
Target: DNA gyrase
Pefloxacin is a synthetic chemotherapeutic agent used to treat severe and life-threatening bacterial infections. Pefloxacin is commonly referred to as afluoroquinolone (or quinolone) drug and is a member of the fluoroquinolone class of antibacterials. It is an analog of norfloxacin. It is a synthetic fluoroquinolone, belonging to the 3rd generation of quinolones. Pefloxacin is extensively prescribed in France. Pefloxacin has not been approved for use in the United States.
The bactericidal action of pefloxacin results from interference with the activity of the bacterial enzymes DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, which are needed for the transcription and replication of bacterial DNA. DNA gyrase appears to be the primary quinolone target for gram-negative bacteria. Topoisomerase IV appears to be the preferential target in gram-positive organisms. Interference with these two topoisomerases results in strand breakage of the bacterial chromosome, supercoiling, and resealing. As a result DNA replication and transcription is inhibited. References: | |||||

Pefloxacin Dilution Calculator

Pefloxacin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9998 mL | 14.9988 mL | 29.9976 mL | 59.9952 mL | 74.994 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6 mL | 2.9998 mL | 5.9995 mL | 11.999 mL | 14.9988 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3 mL | 1.4999 mL | 2.9998 mL | 5.9995 mL | 7.4994 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.06 mL | 0.3 mL | 0.6 mL | 1.1999 mL | 1.4999 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.03 mL | 0.15 mL | 0.3 mL | 0.6 mL | 0.7499 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Pefloxacin is a an antibacterial agent and prevents bacterial DNA replication by inhibiting DNA gyrase (topoisomerse)
- (+)-MK 801
Catalog No.:BCC1288
CAS No.:70449-94-4
- 17alpha-Neriifolin
Catalog No.:BCN4269
CAS No.:7044-31-7
- Dihydrotamarixetin
Catalog No.:BCN4268
CAS No.:70411-27-7
- 4(15),11-Oppositadien-1-ol
Catalog No.:BCN4267
CAS No.:70389-96-7
- Voleneol
Catalog No.:BCN4266
CAS No.:70389-88-7
- 6alpha-Hydroxynidorellol
Catalog No.:BCN4598
CAS No.:70387-38-1
- Lornoxicam
Catalog No.:BCC4425
CAS No.:70374-39-9
- Sideritoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6689
CAS No.:70360-12-2
- Avobenzone
Catalog No.:BCC4891
CAS No.:70356-09-1
- Methyl Kakuol
Catalog No.:BCN8243
CAS No.:70342-29-9
- 3-Benzoylthiazolidine-2-thione
Catalog No.:BCC8624
CAS No.:70326-37-3
- Pertussis Toxin
Catalog No.:BCC7565
CAS No.:70323-44-3
- Pefloxacin Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4821
CAS No.:70458-95-6
- Norfloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4688
CAS No.:70458-96-7
- Corymbol
Catalog No.:BCN6617
CAS No.:7047-54-3
- Schizanthine A
Catalog No.:BCN1936
CAS No.:70474-24-7
- Petasinine
Catalog No.:BCN1988
CAS No.:70474-33-8
- Petasinoside
Catalog No.:BCN1989
CAS No.:70474-34-9
- Mitoxantrone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4924
CAS No.:70476-82-3
- ARP 100
Catalog No.:BCC2370
CAS No.:704888-90-4
- 2'-Hydroxy-5'-methoxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN4270
CAS No.:705-15-7
- 3,5-Dimethoxybenzylalcohol
Catalog No.:BCN3760
CAS No.:705-76-0
- α-Conotoxin PnIA
Catalog No.:BCC5978
CAS No.:705300-84-1
- NS 3763
Catalog No.:BCC7275
CAS No.:70553-45-6
Interspecies scaling of excretory amounts using allometry - retrospective analysis with rifapentine, aztreonam, carumonam, pefloxacin, miloxacin, trovafloxacin, doripenem, imipenem, cefozopran, ceftazidime, linezolid for urinary excretion and rifapentine, cabotegravir, and dolutegravir for fecal excretion.[Pubmed:26711252]
Xenobiotica. 2016 Sep;46(9):784-92.
1. Interspecies allometry scaling for prediction of human excretory amounts in urine or feces was performed for numerous antibacterials. Antibacterials used for urinary scaling were: rifapentine, Pefloxacin, trovafloxacin (Gr1/low; <10%); miloxacin, linezolid, PNU-142300 (Gr2/medium; 10-40%); aztreonam, carumonam, cefozopran, doripenem, imipenem, and ceftazidime (Gr3/high; >50%). Rifapentine, cabotegravir, and dolutegravir was used for fecal scaling (high; >50%). 2. The employment of allometry equation: Y = aW(b) enabled scaling of urine/fecal amounts from animal species. Corresponding predicted amounts were converted into % recovery by considering the respective human dose. Comparison of predicted/observed values enabled fold difference and error calculations (mean absolute error [MAE] and root mean square error [RMSE]). Comparisons were made for urinary/fecal data; and qualitative assessment was made amongst Gr1/Gr2/Gr3 for urine. 3. Average correlation coefficient for the allometry scaling was >0.995. Excretory amount predictions were largely within 0.75- to 1.5-fold differences. Average MAE and RMSE were within +/-22% and 23%, respectively. Although robust predictions were achieved for higher urinary/fecal excretion (>50%), interspecies scaling was applicable for low/medium excretory drugs. 4. Based on the data, interspecies scaling of urine or fecal excretory amounts may be potentially used as a tool to understand the significance of either urinary or fecal routes of elimination in humans in early development.
Comparison between Radioanalysis and (19)F Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in the Determination of Mass Balance, Metabolism, and Distribution of Pefloxacin.[Pubmed:28188298]
Drug Metab Dispos. 2017 Apr;45(4):399-408.
Mass balance and metabolism studies using radiolabeled substances are well recognized as an important part of the drug development process. In this study, we directly assessed the use of fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance ((19)F NMR) to achieve quantitative mass balance, metabolism, and distribution information for fluorinated compounds, without the need for radiolabeled synthesis or study. As a test case, the disposition of Pefloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, was evaluated in rats using quantitative (19)F NMR in parallel with a radiolabeled study. Urine, bile, and feces samples were collected over specific periods after oral administration of either 25 mg/kg [(14)C]Pefloxacin or 25 mg/kg Pefloxacin and were subsequently profiled by radioactivity or (19)F NMR, respectively. The percentage of dose excreted in each matrix was comparable between the two methods, with the total dose recovered by radioactivity and (19)F NMR determined to be 86.8% and 81.8%, respectively. In addition, plasma samples were collected to determine the exposure of Pefloxacin and its circulating metabolites. The plasma exposure of Pefloxacin determined by (19)F NMR was within 5% to that calculated by a validated liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry bioanalytical method. By both methods, Pefloxacin was identified as the major circulating entity, with Pefloxacin glucuronide as the major circulating metabolite. Quantitative analysis of metabolites in excreta was generally comparable between the two methods. In selected tissues, both methods indicated that the parent drug accounted for most of the drug-related material. In summary, we have demonstrated that (19)F NMR can be used as an alternative method to conventional radiolabeled studies for compounds containing fluorine without the need for radiolabeled synthesis/study.
Study of a water-soluble fluorescent sensor based on the Eu(III) pefloxacin complex.[Pubmed:27491804]
Luminescence. 2017 May;32(3):382-386.
The antibiotic type organic structure Pefloxacin binds well with europium (III) ions as a useful scaffold for assembling optical probes and allows energy transfer from ligand to metal ions through coordination linkages. This water-soluble chemosensor demonstrated significant 'off-on (red)' changes from an alkaline to a neutral environment (pH 14-8). The emission changed from red to blue under acidic conditions (pH 7-2). The whole process was completely reversible and effective within the pH range 2 to 14. Moreover, this probe system exhibited distinct luminescence quenching upon the addition of Cu(2+) or Fe(3)(+) . This general modular route will permit easy detection and the concept can be extended to a variety of quinolones for sensing purposes.


