OSU-03012 (AR-12)Potent PDK1 inhibitor CAS# 742112-33-0 |
- PDK1 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1843
CAS No.:1001409-50-2
- GSK2334470
Catalog No.:BCC4982
CAS No.:1227911-45-6
- Radicicol
Catalog No.:BCC2131
CAS No.:12772-57-5
- BX-912
Catalog No.:BCC1250
CAS No.:702674-56-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

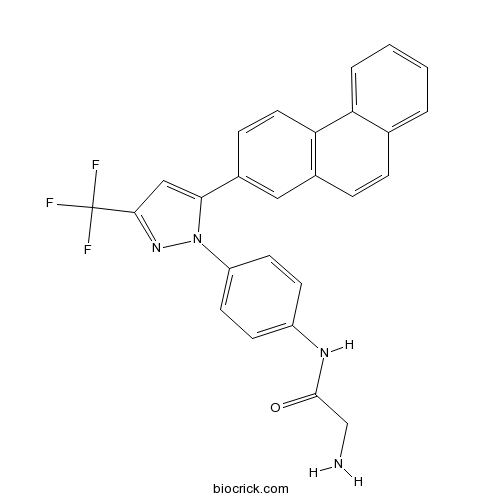
| Cas No. | 742112-33-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10027278 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H19F3N4O | M.Wt | 460.45 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-amino-N-[4-[5-phenanthren-2-yl-3-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazol-1-yl]phenyl]acetamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C=CC3=C2C=CC(=C3)C4=CC(=NN4C5=CC=C(C=C5)NC(=O)CN)C(F)(F)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YULUCECVQOCQFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H19F3N4O/c27-26(28,29)24-14-23(33(32-24)20-10-8-19(9-11-20)31-25(34)15-30)18-7-12-22-17(13-18)6-5-16-3-1-2-4-21(16)22/h1-14H,15,30H2,(H,31,34) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | PDPK1 (PDK1) inhibitor; inhibits Akt signaling. Induces apoptosis of PC-3 and medulloblastoma cells, and inhibits growth of a number of tumor cell lines. Sensitizes radiotherapy-induced cell death and enhances cytotoxic effects of chemotherapeutic agents in vitro. Attenuates tumor growth of medulloblastoma xenografts in mice. |

OSU-03012 (AR-12) Dilution Calculator

OSU-03012 (AR-12) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1718 mL | 10.8589 mL | 21.7179 mL | 43.4358 mL | 54.2947 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4344 mL | 2.1718 mL | 4.3436 mL | 8.6872 mL | 10.8589 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2172 mL | 1.0859 mL | 2.1718 mL | 4.3436 mL | 5.4295 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0434 mL | 0.2172 mL | 0.4344 mL | 0.8687 mL | 1.0859 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0217 mL | 0.1086 mL | 0.2172 mL | 0.4344 mL | 0.5429 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
OSU-03012 (AR-12) is an inhibitor of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK-1) with IC50 value of 5μm, which shows 2-fold higher potency over OSU-02067 [1].
OSU-03012 has represented to suppress PC-3 cell proliferation and induce apoptosis in PC-3 cells. Expression of the constitutively active forms of PDK-1 and Akt has revealed to reduce OSU-03012-induced apoptosis in PC-3 cell [1].
OSU-03012?could potently inhibit the growth of?primary human VS cells?and malignant schwannoma HMS-97 cells in?a dose-dependent manner. In contrast, normal human Schwann cells showed to be more resistant to OSU-03012. Additionally, OSU-03012 revealed to inhibit phosphorylation of AKT at the threonine-308 site in both VS cells and HMS-97 cells [2].
References:
[1] Zhu J1,?Huang JW,?Tseng PH,?Yang YT,?Fowble J,?Shiau CW,?Shaw YJ,?Kulp SK,?Chen CS. From the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib to a novel class of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 inhibitors. Cancer Res.?2004 Jun 15;64(12):4309-18.
[2] Lee TX1,?Packer MD,?Huang J,?Akhmametyeva EM,?Kulp SK,?Chen CS,?Giovannini M,?Jacob A,?Welling DB,?Chang LS. Growth inhibitory and anti-tumour activities of OSU-03012, a novel PDK-1 inhibitor, on vestibular schwannoma and malignant schwannoma cells. Eur J Cancer.?2009 Jun;45(9):1709-20.
- Carbenoxolone disodium
Catalog No.:BCC3745
CAS No.:7421-40-1
- Vintafolide
Catalog No.:BCC5265
CAS No.:742092-03-1
- 3-Bromo-7-nitroindazole
Catalog No.:BCC6770
CAS No.:74209-34-0
- Uplandicine
Catalog No.:BCN2055
CAS No.:74202-10-1
- Doxazosin
Catalog No.:BCC4218
CAS No.:74191-85-8
- Cyclokievitone
Catalog No.:BCC8159
CAS No.:74175-82-9
- Haginin A
Catalog No.:BCN6861
CAS No.:74174-29-1
- R547
Catalog No.:BCC3927
CAS No.:741713-40-6
- 2,3-Dehydrokievitone
Catalog No.:BCN4294
CAS No.:74161-25-4
- Pimobendan
Catalog No.:BCC2294
CAS No.:74150-27-9
- Bisdethiobis(methylthio)gliotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN7351
CAS No.:74149-38-5
- DSC
Catalog No.:BCC2800
CAS No.:74124-79-1
- Doronenine
Catalog No.:BCN2066
CAS No.:74217-57-5
- Baogongteng A
Catalog No.:BCN1874
CAS No.:74239-84-2
- p-Chlorophenylalanine
Catalog No.:BCC5689
CAS No.:7424-00-2
- 7-Acetylintermedine
Catalog No.:BCN1998
CAS No.:74243-01-9
- 12-Oxograndiflorenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7624
CAS No.:74284-42-7
- Triptophenolide
Catalog No.:BCN2546
CAS No.:74285-86-2
- Sinapine thiocyanate
Catalog No.:BCN2765
CAS No.:7431-77-8
- Quercetin-3-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN3878
CAS No.:7431-83-6
- Somatostatin 1-28
Catalog No.:BCC5715
CAS No.:74315-46-1
- Z-Trp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2750
CAS No.:7432-21-5
- Schisandrin A
Catalog No.:BCN5815
CAS No.:7432-28-2
- 4',4'''-Di-O-methylcupressuflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4295
CAS No.:74336-91-7
Needle-Free Delivery of Acetalated Dextran-Encapsulated AR-12 Protects Mice from Francisella tularensis Lethal Challenge.[Pubmed:26787696]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Mar 25;60(4):2052-62.
Francisella tularensiscauses tularemia and is a potential biothreat. Given the limited antibiotics for treating tularemia and the possible use of antibiotic-resistant strains as a biowarfare agent, new antibacterial agents are needed. AR-12 is an FDA-approved investigational new drug (IND) compound that induces autophagy and has shown host-directed, broad-spectrum activityin vitroagainstSalmonella entericaserovar Typhimurium andF. tularensis We have shown that AR-12 encapsulated within acetalated dextran (Ace-DEX) microparticles (AR-12/MPs) significantly reduces host cell cytotoxicity compared to that with free AR-12, while retaining the ability to controlS.Typhimurium within infected human macrophages. In the present study, the toxicity and efficacy of AR-12/MPs in controlling virulent type AF. tularensisSchuS4 infection were examinedin vitroandin vivo No significant toxicity of blank MPs or AR-12/MPs was observed in lung histology sections when the formulations were given intranasally to uninfected mice. In histology sections from the lungs of intranasally infected mice treated with the formulations, increased macrophage infiltration was observed for AR-12/MPs, with or without suboptimal gentamicin treatment, but not for blank MPs, soluble AR-12, or suboptimal gentamicin alone. AR-12/MPs dramatically reduced the burden ofF. tularensisin infected human macrophages, in a manner similar to that of free AR-12. However,in vivo, AR-12/MPs significantly enhanced the survival ofF. tularensisSchuS4-infected mice compared to that seen with free AR-12. In combination with suboptimal gentamicin treatment, AR-12/MPs further improved the survival ofF. tularensisSchuS4-infected mice. These studies provide support for Ace-DEX-encapsulated AR-12 as a promising new therapeutic agent for tularemia.
Antitumor/Antifungal Celecoxib Derivative AR-12 is a Non-Nucleoside Inhibitor of the ANL-Family Adenylating Enzyme Acetyl CoA Synthetase.[Pubmed:27088128]
ACS Infect Dis. 2016 Apr 8;2(4):268-280.
AR-12/OSU-03012 is an antitumor celecoxib-derivative that has progressed to Phase I clinical trial as an anticancer agent and has activity against a number of infectious agents including fungi, bacteria and viruses. However, the mechanism of these activities has remained unclear. Based on a chemical-genetic profiling approach in yeast, we have found that AR-12 is an ATP-competitive, time-dependent inhibitor of yeast acetyl coenzyme A synthetase. AR-12-treated fungal cells show phenotypes consistent with the genetic reduction of acetyl CoA synthetase activity, including induction of autophagy, decreased histone acetylation, and loss of cellular integrity. In addition, AR-12 is a weak inhibitor of human acetyl CoA synthetase ACCS2. Acetyl CoA synthetase activity is essential in many fungi and parasites. In contrast, acetyl CoA is primarily synthesized by an alternate enzyme, ATP-citrate lyase, in mammalian cells. Taken together, our results indicate that AR-12 is a non-nucleoside acetyl CoA synthetase inhibitor and that acetyl CoA synthetase may be a feasible antifungal drug target.
The Celecoxib Derivative AR-12 Has Broad-Spectrum Antifungal Activity In Vitro and Improves the Activity of Fluconazole in a Murine Model of Cryptococcosis.[Pubmed:27645246]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Nov 21;60(12):7115-7127.
Only one new class of antifungal drugs has been introduced into clinical practice in the last 30 years, and thus the identification of small molecules with novel mechanisms of action is an important goal of current anti-infective research. Here, we describe the characterization of the spectrum of in vitro activity and in vivo activity of AR-12, a celecoxib derivative which has been tested in a phase I clinical trial as an anticancer agent. AR-12 inhibits fungal acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) synthetase in vitro and is fungicidal at concentrations similar to those achieved in human plasma. AR-12 has a broad spectrum of activity, including activity against yeasts (e.g., Candida albicans, non-albicans Candida spp., Cryptococcus neoformans), molds (e.g., Fusarium, Mucor), and dimorphic fungi (Blastomyces, Histoplasma, and Coccidioides) with MICs of 2 to 4 mug/ml. AR-12 is also active against azole- and echinocandin-resistant Candida isolates, and subinhibitory AR-12 concentrations increase the susceptibility of fluconazole- and echinocandin-resistant Candida isolates. Finally, AR-12 also increases the activity of fluconazole in a murine model of cryptococcosis. Taken together, these data indicate that AR-12 represents a promising class of small molecules with broad-spectrum antifungal activity.
AR-12 Inhibits Multiple Chaperones Concomitant With Stimulating Autophagosome Formation Collectively Preventing Virus Replication.[Pubmed:27187154]
J Cell Physiol. 2016 Oct;231(10):2286-302.
We have recently demonstrated that AR-12 (OSU-03012) reduces the function and ATPase activities of multiple HSP90 and HSP70 family chaperones. Combined knock down of chaperones or AR-12 treatment acted to reduce the expression of virus receptors and essential glucosidase proteins. Combined knock down of chaperones or AR-12 treatment inactivated mTOR and elevated ATG13 S318 phosphorylation concomitant with inducing an endoplasmic reticulum stress response that in an eIF2alpha-dependent fashion increased Beclin1 and LC3 expression and autophagosome formation. Over-expression of chaperones prevented the reduction in receptor/glucosidase expression, mTOR inactivation, the ER stress response, and autophagosome formation. AR-12 reduced the reproduction of viruses including Mumps, Influenza, Measles, Junin, Rubella, HIV (wild type and protease resistant), and Ebola, an effect replicated by knock down of multiple chaperone proteins. AR-12-stimulated the co-localization of Influenza, EBV and HIV virus proteins with LC3 in autophagosomes and reduced viral protein association with the chaperones HSP90, HSP70, and GRP78. Knock down of Beclin1 suppressed drug-induced autophagosome formation and reduced the anti-viral protection afforded by AR-12. In an animal model of hemorrhagic fever virus, a transient exposure of animals to low doses of AR-12 doubled animal survival from approximately 30% to approximately 60% and suppressed liver damage as measured by ATL, GGT and LDH release. Thus through inhibition of chaperone protein functions; reducing the production, stability and processing of viral proteins; and stimulating autophagosome formation/viral protein degradation, AR-12 acts as a broad-specificity anti-viral drug in vitro and in vivo. We argue future patient studies with AR-12 are warranted. J. Cell. Physiol. 231: 2286-2302, 2016. (c) 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Multi-kinase inhibitors can associate with heat shock proteins through their NH2-termini by which they suppress chaperone function.[Pubmed:26887051]
Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 15;7(11):12975-96.
We performed proteomic studies using the GRP78 chaperone-inhibitor drug AR-12 (OSU-03012) as bait. Multiple additional chaperone and chaperone-associated proteins were shown to interact with AR-12, including: GRP75, HSP75, BAG2; HSP27; ULK-1; and thioredoxin. AR-12 down-regulated in situ immuno-fluorescence detection of ATP binding chaperones using antibodies directed against the NH2-termini of the proteins but only weakly reduced detection using antibodies directed against the central and COOH portions of the proteins. Traditional SDS-PAGE and western blotting assessment methods did not exhibit any alterations in chaperone detection. AR-12 altered the sub-cellular distribution of chaperone proteins, abolishing their punctate speckled patterning concomitant with changes in protein co-localization. AR-12 inhibited chaperone ATPase activity, which was enhanced by sildenafil; inhibited chaperone - chaperone and chaperone - client interactions; and docked in silico with the ATPase domains of HSP90 and of HSP70. AR-12 combined with sildenafil in a GRP78 plus HSP27 -dependent fashion to profoundly activate an eIF2alpha/ATF4/CHOP/Beclin1 pathway in parallel with inactivating mTOR and increasing ATG13 phosphorylation, collectively resulting in formation of punctate toxic autophagosomes. Over-expression of [GRP78 and HSP27] prevented: AR-12 -induced activation of ER stress signaling and maintained mTOR activity; AR-12 -mediated down-regulation of thioredoxin, MCL-1 and c-FLIP-s; and preserved tumor cell viability. Thus the inhibition of chaperone protein functions by AR-12 and by multi-kinase inhibitors very likely explains why these agents have anti-tumor effects in multiple genetically diverse tumor cell types.
Small-molecule inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling inhibit Wnt/beta-catenin pathway cross-talk and suppress medulloblastoma growth.[Pubmed:20028853]
Cancer Res. 2010 Jan 1;70(1):266-76.
Activation of the beta-catenin and receptor kinase pathways occurs often in medulloblastoma, the most common pediatric malignant brain tumor. In this study, we show that molecular cross-talk between the beta-catenin and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathways is crucial to sustain medulloblastoma pathophysiology. Constitutive activation of phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1), Akt, and phosphorylation of [corrected] glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK-3beta) was detected by immunohistochemistry in all primary medulloblastomas examined (n = 41). Small-molecule inhibitors targeting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway affected beta-catenin signaling by activation [corrected] of GSK-3beta, [corrected] resulting in cytoplasmic retention of beta-catenin and reduced expression of its target genes cyclin D1 and c-Myc. The PDK1 inhibitor OSU03012 induced mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis of medulloblastoma cells and enhanced the cytotoxic effects of chemotherapeutic drugs in a synergistic or additive manner. In vivo, OSU03012 inhibited the growth of established medulloblastoma xenograft tumors in a dose-dependent manner and augmented the antitumor effects of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor CCI-779. These findings demonstrate the importance of cross-talk between the PI3K/Akt and beta-catenin pathways in medulloblastoma and rationalize the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway as a therapeutic target in treatment of this disease.
OSU-03012 promotes caspase-independent but PERK-, cathepsin B-, BID-, and AIF-dependent killing of transformed cells.[Pubmed:16622074]
Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Aug;70(2):589-603.
We determined one mechanism by which the putative phosphoinositide-dependent kinase (PDK)-1 inhibitor 2-amino-N-{4-[5-(2-phenanthrenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]-phenyl}ace tamide (OSU-03012) killed primary human glioma and other transformed cells. OSU-03012 caused a dose-dependent induction of cell death that was not altered by p53 mutation, expression of ERBB1 vIII, or loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 function. OSU-03012 promoted cell killing to a greater extent in glioma cells than in nontransformed astrocytes. OSU-03012 and ionizing radiation caused an additive, caspase-independent elevation in cell killing in 96-h viability assays and true radiosensitization in colony formation assays. In a cell type-specific manner, combined exposure to OSU-03012 with a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT inhibitors, or parallel molecular interventions resulted in a greater than additive induction of cell killing that was independent of AKT activity and caspase function. OSU-03012 lethality as a single agent or when combined with signaling modulators was not modified in cells lacking expression of BIM or of BAX/BAK. OSU-03012 promoted the release of cathepsin B from the lysosomal compartment and release of AIF from mitochondria. Loss of BH3-interacting domain (BID) function, overexpression of BCL(XL), and inhibition of cathepsin B function suppressed cell killing and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) release from mitochondria. In protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase-/- cells, the lethality of OSU-03012 was attenuated which correlated with reduced cleavage of BID and with suppression of cathepsin B and AIF release into the cytosol. Our data demonstrate that OSU-03012 promotes glioma cell killing that is dependent on endoplasmic reticulum stress, lysosomal dysfunction, and BID-dependent release of AIF from mitochondria, and whose lethality is enhanced by irradiation or by inhibition of protective signaling pathways.
From the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib to a novel class of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 inhibitors.[Pubmed:15205346]
Cancer Res. 2004 Jun 15;64(12):4309-18.
The blockade of Akt activation through the inhibition of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK-1) represents a major signaling mechanism whereby celecoxib mediates apoptosis. Celecoxib, however, is a weak PDK-1 inhibitor (IC(50), 48 microM), requiring at least 30 microM to exhibit discernable effects on the growth of tumor cells in vitro. Here, we report the structure-based optimization of celecoxib to develop PDK-1 inhibitors with greater potency in enzyme inhibition and growth inhibition. Kinetics of PDK-1 inhibition by celecoxib with respect to ATP suggest that celecoxib derivatives inhibit PDK-1 by competing with ATP for binding, a mechanism reminiscent to that of many kinase inhibitors. Structure-activity analysis together with molecular modeling was used to generate compounds that were tested for their potency in inhibiting PDK-1 kinase activity and in inducing apoptosis in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Docking of potent compounds into the ATP-binding site of PDK-1 was performed for lead optimization, leading to two compounds, OSU-03012 and OSU-03013, with IC(50) values in PDK-1 inhibition and apoptosis induction in the low microM range. Exposure of PC-3 cells to these agents led to Akt dephosphorylation and inhibition of p70 S6 kinase activity. Moreover, overexpression of constitutively active forms of PDK-1 and Akt partially protected OSU-03012-induced apoptosis. Screening in a panel of 60 cell lines and more extensive testing in PC-3 cells indicated that the mean concentration for total growth inhibition was approximately 3 microM for both agents. Considering the conserved role of PDK-1/Akt signaling in promoting tumorigenesis, these celecoxib analogs are of translational relevance for cancer prevention and therapy.


