R547CDK1/2/4 inhibitor,ATP-competitive CAS# 741713-40-6 |
- LY2835219
Catalog No.:BCC1113
CAS No.:1231930-82-7
- Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202)
Catalog No.:BCC1105
CAS No.:186692-46-6
- Nu 6027
Catalog No.:BCC1154
CAS No.:220036-08-8
- SNS-032 (BMS-387032)
Catalog No.:BCC1152
CAS No.:345627-80-7
- AT7519 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1376
CAS No.:902135-91-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 741713-40-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6918852 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H21F2N5O4S | M.Wt | 441.45 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (113.26 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
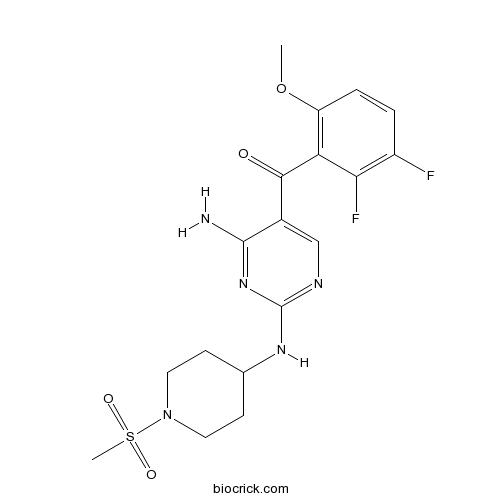
| Chemical Name | [4-amino-2-[(1-methylsulfonylpiperidin-4-yl)amino]pyrimidin-5-yl]-(2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C(=C(C=C1)F)F)C(=O)C2=CN=C(N=C2N)NC3CCN(CC3)S(=O)(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JRNJNYBQQYBCLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H21F2N5O4S/c1-29-13-4-3-12(19)15(20)14(13)16(26)11-9-22-18(24-17(11)21)23-10-5-7-25(8-6-10)30(2,27)28/h3-4,9-10H,5-8H2,1-2H3,(H3,21,22,23,24) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | R547 is a potent ATP-competitive inhibitor of CDK1/2/4 with Ki values of 2 nM/3 nM/1 nM, respectively. | ||||||
| Targets | CDK4/CyclinD1 | CDK1/CyclinB | CDK2/CyclinE | PKA | PKB | ||
| IC50 | 1 nM(Ki) | 2 nM(Ki) | 3 nM(Ki) | >5 μM(Ki) | >5 μM(Ki) | ||

R547 Dilution Calculator

R547 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2653 mL | 11.3263 mL | 22.6526 mL | 45.3052 mL | 56.6316 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4531 mL | 2.2653 mL | 4.5305 mL | 9.061 mL | 11.3263 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2265 mL | 1.1326 mL | 2.2653 mL | 4.5305 mL | 5.6632 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0453 mL | 0.2265 mL | 0.4531 mL | 0.9061 mL | 1.1326 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0227 mL | 0.1133 mL | 0.2265 mL | 0.4531 mL | 0.5663 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
R547 is a novel, selective inhibitor of cell cycle and transcriptional cyclin dependent kinases with a Ki of median 2 nM for CDK1/cyclin B, CDK2/cyclin E, and CDK4/cyclin D1((Ki=0.001,0.003,and 0.001 μM for CDK1,CDK2, and CDK4,respectively).[1]
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a family of protein kinases regulating the cell cycle, transcription, mRNA processing, and the differentiation of nerve cells which considered a potential anticancer target. CDK inhibitors such as Seliciclib are undergoing clinical trials. Although it was originally developed as a potential anti-cancer drug, in recent laboratory tests Seliciclib has also proven to induce apoptosis in neutrophil granulocytes, which mediate inflammation.[2].
R547 inhibited the proliferation of tumor cell lines and is active in all 19 cell lines tested irrespective of tissue of origin, multidrug resistance (MDR), p53, or retinoblastoma status. R547 possessing both 5-and 6-fluoro substitution culminated in an Inhibitor with low, single-digit nanomolar potency against the CDKs and excellent cellular potency (IC50=0.08 μM,HCT116 cell line). R547 administered orally at dose of 40 mg/kg daily in colon, lung, breast, prostate, and melanoma human tumor xenograft models shows significant TGI (79-99%). R547 is equally efficacious (TGI, 61-95%) when dosed with 40 mg/kg i.v. once weekly. These doses of R547 are not toxic and did not result in body weight loss. R547 does not show signs of overt toxicity during the course of the 3-week study and any gross pathology at necropsies done at the end of the studies. [3]R547 inhibits tumor growth up to 95% in the HCT116 human colorectal tumor xenograft model in nude mice . R547 causes significant TGI in all of the models tested when dosed orally and i.v. at or below the maximum tolerated dose. R547 inhibits phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein in tumors at the efficacious exposures in tumor xenograft models, providing a pharmacodynamic biomarker for clinical use. R547 reported here suggests that this is a promising molecule for evaluation in the treatment of solid tumors. [4]
References:
1. Davis MI1, Hunt JP, Herrgard S, Ciceri P, Wodicka LM, Pallares G, Hocker M, Treiber DK, Zarrinkar PP. “Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity.” Nat Biotechnol. 2011, 29(11):1046-51.
2. Rossi, Adriano G. “Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors enhance the resolution of inflammation by promoting inflammatory cell apoptosis.” 2006. Nature Medicine 12 .
3. Rodriguez A , et al. Mol Cancer Ther, 2006, 5(11), 2644-2658.
4. Chu XJ, et al. J Med Chem, 2006, 49(22), 6549-6560.
- 2,3-Dehydrokievitone
Catalog No.:BCN4294
CAS No.:74161-25-4
- Pimobendan
Catalog No.:BCC2294
CAS No.:74150-27-9
- Bisdethiobis(methylthio)gliotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN7351
CAS No.:74149-38-5
- DSC
Catalog No.:BCC2800
CAS No.:74124-79-1
- Norjuziphine
Catalog No.:BCN3367
CAS No.:74119-87-2
- SKF 83822 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7252
CAS No.:74115-10-9
- Ketorolac tromethamine salt
Catalog No.:BCC4431
CAS No.:74103-07-4
- Ketorolac
Catalog No.:BCC5190
CAS No.:74103-06-3
- ACV 1
Catalog No.:BCC5989
CAS No.:740980-24-9
- Cudratricusxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN7649
CAS No.:740810-42-8
- Macamide B
Catalog No.:BCN1366
CAS No.:74058-71-2
- Ketanserin
Catalog No.:BCC5050
CAS No.:74050-98-9
- Haginin A
Catalog No.:BCN6861
CAS No.:74174-29-1
- Cyclokievitone
Catalog No.:BCC8159
CAS No.:74175-82-9
- Doxazosin
Catalog No.:BCC4218
CAS No.:74191-85-8
- Uplandicine
Catalog No.:BCN2055
CAS No.:74202-10-1
- 3-Bromo-7-nitroindazole
Catalog No.:BCC6770
CAS No.:74209-34-0
- Vintafolide
Catalog No.:BCC5265
CAS No.:742092-03-1
- Carbenoxolone disodium
Catalog No.:BCC3745
CAS No.:7421-40-1
- OSU-03012 (AR-12)
Catalog No.:BCC1255
CAS No.:742112-33-0
- Doronenine
Catalog No.:BCN2066
CAS No.:74217-57-5
- Baogongteng A
Catalog No.:BCN1874
CAS No.:74239-84-2
- p-Chlorophenylalanine
Catalog No.:BCC5689
CAS No.:7424-00-2
- 7-Acetylintermedine
Catalog No.:BCN1998
CAS No.:74243-01-9
In vitro and in vivo activity of R547: a potent and selective cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor currently in phase I clinical trials.[Pubmed:17121911]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Nov;5(11):2644-58.
The cyclin-dependent protein kinases are key regulators of cell cycle progression. Aberrant expression or altered activity of distinct cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) complexes results in escape of cells from cell cycle control, leading to unrestricted cell proliferation. CDK inhibitors have the potential to induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells, and identifying small-molecule CDK inhibitors has been a major focus in cancer research. Several CDK inhibitors are entering the clinic, the most recent being selective CDK2 and CDK4 inhibitors. We have identified a diaminopyrimidine compound, R547, which is a potent and selective ATP-competitive CDK inhibitor. In cell-free assays, R547 effectively inhibited CDK1/cyclin B, CDK2/cyclin E, and CDK4/cyclin D1 (K(i) = 1-3 nmol/L) and was inactive (K(i) > 5,000 nmol/L) against a panel of >120 unrelated kinases. In vitro, R547 effectively inhibited the proliferation of tumor cell lines independent of multidrug resistant status, histologic type, retinoblastoma protein, or p53 status, with IC(50)s R547 reduced phosphorylation of the cellular retinoblastoma protein at specific CDK phosphorylation sites at the same concentrations that induced cell cycle arrest, suggesting a potential pharmacodynamic marker for clinical use. In vivo, R547 showed antitumor activity in all of the models tested to date, including six human tumor xenografts and an orthotopic syngeneic rat model. R547 was efficacious with daily oral dosing as well as with once weekly i.v. dosing in established human tumor models and at the targeted efficacious exposures inhibited phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein in the tumors. The selective kinase inhibition profile and the preclinical antitumor activity of R547 suggest that it may be promising for development for use in the treatment of solid tumors. R547 is currently being evaluated in phase I clinical trials.
Discovery of [4-Amino-2-(1-methanesulfonylpiperidin-4-ylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6- methoxyphenyl)methanone (R547), a potent and selective cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with significant in vivo antitumor activity.[Pubmed:17064073]
J Med Chem. 2006 Nov 2;49(22):6549-60.
The cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and their cyclin partners are key regulators of the cell cycle. Since deregulation of CDKs is found with high frequency in many human cancer cells, pharmacological inhibition of CDKs with small molecules has the potential to provide an effective strategy for the treatment of cancer. The 2,4-diamino-5-ketopyrimidines 6 reported here represent a novel class of potent and ATP-competitive inhibitors that selectively target the cyclin-dependent kinase family. This diaminopyrimidine core with a substituted 4-piperidine moiety on the C2-amino position and 2-methoxybenzoyl at the C5 position has been identified as the critical structure responsible for the CDK inhibitory activity. Further optimization has led to a good number of analogues that show potent inhibitory activities against CDK1, CDK2, and CDK4 but are inactive against a large panel of serine/threonine and tyrosine kinases (K(i) > 10 microM). As one of these representative analogues, compound 39 (R547) has the best CDK inhibitory activities (K(i) = 0.001, 0.003, and 0.001 microM for CDK1, CDK2, and CDK4, respectively) and excellent in vitro cellular potency, inhibiting the growth of various human tumor cell lines including an HCT116 cell line (IC(50) = 0.08 microM). An X-ray crystal structure of 39 bound to CDK2 has been determined in this study, revealing a binding mode that is consistent with our SAR. Compound 39 demonstrates significant in vivo efficacy in the HCT116 human colorectal tumor xenograft model in nude mice with up to 95% tumor growth inhibition. On the basis of its superior overall profile, 39 was chosen for further evaluation and has progressed into Phase I clinical trial for the treatment of cancer.


