NS309Positive modulator of KCa2 and KCa3.1 channels CAS# 18711-16-5 |
- Dofetilide
Catalog No.:BCC3770
CAS No.:115256-11-6
- Repaglinide
Catalog No.:BCC2504
CAS No.:135062-02-1
- Dronedarone
Catalog No.:BCN2176
CAS No.:141626-36-0
- TRAM-34
Catalog No.:BCC1122
CAS No.:289905-88-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 18711-16-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11637204 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C8H4Cl2N2O2 | M.Wt | 231.04 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (432.83 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
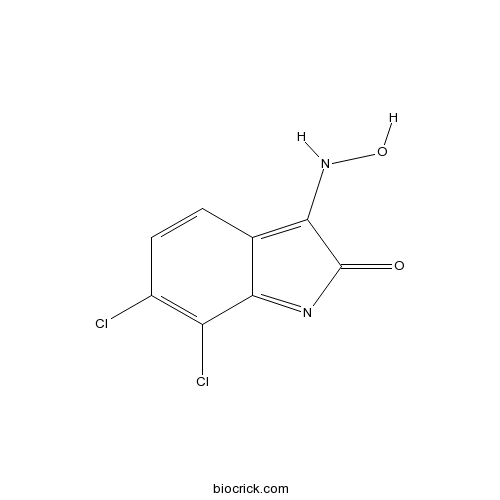
| Chemical Name | 6,7-dichloro-3-(hydroxyamino)indol-2-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C2=NC(=O)C(=C21)NO)Cl)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CVOUSAVHMDXCKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H4Cl2N2O2/c9-4-2-1-3-6(5(4)10)11-8(13)7(3)12-14/h1-2,14H,(H,11,12,13) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Positive modulator of small- and intermediate- conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels (KCa2 and KCa3.1 channels); increases Ca2+ sensitivity. Displays no activity at BK channels. |

NS309 Dilution Calculator

NS309 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3283 mL | 21.6413 mL | 43.2825 mL | 86.5651 mL | 108.2064 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8657 mL | 4.3283 mL | 8.6565 mL | 17.313 mL | 21.6413 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4328 mL | 2.1641 mL | 4.3283 mL | 8.6565 mL | 10.8206 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0866 mL | 0.4328 mL | 0.8657 mL | 1.7313 mL | 2.1641 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0433 mL | 0.2164 mL | 0.4328 mL | 0.8657 mL | 1.0821 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
NS309 is a Ca2+-activated IK/SK potassium channel activator.
- N,N'-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)oxamide
Catalog No.:BCC9061
CAS No.:1871-89-2
- Sinapine
Catalog No.:BCN1815
CAS No.:18696-26-9
- Pafuramidine
Catalog No.:BCC1832
CAS No.:186953-56-0
- 2B-(SP)
Catalog No.:BCC5817
CAS No.:186901-17-7
- Moxifloxacin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2507
CAS No.:186826-86-8
- ML 10302 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7695
CAS No.:186826-17-5
- Ginsenoside Rg5
Catalog No.:BCN3551
CAS No.:186763-78-0
- Alisol A 24-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN2344
CAS No.:18674-16-3
- N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
Catalog No.:BCC6495
CAS No.:1867-73-8
- Ketamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5982
CAS No.:1867-66-9
- H-D-Tyr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3137
CAS No.:186698-58-8
- Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202)
Catalog No.:BCC1105
CAS No.:186692-46-6
- Clauszoline M
Catalog No.:BCN4683
CAS No.:187110-72-1
- Luliconazole
Catalog No.:BCC1711
CAS No.:187164-19-8
- Cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3114
CAS No.:18719-76-1
- Oseltamivir acid
Catalog No.:BCC1826
CAS No.:187227-45-8
- PA-824
Catalog No.:BCC1106
CAS No.:187235-37-6
- Kimcuongin
Catalog No.:BCN7472
CAS No.:1872403-23-0
- Z-VAD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1126
CAS No.:187389-52-2
- Boc-D-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1128
CAS No.:187389-53-3,634911-80-1
- ER 50891
Catalog No.:BCC7783
CAS No.:187400-85-7
- Methylisopelletierine
Catalog No.:BCN1160
CAS No.:18747-42-7
- Sitoindoside I
Catalog No.:BCN1161
CAS No.:18749-71-8
- N-Aminophthalimide
Catalog No.:BCC9085
CAS No.:1875-48-5
IKCa agonist (NS309)-elicited all-or-none dehydration response of human red blood cells is cell-age dependent.[Pubmed:21937109]
Cell Calcium. 2011 Nov;50(5):444-8.
Elevated [Ca(2+)](i) in human red blood cells (RBCs) activates IK1 K(+) channels leading to cell dehydration. NS309, a powerful IK1 agonist, has been shown to activate IK1 channels even at sub-physiological [Ca(2+)](i) levels. An intriguing feature of this response is its all-or-none nature, with responsive cells dehydrating fully and refractory cells retaining normal volume. We investigated the mechanism of this response suspecting cell-age involvement. We expected the younger cells, with the more vigorous plasma membrane Ca(2+) pumps (PMCA), to be the refractory cells because of their lower [Ca(2+)](i). Osmotic fragility measurements and density separation through phthalate oil were used to monitor red cell dehydration. The fraction of glycosilated haemoglobin (Hb A1c) was used to estimate the mean age of density fractionated cells. The results showed that inhibition of the PMCA by vanadate abolished the all-or-none response, that the mean age of the responsive cells was young, contrary to expectations, and that pump inhibition subsequent to an all-or-none response caused the refractory cells to dehydrate fully, suggesting that the all-or-none response resulted from a reduced efficiency of NS309 to increase the Ca(2+) sensitivity of IK1 channels in aged RBCs.
NS309 decreases rat detrusor smooth muscle membrane potential and phasic contractions by activating SK3 channels.[Pubmed:23145946]
Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;168(7):1611-25.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Overactive bladder (OAB) is often associated with abnormally increased detrusor smooth muscle (DSM) contractions. We used NS309, a selective and potent opener of the small or intermediate conductance Ca(2+) -activated K(+) (SK or IK, respectively) channels, to evaluate how SK/IK channel activation modulates DSM function. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: We employed single-cell RT-PCR, immunocytochemistry, whole cell patch-clamp in freshly isolated rat DSM cells and isometric tension recordings of isolated DSM strips to explore how the pharmacological activation of SK/IK channels with NS309 modulates DSM function. KEY RESULTS: We detected SK3 but not SK1, SK2 or IK channels expression at both mRNA and protein levels by RT-PCR and immunocytochemistry in DSM single cells. NS309 (10 muM) significantly increased the whole cell SK currents and hyperpolarized DSM cell resting membrane potential. The NS309 hyperpolarizing effect was blocked by apamin, a selective SK channel inhibitor. NS309 inhibited the spontaneous phasic contraction amplitude, force, frequency, duration and tone of isolated DSM strips in a concentration-dependent manner. The inhibitory effect of NS309 on spontaneous phasic contractions was blocked by apamin but not by TRAM-34, indicating no functional role of the IK channels in rat DSM. NS309 also significantly inhibited the pharmacologically and electrical field stimulation-induced DSM contractions. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: Our data reveal that SK3 channel is the main SK/IK subtype in rat DSM. Pharmacological activation of SK3 channels with NS309 decreases rat DSM cell excitability and contractility, suggesting that SK3 channels might be potential therapeutic targets to control OAB associated with detrusor overactivity.
Activation of endothelial and epithelial K(Ca) 2.3 calcium-activated potassium channels by NS309 relaxes human small pulmonary arteries and bronchioles.[Pubmed:22506557]
Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Sep;167(1):37-47.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Small (K(Ca) 2) and intermediate (K(Ca) 3.1) conductance calcium-activated potassium channels (K(Ca) ) may contribute to both epithelium- and endothelium-dependent relaxations, but this has not been established in human pulmonary arteries and bronchioles. Therefore, we investigated the expression of K(Ca) 2.3 and K(Ca) 3.1 channels, and hypothesized that activation of these channels would produce relaxation of human bronchioles and pulmonary arteries. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: Channel expression and functional studies were conducted in human isolated small pulmonary arteries and bronchioles. K(Ca) 2 and K(Ca) 3.1 currents were examined in human small airways epithelial (HSAEpi) cells by whole-cell patch clamp techniques. RESULTS: While K(Ca) 2.3 expression was similar, K(Ca) 3.1 protein was more highly expressed in pulmonary arteries than bronchioles. Immunoreactive K(Ca) 2.3 and K(Ca) 3.1 proteins were found in both endothelium and epithelium. K(Ca) currents were present in HSAEpi cells and sensitive to the K(Ca) 2.3 blocker UCL1684 and the K(Ca) 3.1 blocker TRAM-34. In pulmonary arteries contracted by U46619 and in bronchioles contracted by histamine, the K(Ca) 2.3/ K(Ca) 3.1 activator, NS309, induced concentration-dependent relaxations. NS309 was equally potent in relaxing pulmonary arteries, but less potent in bronchioles, than salbutamol. NS309 relaxations were blocked by the K(Ca) 2 channel blocker apamin, while the K(Ca) 3.1 channel blocker, charybdotoxin failed to reduce relaxation to NS309 (0.01-1 microM). CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: K(Ca) 2.3 and K(Ca) 3.1 channels are expressed in the endothelium of human pulmonary arteries and epithelium of bronchioles. K(Ca) 2.3 channels contributed to endo- and epithelium-dependent relaxations suggesting that these channels are potential targets for treatment of pulmonary hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Compromised endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization-mediated dilations can be rescued by NS309 in obese Zucker rats.[Pubmed:25047389]
Microcirculation. 2014 Nov;21(8):747-53.
OBJECTIVE: NO and a non-NO/prostacyclin EDH mechanism are major contributors of vascular tone and cerebral blood flow. However, the effect of metabolic syndrome on EDH-mediated responses in cerebral vessels remains unknown and may offer another avenue for therapeutic targeting. The purpose of this study was to investigate EDH-dependent responses in cerebral arteries during metabolic syndrome. METHODS: EDH-dependent dilations were assessed in MCAs isolated from nondiabetic obese and lean Zucker rats in the presence and absence of NS309, an activator of SKCa and IKCa channels. IKCa channel expression and activity were assessed by western blotting and pressure myography, respectively. RESULTS: EDH-mediated dilations were significantly attenuated in the obese compared to the lean Zucker rat MCA. Luminal delivery of 1 muM NS309 enhanced EDH-mediated responses in lean and obese Zucker cerebral vessels. Both dose-dependent dilations to luminal NS309 and IKCa protein expression in pooled cerebral arteries were comparable between the two groups. CONCLUSIONS: Our results suggest that pharmacological targeting of IKCa channels can rescue EDH-mediated dilations in obese Zucker rat MCAs. Compromised EDH-mediated dilations in obesity are not due to impaired IKCa channel expression or activity.
Endothelial Ca+-activated K+ channels in normal and impaired EDHF-dilator responses--relevance to cardiovascular pathologies and drug discovery.[Pubmed:19302590]
Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;157(4):509-26.
The arterial endothelium critically contributes to blood pressure control by releasing vasodilating autacoids such as nitric oxide, prostacyclin and a third factor or pathway termed 'endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor' (EDHF). The nature of EDHF and EDHF-signalling pathways is not fully understood yet. However, endothelial hyperpolarization mediated by the Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels (K(Ca)) has been suggested to play a critical role in initializing EDHF-dilator responses in conduit and resistance-sized arteries of many species including humans. Endothelial K(Ca) currents are mediated by the two K(Ca) subtypes, intermediate-conductance K(Ca) (KCa3.1) (also known as, a.k.a. IK(Ca)) and small-conductance K(Ca) type 3 (KCa2.3) (a.k.a. SK(Ca)). In this review, we summarize current knowledge about endothelial KCa3.1 and KCa2.3 channels, their molecular and pharmacological properties and their specific roles in endothelial function and, particularly, in the EDHF-dilator response. In addition we focus on recent experimental evidences derived from KCa3.1- and/or KCa2.3-deficient mice that exhibit severe defects in EDHF signalling and elevated blood pressures, thus highlighting the importance of the KCa3.1/KCa2.3-EDHF-dilator system for blood pressure control. Moreover, we outline differential and overlapping roles of KCa3.1 and KCa2.3 for EDHF signalling as well as for nitric oxide synthesis and discuss recent evidence for a heterogeneous (sub) cellular distribution of KCa3.1 (at endothelial projections towards the smooth muscle) and KCa2.3 (at inter-endothelial borders and caveolae), which may explain their distinct roles for endothelial function. Finally, we summarize the interrelations of altered KCa3.1/KCa2.3 and EDHF system impairments with cardiovascular disease states such as hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis and discuss the therapeutic potential of KCa3.1/KCa2.3 openers as novel types of blood pressure-lowering drugs.
Activation of human IK and SK Ca2+ -activated K+ channels by NS309 (6,7-dichloro-1H-indole-2,3-dione 3-oxime).[Pubmed:15471565]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Oct 11;1665(1-2):1-5.
We have identified and characterized the compound NS309 (6,7-dichloro-1H-indole-2,3-dione 3-oxime) as a potent activator of human Ca2+ -activated K+ channels of SK and IK types, whereas it is devoid of effect on BK type channels. IK- and SK-channels have previously been reported to be activated by the benzimidazolinone, 1-EBIO and more potently by its dichloronated-analogue, DC-EBIO. NS309 is at least 1000 times more potent than 1-EBIO and at least 30 times more potent than DC-EBIO when the compounds are compared on the same cell.


