LornoxicamCOX-1/COX-2 inhibitor CAS# 70374-39-9 |
- Mosapride
Catalog No.:BCC4078
CAS No.:112885-41-3
- Pizotifen
Catalog No.:BCC4215
CAS No.:15574-96-6
- Pizotifen Malate
Catalog No.:BCC4825
CAS No.:5189-11-7
- Fluvoxamine
Catalog No.:BCC4214
CAS No.:54739-18-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 70374-39-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 54690031 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H10ClN3O4S2 | M.Wt | 371.82 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Chlortenoxicam; Ro 13-9297; TS110 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 3.8 mg/mL (10.22 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
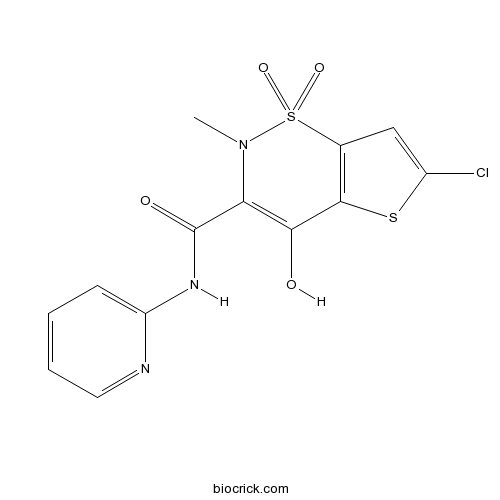
| Chemical Name | 6-chloro-4-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-N-pyridin-2-ylthieno[2,3-e]thiazine-3-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CN1C(=C(C2=C(S1(=O)=O)C=C(S2)Cl)O)C(=O)NC3=CC=CC=N3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WLHQHAUOOXYABV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H10ClN3O4S2/c1-17-10(13(19)16-9-4-2-3-5-15-9)11(18)12-7(23(17,20)21)6-8(14)22-12/h2-6,18H,1H3,(H,15,16,19) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Lornoxicam, a COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitor, is a new nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Target: COX
Lornoxicam showed a balanced inhibition of COX-1/-2 exhibiting the lowest IC50 (0.005 microM/0.008 microM) of the large panel of NSAIDs tested. lornoxicam showed a marked inhibition of IL-6 formation (IC50 54 microM) while the formation ofTNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-8 was only moderately affected [1]. Lornoxicam is effective in the treatment of patients with activated osteoarthritis; the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of lornoxicam are significantly superior to those of rofecoxib without inferiority in tolerability [2]. Lornoxicam was fully effective for prevention of hyperalgesia [3]. References: | |||||

Lornoxicam Dilution Calculator

Lornoxicam Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6895 mL | 13.4474 mL | 26.8947 mL | 53.7895 mL | 67.2368 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5379 mL | 2.6895 mL | 5.3789 mL | 10.7579 mL | 13.4474 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2689 mL | 1.3447 mL | 2.6895 mL | 5.3789 mL | 6.7237 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0538 mL | 0.2689 mL | 0.5379 mL | 1.0758 mL | 1.3447 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0269 mL | 0.1345 mL | 0.2689 mL | 0.5379 mL | 0.6724 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: A potent COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitor with IC50 values of 5 nM and 8 nM, respectively.
Lornoxicam, a new nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) belonging to the oxicam class. By intensively inhibit COX-1 and COX-2, this drug, both in oral and parenteral formulations, shows remarkable analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties. [1]
In vitro: Studies on intact human cells showed that lornoxicam intensively inhibit COX-1 and COX-2 with the lowest IC50 among a large panel of NSAIDs tested. Similar findings were obtained in the whole blood for COX-1/-2. In addition lornoxicam suppressed NO formation in a dose-dependently manner with an IC50 of 65 μM. [2]
In vivo: In vivo studies found that Lornoxicam was as effective as comparative NSAIDs and that 8 mg Lornoxicam was more effective than 10 mg morphine as a pain-reliever after oral surgery. Orally administration of lornoxicam at 16-24 mg daily was more effective than tramadol at 300 mg daily in pain-alleviating after knee surgery. Compared to naproxen, Lornoxicam showed higher therapeutic potency and lower gastrointestinal toxicity. This was probably due to the short half-life of lornoxicam as compared to the other oxicams. [3]
Clinical trials: A clinical study was performed to assess the efficacy and tolerability of intravenous lornoxicam in Indian patients with postoperative pain or other acute painful traumatic conditions. Patients were treated for 3 days with intravenous lornoxicam at a dosage of 8 mg twice or three times daily. Study demonstrated that intravenous lornoxicam is a powerful NSAID with an optimal efficacy/toxicity ratio and thus could be a reasonable therapeutic option for patients with painful traumatic conditions requiring parenteral NSAIDs. [4]
References:
[1]Balfour JA, Fitton A and Barradell LB. Lornoxicam, a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic potential in the management of painful and inflammatory conditions. Drugs. 1996 Apr; 51(4): 639-57.
[2]Berg J, Fellier H, Christoph T, Grarup J and Stimmeder D. The analgesic NSAID lornoxicam inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX)-1/-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and the formation of interleukin (IL)-6 in vitro. Inflamm Res. 1999 Jul; 48(7): 369-79.
[3]Radhofer-Welte S and Rabasseda X. Lornoxicam, a new potent NSAID with an improved tolerability profile. Drugs Today (Barc). 2000 Jan; 36(1): 55-76.
[4]Sharma A, Pingle A, and Baliga VP. Lornoxicam efficacy in acute pain (LEAP) trial. J Indian Med Assoc. 2008 Dec; 106(12): 811-3.
- Sideritoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6689
CAS No.:70360-12-2
- Avobenzone
Catalog No.:BCC4891
CAS No.:70356-09-1
- Methyl Kakuol
Catalog No.:BCN8243
CAS No.:70342-29-9
- 3-Benzoylthiazolidine-2-thione
Catalog No.:BCC8624
CAS No.:70326-37-3
- Pertussis Toxin
Catalog No.:BCC7565
CAS No.:70323-44-3
- Fluoroorotic Acid, Ultra Pure
Catalog No.:BCC1209
CAS No.:703-95-7
- Ivermectin
Catalog No.:BCC1251
CAS No.:70288-86-7
- CP 775146
Catalog No.:BCC7881
CAS No.:702680-17-9
- BX795
Catalog No.:BCC3635
CAS No.:702675-74-9
- BX-912
Catalog No.:BCC1250
CAS No.:702674-56-4
- Physalin H
Catalog No.:BCN7917
CAS No.:70241-09-7
- (±)-Lauroylcarnitine chloride
Catalog No.:BCC6690
CAS No.:7023-03-2
- 6alpha-Hydroxynidorellol
Catalog No.:BCN4598
CAS No.:70387-38-1
- Voleneol
Catalog No.:BCN4266
CAS No.:70389-88-7
- 4(15),11-Oppositadien-1-ol
Catalog No.:BCN4267
CAS No.:70389-96-7
- Dihydrotamarixetin
Catalog No.:BCN4268
CAS No.:70411-27-7
- 17alpha-Neriifolin
Catalog No.:BCN4269
CAS No.:7044-31-7
- (+)-MK 801
Catalog No.:BCC1288
CAS No.:70449-94-4
- Pefloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4231
CAS No.:70458-92-3
- Pefloxacin Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4821
CAS No.:70458-95-6
- Norfloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4688
CAS No.:70458-96-7
- Corymbol
Catalog No.:BCN6617
CAS No.:7047-54-3
- Schizanthine A
Catalog No.:BCN1936
CAS No.:70474-24-7
- Petasinine
Catalog No.:BCN1988
CAS No.:70474-33-8
Effects of intravenous ibuprofen and lornoxicam on erythrocyte deformability in rats undergoing hind limb ischemia reperfusion injury.[Pubmed:28127969]
Bratisl Lek Listy. 2016;117(12):722-725.
BACKGROUND AND AIM: Acute hind limb ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury is a common consequence of abdominal aorta crossclamping during aortic surgery. Erythrocyte deformability is affected by I/R process and may lead to increased tissue and organ injury. Lornoxicam and intravenous ibuprofen are becoming commonly used as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) for postoperative analgesia. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effects of Lornoxicam (2 mg/kg iv) and intravenous ibuprofen (30 mg/kg iv) on erythrocyte deformability in I/R model in rats. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Four study groups, each containing 6 Wistar rats were created. Laparotomy was performed in all groups under general anesthesia with ketamine and xylazine. In all groups except sham group, ischemia and reperfusion were achieved by clamping and declamping the infrarenal abdominal aorta for 120 minutes. Rats in Group IR+L received intravenous infusion of Lornoxicam (2 mg/kg) while rats in Group IR+I received intravenous infusion of ibubrofen (30 mg/kg) following 2 hours of ischemic period. At the end of reperfusion period, erythrocyte packs were prepared from heparinized blood samples. Erythrocyte suspensions with hematocrit at a concentration of 5% in a phosphatebuffered saline (PBS) were used in order to perform deformability measurements. The value of p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS: Relative resistance has increased in ischemia reperfusion group when compared to control group (p < 0.0001). Lornoxicam or ibuprofen intravenous treatments did not change the erythrocyte deformability during ischemia reperfusion period in rats (p=0.851, p=0.690). CONCLUSION: Intravenous ibuprofen or Lornoxicam administrations during ischemia reperfusion period in rats have no negative effect on erythrocyte deformability. The findings of the study should be supported with more detailed and extensive clinical/experimental studies in the future (Fig. 1, Ref. 18).
Lornoxicam Immediate-Release Tablets: Formulation and Bioequivalence Study in Healthy Mediterranean Volunteers Using a Validated LC-MS/MS Method.[Pubmed:28176487]
Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2017 Nov;6(6):564-569.
This study aimed to demonstrate interchangeability between 2 Lornoxicam tablet formulations under fasting conditions among Mediterranean Arabs by using a newly validated high-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. A single-oral solid dosage form (8 mg/tablet), randomized, open-label, 2-way crossover study was conducted on 30 healthy male volunteers. Blood samples were collected prior to dosing and over a 24-hour period, and the washout period was 9 days. Statistical comparison of the main pharmacokinetic parameters showed no significant difference between generic and branded products. The point estimates (ratios of geometric mean %) were 90.91, 96.34, and 94.86 for Cmax, AUC0-last , and AUC0-infinity , respectively. The 90% confidence intervals were within the predefined limits of 80.00%-125.00%, as specified by the international guidelines. This study showed that both formulations met the regulatory criteria for bioequivalence.
Formulation of Niosomal Gel for Enhanced Transdermal Lornoxicam Delivery: In-Vitro and In-Vivo Evaluation.[Pubmed:28240177]
Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(1):122-133.
BACKGROUND: The objective of this study was to investigate the potential of niosomal gels as a transdermal delivery system to improve the permeation and anti-inflammatory activity of Lornoxicam (LX). METHODS: LX niosomes were prepared by thin film hydration technique and were characterized using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), Particle Size analysis and Zeta potential determination. LX niosomal gel/LX loaded gel were prepared using Carbopol 934 (2%) and were evaluated for their physical appearance, pH and rheological behaviour. Ex vivo skin permeation test was performed on dorsal region of wistar rats. In vivo studies comprised skin irritation test and anti-inflammatory activity study. RESULTS: The prepared LX niosomes exhibited an entrapment efficiency of more than 66% and a particle size diameter ranging from 295 nm to 1298 nm, with negatively charged zeta potential. TEM electron micrographs revealed spherical shaped vesicles. The release pattern of drug was analyzed and found to follow Higuchi's model. Rheology studies revealed the pseudoplastic behaviour of LX niosomal gel. They exhibited a one and half fold increase in drug permeated through rat skin, when compared to free drug. Skin irritation test proved the non-irritancy of LX niosomal gels, when applied to dorsal region of Wistar rats. Percentage edema inhibition of LX niosomes was significantly higher (P<0.05) than that of free LX group showing an enhanced anti-inflammatory activity of LX niosomes. CONCLUSION: These findings revealed that LX loaded niosomal gels could be a potential transdermal drug delivery system.
A pharmaceutical study on lornoxicam fast disintegrating tablets: formulation and in vitro and in vivo evaluation.[Pubmed:28283842]
Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2017 Jun;7(3):450-459.
Lornoxicam is an anti-inflammatory drug used to relieve rheumatoid arthritis pain, but the low water solubility and bitter taste of the drug present challenges for formulation as fast disintegrating tablets (FDTs). Complexation of the drug with beta-cyclodextrin was initially carried out to increase the drug solubility and to mask its bitter taste. Tablets were prepared by direct compression of drug complex (DC), F-Melt, mannitol, crospovidone, and sodium starch glycolate (SSG). FDTs were characterized in terms of disintegration time (DT) and dissolution. A bioequivalence study was carried out using (Zeficam(R) tablets (Eva Pharma) as reference with the help of human volunteers (n = 4). The chosen formula (F2, DC 24 mg, F-Melt 88.4 mg, and crospovidone 5 mg) exhibited the shortest in vitro (18 s) and in vivo DT (13 s), and the percent drug released after Q6min was 95.90%. Following administration of F2 and Zeficam(R), the respective maximum drug plasma concentrations (Cmax) were 510 and 532.5 ng/mL, at times (Tmax) of 1 and 2.5 h, of mean residence times (MRTs) of 12.25 and 11.35 h and of areas under the plasma curve [AUC(0-24)] of 5080.253 and 4815.775 ng/h/mL. There were significant differences in Tmax and MRT of both treatments (p < 0.05). Moreover, the volunteers found F2 to be palatable. FDTs could be considered as promising dosage forms for Lornoxicam as they exhibited a short in vivo DT and an increased rate of drug release and attained a relative bioavailability of 105.49%. This could offer a fast relief of pain accompanying rheumatoid arthritis.


