MosaprideCAS# 112885-41-3 |
- Mc-MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1735
CAS No.:1401963-15-2
- Docetaxel Trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1535
CAS No.:148408-66-6
- Colchicine
Catalog No.:BCN6271
CAS No.:64-86-8
- D-64131
Catalog No.:BCC1510
CAS No.:74588-78-6
- 7-Xylosyltaxol
Catalog No.:BCN5341
CAS No.:90332-66-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 112885-41-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 119584 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H25ClFN3O3 | M.Wt | 421.89 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
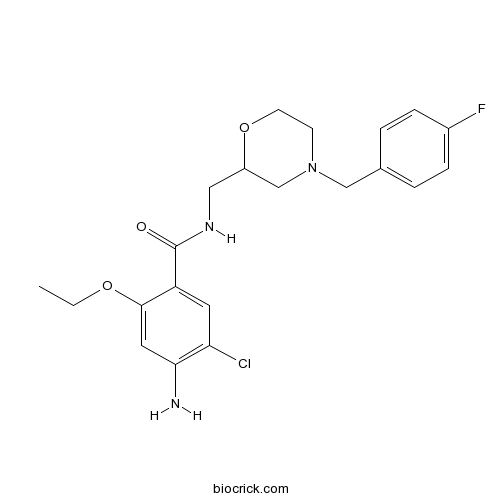
| Chemical Name | 4-amino-5-chloro-2-ethoxy-N-[[4-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]morpholin-2-yl]methyl]benzamide | ||
| SMILES | CCOC1=CC(=C(C=C1C(=O)NCC2CN(CCO2)CC3=CC=C(C=C3)F)Cl)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YPELFRMCRYSPKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H25ClFN3O3/c1-2-28-20-10-19(24)18(22)9-17(20)21(27)25-11-16-13-26(7-8-29-16)12-14-3-5-15(23)6-4-14/h3-6,9-10,16H,2,7-8,11-13,24H2,1H3,(H,25,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Mosapride Dilution Calculator

Mosapride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3703 mL | 11.8514 mL | 23.7029 mL | 47.4057 mL | 59.2572 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4741 mL | 2.3703 mL | 4.7406 mL | 9.4811 mL | 11.8514 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.237 mL | 1.1851 mL | 2.3703 mL | 4.7406 mL | 5.9257 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0474 mL | 0.237 mL | 0.4741 mL | 0.9481 mL | 1.1851 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0237 mL | 0.1185 mL | 0.237 mL | 0.4741 mL | 0.5926 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Mosapride is a gastroprokinetic agent that acts as a selective 5HT4 agonist.
- Fmoc-2-Nal-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3292
CAS No.:112883-43-9
- Fmoc-N-Me-Nle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3299
CAS No.:112883-42-8
- Fmoc-D-Nle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3300
CAS No.:112883-41-7
- Fmoc-D-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3532
CAS No.:112883-40-6
- (24S)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1291
CAS No.:112849-14-6
- (24R)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1289
CAS No.:112828-09-8
- 24R-Calcipotriol
Catalog No.:BCC1304
CAS No.:112827-99-3
- Methyllycaconitine citrate
Catalog No.:BCC6897
CAS No.:112825-05-5
- Dynole 34-2
Catalog No.:BCC7891
CAS No.:1128165-88-7
- 1-Cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8464
CAS No.:112811-72-0
- 1-Cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC8465
CAS No.:112811-71-9
- Gatifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC1064
CAS No.:112811-59-3
- Mosapride Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC1065
CAS No.:112885-42-4
- Raltitrexed
Catalog No.:BCC4457
CAS No.:112887-68-0
- BzATP triethylammonium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7643
CAS No.:112898-15-4
- Boc-D-Asp(OcHex)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3372
CAS No.:112898-18-7
- HU 211
Catalog No.:BCC5946
CAS No.:112924-45-5
- PD128907 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4469
CAS No.:112960-16-4
- Calcipotriol
Catalog No.:BCC1444
CAS No.:112965-21-6
- Tokinolide B
Catalog No.:BCN2753
CAS No.:112966-16-2
- IM-12
Catalog No.:BCC5487
CAS No.:1129669-05-1
- Estradiol diproppionate
Catalog No.:BCC8960
CAS No.:113-38-2
- Chlorprothixene
Catalog No.:BCC3753
CAS No.:113-59-7
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4526
CAS No.:113-92-8
Mosapride for gastroesophageal reflux disease in neurologically impaired patients.[Pubmed:27561215]
Pediatr Int. 2017 Mar;59(3):347-351.
BACKGROUND: The prokinetic agent cisapride is effective for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in infants and children, but is no longer used for this purpose because of safety concerns. Therefore, other pharmacological agents need to be investigated for efficacy in GERD treatment. In this study, we examined the effectiveness and safety of Mosapride for the treatment of neurologically impaired children and adolescents with GERD. METHODS: Mosapride (0.3 mg/kg/day) was administered to 11 neurologically impaired patients with GERD (five male; median age, 12.3 years). Esophageal acid exposure was measured using esophageal pH monitoring before and at >5 days after the start of Mosapride treatment. The pressure and length of the lower esophageal sphincter were compared before and after Mosapride treatment. RESULTS: In the 11 patients, median reflux index (percentage of the total monitoring period during which recorded pH was <4.0) was 17.5% (range, 4.4-59%) before and 8.2% (range, 2.8-20.7%) after Mosapride treatment (P = 0.02). Median esophageal clearance was 1.0 min/reflux (range, 0.5-2.1 min/reflux) before and 0.7 min/reflux (range, 0.4-1.2 min/reflux) after treatment with Mosapride (P = 0.02). The median number of reflux episodes before (219) and after (122) drug treatment did not differ significantly. CONCLUSION: The decreased reflux index in neurologically impaired patients with GERD is due to Mosapride, therefore Mosapride may be a candidate for GERD treatment.
Drug-induced Liver Injury Associated with Mosapride Citrate: A Report of Two Cases.[Pubmed:28049998]
Intern Med. 2017;56(1):41-45.
We herein report two cases of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) due to Mosapride. Case 1: A 78-year-old man was admitted with elevated transaminase levels. The cessation of Mosapride led to the improvement of elevated liver enzyme levels. Case 2: A 54-year-old man was admitted with jaundice. Mosapride was discontinued immediately, and methylprednisolone was administered for acute liver failure. The patient's data showed improvement, and he was discharged on Day 32. In both cases, Mosapride gave a positive response to a drug-induced lymphocyte stimulation test (DLST), and the patient's score based on the criteria for DILI was "highly probable".
A Double-blind, Randomized, Multicenter Clinical Trial Investigating the Efficacy and Safety of Esomeprazole Single Therapy Versus Mosapride and Esomeprazole Combined Therapy in Patients with Esophageal Reflux Disease.[Pubmed:28192647]
J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017 Apr 30;23(2):218-228.
Background/Aims: We aim to evaluate the efficacy and safety of combination therapy in erosive reflux disease (ERD) patients by comparing endoscopic healing rates according to the Los Angeles classification for esomeprazole alone, and esomeprazole plus Mosapride. Methods: A total of 116 ERD patients were randomized to receive esomeprazole 40 mg once daily plus Mosapride 5 mg 3 times daily (E+M group), or esomeprazole plus placebo (E only group) for 8 weeks. Patients recorded gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptom questionnaire at weeks 4 and 8. The primary endpoint was the endoscopic healing rate of ERD after 8 weeks of treatment. Results: Endoscopic healing rates according to the Los Angeles classification was 32 (66.7%) in the E+M group and 26 (60.5%) in the E only group, but there was no statistically significant difference between the groups. Only at 4 weeks, the total GERD symptom score changes relative to the baseline significantly improved in the E+M group than that of the E only group (-13.4 +/- 14.7 vs -8.0 +/- 12.3, P = 0.041), and upper abdominal pain and belching score changes showed significantly improved in the E+M group than that of the E only group (P = 0.018 and P = 0.013, respectively). Conclusions: The combination of a proton pump inhibitor with Mosapride shows a tendency for upper abdominal pain, belching, and total GERD symptoms scores to improve more rapidly. This suggests that combination therapy with esomeprazole and Mosapride will be useful for rapid improvement of specific GERD symptoms, such as upper abdominal pain and belching in ERD patients.
Mosapride, a selective serotonin 5-HT4 receptor agonist, and alogliptin, a selective dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, exert synergic effects on plasma active GLP-1 levels and glucose tolerance in mice.[Pubmed:26497774]
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015 Dec;110(3):e18-21.
Pharmacologic stimulation of serotonin 5-HT4 receptors increased plasma active glucagon-like-peptide-1 (GLP-1) levels independent of feeding, and that pharmacologic stimulation of 5-HT4 receptors and pharmacologic inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 exerted synergic effects on plasma active GLP-1 levels and glucose tolerance in mice.


