D-64131Tubulin polymerization inhibitor CAS# 74588-78-6 |
- Mc-MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1735
CAS No.:1401963-15-2
- Monomethyl auristatin E
Catalog No.:BCC1775
CAS No.:474645-27-7
- CYT997 (Lexibulin)
Catalog No.:BCC4601
CAS No.:917111-44-5
- MPC 6827 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8040
CAS No.:917369-31-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 74588-78-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3921152 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H13NO2 | M.Wt | 251.28 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (397.96 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
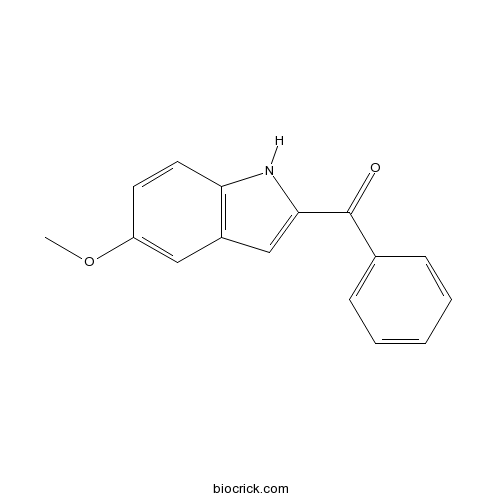
| Chemical Name | (5-methoxy-1H-indol-2-yl)-phenylmethanone | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC2=C(C=C1)NC(=C2)C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ICMIJSRDISNKOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H13NO2/c1-19-13-7-8-14-12(9-13)10-15(17-14)16(18)11-5-3-2-4-6-11/h2-10,17H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Novel inhibitor of tubulin polymerization; cytotoxic and inhibits tumor cell proliferation in vitro (IC50 = 74 nM). Prevents growth of tumor models in mice following oral administration in vivo. |

D-64131 Dilution Calculator

D-64131 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.9796 mL | 19.8981 mL | 39.7962 mL | 79.5925 mL | 99.4906 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7959 mL | 3.9796 mL | 7.9592 mL | 15.9185 mL | 19.8981 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.398 mL | 1.9898 mL | 3.9796 mL | 7.9592 mL | 9.9491 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0796 mL | 0.398 mL | 0.7959 mL | 1.5918 mL | 1.9898 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0398 mL | 0.199 mL | 0.398 mL | 0.7959 mL | 0.9949 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
D-64131 is a tubulin polymerization inhibitor with an IC50 value of 0.53 μM. [1]
The polymerization of bovine brain tubulin as well as binding of [3H] colchicine to biotinylated αβ-tubulin was dose-dependently inhibited by D-64131. Many cancer cells display abnormal microtubule structures, such as fragmented mitotic spindles or multiple spindle poles after treatment with D-64131. Nuclear blebbing and abnormal nuclear structures typical for apoptotic cells are detectable in many cells treated with D-64131. In nude mice, D-64131 proved to be well tolerated and highly active against the human amelanoic melanoma MEXF 989 tumor xenograft. D-64131 treatment resulted in significant tumor growth inhibition during treatment. [1]
Reference:
1. Beckers T, Reissmann T, Schmidt M et al. 2-aroylindoles, a novel class of potent, orally active small molecule tubulin inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2002 Jun 1;62(11):3113-9.
- Isomedicarpin
Catalog No.:BCN4297
CAS No.:74560-05-7
- Cristacarpin
Catalog No.:BCN3935
CAS No.:74515-47-2
- UBP 302
Catalog No.:BCC7256
CAS No.:745055-91-8
- UBP 296
Catalog No.:BCC7255
CAS No.:745055-86-1
- Ivachtin
Catalog No.:BCC2357
CAS No.:745046-84-8
- MMAF
Catalog No.:BCC5144
CAS No.:745017-94-1
- Alprostadil
Catalog No.:BCC4963
CAS No.:745-65-3
- Casegravol
Catalog No.:BCN4591
CAS No.:74474-76-3
- Potassium Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC7581
CAS No.:7447-40-7
- Sauvagine
Catalog No.:BCC5792
CAS No.:74434-59-6
- Symlandine
Catalog No.:BCN1974
CAS No.:74410-74-5
- PAF (C16)
Catalog No.:BCC7522
CAS No.:74389-68-7
- Rubiadin 1-methyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN4298
CAS No.:7460-43-7
- Tetrahydrocoptisine
Catalog No.:BCN2558
CAS No.:7461-02-1
- Tylosin tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4875
CAS No.:74610-55-2
- ent-3Beta-Angeloyloxykaur-16-en-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1365
CAS No.:74635-61-3
- 11-Hydroxydrim-7-en-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN7770
CAS No.:74635-87-3
- Liquiritin Apioside
Catalog No.:BCC8334
CAS No.:74639-14-8
- 1,3,9-Trimethyluric acid
Catalog No.:BCN7393
CAS No.:7464-93-9
- Nuclear yellow
Catalog No.:BCC1810
CAS No.:74681-68-8
- 3-Methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxycinnamaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN1364
CAS No.:74683-19-5
- 4-hydroxy-1-methoxycarbonyl-beta-carboline
Catalog No.:BCN7909
CAS No.:74690-72-5
- 1-Methoxycarbonyl-beta-carboline-N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8205
CAS No.:74690-74-7
- Vibsanin C
Catalog No.:BCN4590
CAS No.:74690-89-4
Dual visible-light photoredox and palladium(ii) catalysis for dehydrogenative C2-acylation of indoles at room temperature.[Pubmed:28682380]
Org Biomol Chem. 2017 Jul 19;15(28):5899-5903.
A highly regioselective direct C2-acylation of N-pyrimidine protected indoles with aldehydes is reported at room temperature through the merger of visible light photoredox and palladium(ii) catalysis. Late-stage acylation of tryptophan, selective mono-acylation of carbazole and the syntheses of tubulin inhibitors D-64131 and D-68144 are also demonstrated.
Indolobenzazepin-7-ones and 6-, 8-, and 9-membered ring derivatives as tubulin polymerization inhibitors: synthesis and structure--activity relationship studies.[Pubmed:19743863]
J Med Chem. 2009 Oct 8;52(19):5916-25.
Several small weight indole derivatives (D-64131, D-24851, BPR0L075, BLF 61-3, and ATI derivatives) are potent tubulin polymerization inhibitors and show nanomolar antiproliferative activity. Among them, indolobenzazepin-7-ones were recently disclosed as potent antimitotic agents. In an effort to improve this structure, we prepared new derivatives in order to evaluate their antiproliferative activity. 5,6,7,9-Tetrahydro-8H-indolo[2,3-e][3]benzazocin-8-one (1m) was found to be the most potent derivative inhibiting the cell growth of several cancer cell lines in the lower nanomolar range.
2-aroylindoles, a novel class of potent, orally active small molecule tubulin inhibitors.[Pubmed:12036922]
Cancer Res. 2002 Jun 1;62(11):3113-9.
2-Aroylindoles with 5-methoxy-1H-2-indolyl-phenylmethanone (D-64131) as the lead structure were discovered as a new class of synthetic, small molecule tubulin inhibitors. By competitively binding with [(3)H]colchicine to alphabeta-tubulin and inhibiting microtubule formation, cycling cells were arrested in the G(2)-M phase of the cell division cycle. The proliferation of tumor cells from 12 of 14 different organs and tissues was inhibited with mean IC(50)s of 62 nM and 24 nM by D-64131 and D-68144, respectively, comparable with the potency of paclitaxel with mean IC(50) of 10 nM. By measuring the cytotoxicity in a human colon carcinoma cell model with ectopic ecdysone-inducible expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(WAF1), specificity toward cycling cells was demonstrated. In contrast to microtubule inhibitors from natural sources, 2-aroylindoles did not alter the polymerization-dependent GTPase activity of beta-tubulin and are not substrates of the multidrug resistance/multidrug resistance protein efflux pump. No cross-resistance toward cell lines with multidrug resistance/multidrug resistance protein independent resistance phenotypes became evident. In animal studies, no signs of systemic toxicity were observed after p.o. dosages of up to 400 mg/kg of D-64131. In xenograft experiments with the human amelanoic melanoma MEXF 989, D-64131 was highly active with treatment resulting in a growth delay of 23.4 days at 400 mg/kg. Therefore, D-64131 and analogues have the potential to be developed for cancer therapy, replacing or supplementing standard therapy regimens with tubulin-targeting drugs from natural sources.
Synthetic 2-aroylindole derivatives as a new class of potent tubulin-inhibitory, antimitotic agents.[Pubmed:11741473]
J Med Chem. 2001 Dec 20;44(26):4535-53.
A new class of simple synthetic antimitotic compounds based on 2-aroylindoles was discovered. (5-Methoxy-1H-2-indolyl)-phenylmethanone (1) as well as analogous 3-fluorophenyl- (36) and 3-methoxyphenyl (3) derivatives displayed high cytotoxicity of IC(50) = 20 to 75 nM against the human HeLa/KB cervical, SK-OV-3 ovarian, and U373 astrocytoma carcinoma cell lines. The inhibition of proliferation correlated with the arrest in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle. In in vitro assays with tubulin isolated from bovine brain, in general antiproliferative activity correlated with inhibition of tubulin polymerization. Thus, the antimitotic activity of 2-aroylindoles is explained by interference with the mitotic spindle apparatus and destabilization of microtubules. In contrast to colchicine, vincristine, nocodazole, or taxol, 1 did not significantly affect the GTPase activity of beta-tubulin. Interestingly, selected compounds inhibited angiogenesis in the chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay. In xenograft experiments, 1 was highly active after oral administration at 200 mg/kg against the human amelanocytic melanoma MEXF 989 in athymic nude mice. We conclude, that 2-aroylindoles constitute an interesting new class of antitubulin agents with the potential to be clinically developed for cancer treatment.


