Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202)CDK inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 186692-46-6 |
- BS-181
Catalog No.:BCC1439
CAS No.:1092443-52-1
- (R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7726
CAS No.:1241675-76-2
- Flavopiridol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3925
CAS No.:131740-09-5
- SNS-032 (BMS-387032)
Catalog No.:BCC1152
CAS No.:345627-80-7
- Dinaciclib (SCH727965)
Catalog No.:BCC3765
CAS No.:779353-01-4
- PHA-848125
Catalog No.:BCC3839
CAS No.:802539-81-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 186692-46-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 160355 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H26N6O | M.Wt | 354.45 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CYC202; R-roscovitine; Seliciclib | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (282.13 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
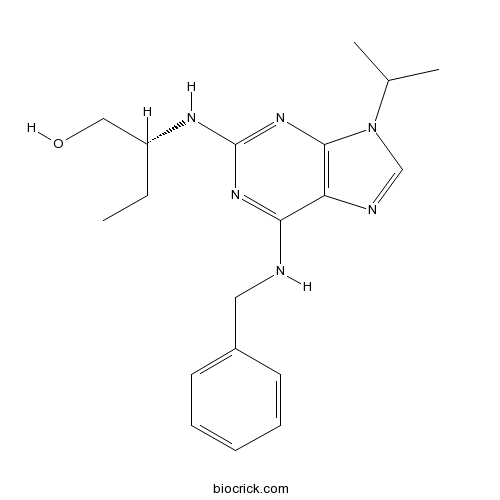
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-[[6-(benzylamino)-9-propan-2-ylpurin-2-yl]amino]butan-1-ol | ||
| SMILES | CCC(CO)NC1=NC2=C(C(=N1)NCC3=CC=CC=C3)N=CN2C(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BTIHMVBBUGXLCJ-OAHLLOKOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H26N6O/c1-4-15(11-26)22-19-23-17(20-10-14-8-6-5-7-9-14)16-18(24-19)25(12-21-16)13(2)3/h5-9,12-13,15,26H,4,10-11H2,1-3H3,(H2,20,22,23,24)/t15-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, selective inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases (cdk). Inhibits cdc2/cyclin B (IC50 = 650 nM), cdk2/cyclin A (IC50 = 700 nM), cdk2/cyclin E (IC50 = 700 nM), cdk5 / p35 (IC50 = 160 nM) and is selective over cdk4/cyclin D1 and cdk6/cyclin D3 (IC50 > 100 μM). Also selective over a wide range of related kinases including ERK1 and ERK2. Arrests L1210 cells in G1 phase. Inhibits phosphorylation of vimentin in vivo. Antimitotic. |

Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202) Dilution Calculator

Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8213 mL | 14.1064 mL | 28.2127 mL | 56.4254 mL | 70.5318 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5643 mL | 2.8213 mL | 5.6425 mL | 11.2851 mL | 14.1064 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2821 mL | 1.4106 mL | 2.8213 mL | 5.6425 mL | 7.0532 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0564 mL | 0.2821 mL | 0.5643 mL | 1.1285 mL | 1.4106 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0282 mL | 0.1411 mL | 0.2821 mL | 0.5643 mL | 0.7053 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Roscovitine, also known as seliciclib or CYC202, is a selective cyclin-dependent kinases (cdk), which are essential cell cycle regulators frequently involved in the deregulation of human tumors, inhibitor that potently inhibits cdc2 (cdc2/cyclin B), cdk2 (cdk2/cyclin A and cdk2/cyclin E) and cdk5 (cdk5/p35) with half maximal inhibition concentration IC50 of 0.65 μM, 0.7 μM, 0.7 μM and 0.16 μM respectively [1].
Roscovitine has been found to inhibit cellular prophase/metaphase transition at micromolar concentrations, where it inhibits progesterone-induced oocyte maturation of Xenopus oocytes and arrests starfish oocytes and sea urchin embryos in late prophase [1].
Additionally, roscovitine is capable of inhibiting extracelluar regulated kinases, erk1 and erk2, with IC50 of 34 μM and 14 μM respectively [1].
References:
[1] Meijer L, Borgne A, Mulner O, Chong JP, Blow JJ, Inagaki N, Inagaki M, Delcros JG, Moulinoux JP. Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5. Eur J Biochem. 1997 Jan 15;243(1-2):527-36.
- 2-NBDG
Catalog No.:BCC6530
CAS No.:186689-07-6
- 4-Methylcinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5034
CAS No.:1866-39-3
- Allyl cinnamate
Catalog No.:BCC8812
CAS No.:1866-31-5
- 1,2-Bis(3-indenyl)ethane
Catalog No.:BCC8413
CAS No.:18657-57-3
- LY 344864
Catalog No.:BCC1716
CAS No.:186544-26-3
- Zibotentan (ZD4054)
Catalog No.:BCC2524
CAS No.:186497-07-4
- Alisol B
Catalog No.:BCN3364
CAS No.:18649-93-9
- Actein
Catalog No.:BCN1159
CAS No.:18642-44-9
- Psoralidin
Catalog No.:BCN5414
CAS No.:18642-23-4
- CP 316819
Catalog No.:BCC6039
CAS No.:186392-43-8
- CP-91149
Catalog No.:BCC3757
CAS No.:186392-40-5
- enantio-7(11)-Eudesmen-4-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1158
CAS No.:186374-63-0
- H-D-Tyr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3137
CAS No.:186698-58-8
- Ketamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5982
CAS No.:1867-66-9
- N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
Catalog No.:BCC6495
CAS No.:1867-73-8
- Alisol A 24-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN2344
CAS No.:18674-16-3
- Ginsenoside Rg5
Catalog No.:BCN3551
CAS No.:186763-78-0
- ML 10302 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7695
CAS No.:186826-17-5
- Moxifloxacin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2507
CAS No.:186826-86-8
- 2B-(SP)
Catalog No.:BCC5817
CAS No.:186901-17-7
- Pafuramidine
Catalog No.:BCC1832
CAS No.:186953-56-0
- Sinapine
Catalog No.:BCN1815
CAS No.:18696-26-9
- N,N'-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)oxamide
Catalog No.:BCC9061
CAS No.:1871-89-2
- NS309
Catalog No.:BCC1809
CAS No.:18711-16-5
Effect of seliciclib (CYC202, R-roscovitine) on lymphocyte alloreactivity and acute kidney allograft rejection in rat.[Pubmed:18497689]
Transplantation. 2008 May 27;85(10):1476-82.
BACKGROUND: T cell stimulation by alloantigens is followed by cell cycle progression, an event that is critically dependent on cyclin-dependent kinases. METHODS: We conducted a study to evaluate whether the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor seliciclib affected rat lymph node cells (LNc) activation and proliferation induced by either concanavalin A or allogeneic splenocytes in vitro and studied the mechanisms underlying the suppressive effect. We also investigated the immunosuppressive properties of seliciclib in vivo. RESULTS: Seliciclib completely inhibited in vitro proliferation of LNc and CD8 T cells, in response to either concanavalin A or allogeneic splenocytes. The percentage of activated LNc was lower in mixed leukocyte reactions (MLR) added with seliciclib than in MLR added with vehicle. The percentages of viable and apoptotic cells at the end of MLR with seliciclib were comparable to those of MLR with vehicle. LNc pre-exposed in MLR to seliciclib did not respond to further stimulation with alloantigens, and neither IL-2 nor IL-15 restored proliferation. These data indicate that the inhibitory effect of seliciclib on T cell alloreactivity is not because of cytotoxic effect but is associated with induction of profound T cell anergy. LNc harvested at the end of the primary MLR with seliciclib did not suppress the proliferation of syngeneic LNc cells toward allogeneic splenocytes, thus excluding that seliciclib induced the formation of regulatory cells. Finally, seliciclib partially prolonged grafted animal survival in a rat model of fully major histocompatibility complex-mismatched kidney transplantation. CONCLUSIONS: Altogether these results document that seliciclib regulates lymphocyte reactivity and may exert an immunosuppressive effect in vivo in the setting of transplantation.
Seliciclib (CYC202, R-roscovitine) enhances the antitumor effect of doxorubicin in vivo in a breast cancer xenograft model.[Pubmed:19003963]
Int J Cancer. 2009 Jan 15;124(2):465-72.
We sought to determine whether seliciclib (CYC202, R-roscovitine) could increase the antitumor effects of doxorubicin, with no increase in toxicity, in an MCF7 breast cancer xenograft model. The efficacy of seliciclib combined with doxorubicin was compared with single agent doxorubicin or seliciclib administered to MCF7 cells and to nude mice bearing established MCF7 xenografts. Post-treatment cells and tumors were examined by cell cycle analysis, immunohistochemistry and real-time PCR. Seliciclib significantly enhanced the antitumor effect of doxorubicin without additional murine toxicity. MIB1 (ki67) immunohistochemistry demonstrated reduced proliferation with treatment. The levels of p21 and p27 increased after treatment with doxorubicin or seliciclib alone or in combination, compared to untreated controls. However, no changes in p53 protein (DO1, CM1), survivin or p53 phosphorylation (SER15) were observed in treated tumors compared with controls. In conclusion, the CDK inhibitor seliciclib (R-roscovitine) enhances the antitumor effect of doxorubicin in MCF7 tumors without increased toxicity with a mechanism that involves cell cycle arrest rather than apoptosis.
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor seliciclib (R-roscovitine; CYC202) decreases the expression of mitotic control genes and prevents entry into mitosis.[Pubmed:18075315]
Cell Cycle. 2007 Dec 15;6(24):3114-31.
The cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor seliciclib (R-roscovitine, CYC202) shows promising antitumor activity in preclinical models and is currently undergoing phase II clinical trials. Inhibition of the CDKs by seliciclib could contribute to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis seen with the drug. However, it is common for drugs to exert multiple effects on gene expression and biochemical pathways. To further our understanding of the molecular pharmacology of seliciclib, we employed cDNA microarrays to determine changes in gene expression profiles induced by the drug in HT29 human colon cancer cells. Concentrations of seliciclib were used that inhibited RB phosphorylation and cell proliferation. An increase in the mRNA expression for CJUN and EGR1 was confirmed by Western blotting, consistent with activation of the ERK1/2 MAPK pathway by seliciclib. Transcripts of key genes required for the progression through mitosis showed markedly reduced expression, including Aurora-A/B (AURK-A/B), Polo-like kinase (PLK), cyclin B2 (CCNB2), WEE1 and CDC25C. Reduced expression of these mitotic genes was also seen at the protein level. siRNA-mediated depletion of Aurora-A protein led to an arrest of cells in the G(2)/M phase, consistent with the effects of seliciclib treatment. Inhibition of mitotic entry following seliciclib treatment was indicated by a reduction of histone H3 phosphorylation, which is catalyzed by Aurora-B, and by decreased expression of mitotic markers, including phospho-protein phosphatase 1 alpha. The results indicate a potential mechanism through which seliciclib prevents entry into mitosis. Gene expression profiling has generated hypotheses that led to an increase in our knowledge of the cellular effects of seliciclib and could provide potential pharmacodynamic or response biomarkers for use in animal models and clinical trials.
Seliciclib (CYC202; r-roscovitine) in combination with cytotoxic agents in human uterine sarcoma cell lines.[Pubmed:17352243]
Anticancer Res. 2007 Jan-Feb;27(1A):273-8.
BACKGROUND: Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) has recently emerged as an interesting approach to treat human malignancies. This was explored in human leiomyosarcoma (LMS) lines, which represent a tumour associated with poor survival, chemo-unresponsiveness and deregulation of cell cycle components. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Using isobologram analysis with MTT chemosensitivity testing, the effects of the CDK inhibitor seliciclib (CYC202, R-roscovitine) when used alone or in combination with paclitaxel was studied in uterine cancer cell lines. Apoptotic endpoints were also examined via Annexin V assay using flow cytometry and Western blotting. RESULTS: Overall seliciclib combined with paclitaxel proved synergistic for all cell lines. This was concomitant with an enhanced apoptotic effect and downregulation of the LAP survivin. CONCLUSION: Our data support the use of seliciclib as part of combination therapy for uterine cancer.
Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by purine analogues: crystal structure of human cdk2 complexed with roscovitine.[Pubmed:9030780]
Eur J Biochem. 1997 Jan 15;243(1-2):518-26.
Cyclin-dependent kinases (cdk) control the cell division cycle (cdc). These kinases and their regulators are frequently deregulated in human tumours. A potent inhibitor of cdks, roscovitine [2-(1-ethyl-2-hydroxyethylamino)-6-benzylamino-9-isopropylpurin e], was identified by screening a series of C2,N6,N9-substituted adenines on purified cdc2/cyclin B. Roscovitine displays high efficiency and high selectivity (Meijer, L., Borgne, A., Mulner, O., Chong, J. P. J., Blow, J. J., Inagaki, N., Inagaki, M., Delcros, J.-G. & Moulinoux, J.-P. (1997) Eur. J. Biochem. 243, 527-536). It behaves as a competitive inhibitor for ATP binding to cdc2. We determined the crystal structure of a complex between cdk2 and roscovitine at 0.24-nm (2.4 A) resolution and refined to an Rfactor of 0.18. The purine portion of the inhibitor binds to the adenine binding pocket of cdk2. The position of the benzyl ring group of the inhibitor enables the inhibitor to make contacts with the enzyme not observed in the ATP-complex structure. Analysis of the position of this benzyl ring explains the specificity of roscovitine in inhibiting cdk2. The structure also reveals that the (R)-stereoisomer of roscovitine is bound to cdk2. The (R)-isomer is about twice as potent in inhibiting cdc2/cyclin B than the (S)-isomer. Results from structure/activity studies and from analysis of the cdk2/roscovitine complex crystal structure should allow the design of even more potent cdk inhibitors.
Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5.[Pubmed:9030781]
Eur J Biochem. 1997 Jan 15;243(1-2):527-36.
Cyclin-dependent kinases (cdk) play an essential role in the intracellular control of the cell division cycle (cdc). These kinases and their regulators are frequently deregulated in human tumours. Enzymatic screening has recently led to the discovery of specific inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases, such as butyrolactone I, flavopiridol and the purine olomoucine. Among a series of C2, N6, N9-substituted adenines tested on purified cdc2/cyclin B, 2-(1-ethyl-2-hydroxyethylamino)-6-benzylamino-9-isopropylpurine (roscovitine) displays high efficiency and high selectivity towards some cyclin-dependent kinases. The kinase specificity of roscovitine was investigated with 25 highly purified kinases (including protein kinase A, G and C isoforms, myosin light-chain kinase, casein kinase 2, insulin receptor tyrosine kinase, c-src, v-abl). Most kinases are not significantly inhibited by roscovitine. cdc2/cyclin B, cdk2/cyclin A, cdk2/cyclin E and cdk5/p35 only are substantially inhibited (IC50 values of 0.65, 0.7, 0.7 and 0.2 microM, respectively). cdk4/cyclin D1 and cdk6/cyclin D2 are very poorly inhibited by roscovitine (IC50 > 100 microM). Extracellular regulated kinases erk1 and erk2 are inhibited with an IC50 of 34 microM and 14 microM, respectively. Roscovitine reversibly arrests starfish oocytes and sea urchin embryos in late prophase. Roscovitine inhibits in vitro M-phase-promoting factor activity and in vitro DNA synthesis in Xenopus egg extracts. It blocks progesterone-induced oocyte maturation of Xenopus oocytes and in vivo phosphorylation of the elongation factor eEF-1. Roscovitine inhibits the proliferation of mammalian cell lines with an average IC50 of 16 microM. In the presence of roscovitine L1210 cells arrest in G1 and accumulate in G2. In vivo phosphorylation of vimentin on Ser55 by cdc2/cyclin B is inhibited by roscovitine. Through its unique selectivity for some cyclin-dependent kinases, roscovitine provides a useful antimitotic reagent for cell cycle studies and may prove interesting to control cells with deregulated cdc2, cdk2 or cdk5 kinase activities.
Chemical inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases.[Pubmed:15157522]
Trends Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;6(10):393-7.
Transient activation o f cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) is responsible for transition through the successive phases of the cell-division cycle. Major changes in the expression and regulation of CDKs have been described in human tumours. Enzymatic screening is starting to uncover chemical inhibitors o f CDKs that arrest the cell cycle at various steps. This review summarizes our knowledge of the first generation inhibitors, their molecular mechanisms of action and their effects on the cell cycle and apoptosis, and discusses their potential as synchronizing agents, as ligands for affinity chromatography and as therapeutic agents.


