Boc-D-FMKPan-caspase inhibitor CAS# 187389-53-3,634911-80-1 |
- Cisplatin
Catalog No.:BCN1552
CAS No.:14283-03-5
- Z-VAD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1126
CAS No.:187389-52-2
- Z-WEHD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1139
CAS No.:210345-00-9
- Z-LEHD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC5117
CAS No.:210345-04-3
- AZ 10417808
Catalog No.:BCC2356
CAS No.:331645-84-2
- Apoptosis Activator 2
Catalog No.:BCC2099
CAS No.:79183-19-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 187389-53-3,634911-80-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16760348 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C11H18FNO5 | M.Wt | 263.26 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | >11.65mg/mL in DMSO | ||
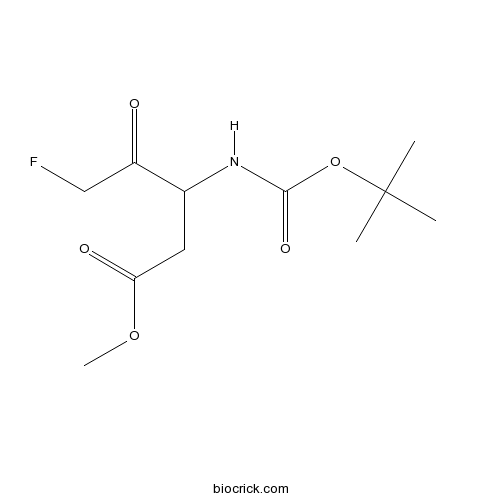
| Chemical Name | methyl 5-fluoro-3-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxycarbonylamino]-4-oxopentanoate | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)OC(=O)NC(CC(=O)OC)C(=O)CF | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MXOOUCRHWJYCAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H18FNO5/c1-11(2,3)18-10(16)13-7(8(14)6-12)5-9(15)17-4/h7H,5-6H2,1-4H3,(H,13,16) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | BOC-D-FMK is a Novel inhibitor of Caspase-3. | |||||
| Targets | Caspase | |||||

Boc-D-FMK Dilution Calculator

Boc-D-FMK Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7985 mL | 18.9926 mL | 37.9853 mL | 75.9705 mL | 94.9632 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7597 mL | 3.7985 mL | 7.5971 mL | 15.1941 mL | 18.9926 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3799 mL | 1.8993 mL | 3.7985 mL | 7.5971 mL | 9.4963 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.076 mL | 0.3799 mL | 0.7597 mL | 1.5194 mL | 1.8993 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.038 mL | 0.1899 mL | 0.3799 mL | 0.7597 mL | 0.9496 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
Boc-D-FMK, a caspase inhibitor, was evaluated for its effect on hepatocyte apoptosis and on survival rate after bile duct ligation in rats.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Boc-D-FMK is a cell-permeable broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor that fully inhibits the pro-apoptotic effect of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) with the half maximal inhibition concentration IC50 value of 39 μM [1].
Boc-D-FMK has been found to reduce the activation of nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB), suppress the phosphorylation of subunit nuclear factor kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor α (IkBα) and inhibits TNF-induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) [2].
Moreover, Boc-D-FMK has also effectively attenuated the hepatocyte apoptosis in bile duct-ligated rats potentially improving the survival rates [3].
References:
[1] Cowburn AS, White JF, Deighton J, Walmsley SR, Chilvers ER. z-VAD-fmk augmentation of TNF alpha-stimulated neutrophil apoptosis is compound specific and does not involve the generation of reactive oxygen species. Blood. 2005 Apr 1;105(7):2970-2. Epub 2004 Nov 30.
[2] Wu X, Guo R, Chen P, Wang Q, Cunningham PN. TNF induces caspase-dependent inflammation in renal endothelial cells through a Rho- and myosin light chain kinase-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):F316-26. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00089.2009. Epub 2009 May 6.
[3] Sheen-Chen SM, Hung KS, Eng HL. Effect of Boc-D-Fmk on hepatocyte apoptosis after bile duct ligation in rat and survival rate after endotoxin challenge. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Aug;23(8 Pt 1):1276-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05368.x. Epub 2008 Mar 27.
- Z-VAD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1126
CAS No.:187389-52-2
- Kimcuongin
Catalog No.:BCN7472
CAS No.:1872403-23-0
- PA-824
Catalog No.:BCC1106
CAS No.:187235-37-6
- Oseltamivir acid
Catalog No.:BCC1826
CAS No.:187227-45-8
- Cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3114
CAS No.:18719-76-1
- Luliconazole
Catalog No.:BCC1711
CAS No.:187164-19-8
- Clauszoline M
Catalog No.:BCN4683
CAS No.:187110-72-1
- NS309
Catalog No.:BCC1809
CAS No.:18711-16-5
- N,N'-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)oxamide
Catalog No.:BCC9061
CAS No.:1871-89-2
- Sinapine
Catalog No.:BCN1815
CAS No.:18696-26-9
- Pafuramidine
Catalog No.:BCC1832
CAS No.:186953-56-0
- 2B-(SP)
Catalog No.:BCC5817
CAS No.:186901-17-7
- ER 50891
Catalog No.:BCC7783
CAS No.:187400-85-7
- Methylisopelletierine
Catalog No.:BCN1160
CAS No.:18747-42-7
- Sitoindoside I
Catalog No.:BCN1161
CAS No.:18749-71-8
- N-Aminophthalimide
Catalog No.:BCC9085
CAS No.:1875-48-5
- MaxiPost
Catalog No.:BCC7984
CAS No.:187523-35-9
- Ethyl rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCC8976
CAS No.:187539-57-7
- Fmoc-D-Arg(Pbf)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3077
CAS No.:187618-60-6
- Tataramide B
Catalog No.:BCN3897
CAS No.:187655-56-7
- PNU 109291
Catalog No.:BCC7408
CAS No.:187665-60-7
- PNU 142633
Catalog No.:BCC7222
CAS No.:187665-65-2
- Fmoc-Asp-OFm
Catalog No.:BCC3467
CAS No.:187671-16-5
- BIO 1211
Catalog No.:BCC3945
CAS No.:187735-94-0
Effect of Boc-D-Fmk on hepatocyte apoptosis after bile duct ligation in rat and survival rate after endotoxin challenge.[Pubmed:18373562]
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Aug;23(8 Pt 1):1276-9.
BACKGROUND AND AIM: Retention and accumulation of toxic hydrophobic bile salts within hepatocytes may cause hepatocyte toxicity by inducing apoptosis. Apoptosis is a pathway of cell death orchestrated by a family of proteases called caspases. Boc-D-FMK is a cell-permeable irreversible inhibitor of caspase and recent data suggest that it might block the processing of many caspases. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the possible effect of Boc-D-FMK on hepatocyte apoptosis and on survival rate after bile duct ligation in the rat. METHODS: Male Sprague-Dawley rats, weighing 280-300 g were randomized to three groups of eight rats each. Group 1 (OBBOC-D) underwent common bile duct ligation and simultaneous treatment with Boc-D-FMK-fmk (dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide [DMSO]). Group 2 (OBZFA) underwent common bile duct ligation and simultaneous treatment with ZFA-fmk (dissolved in DMSO). Group 3 (SHAM) underwent sham operation and simultaneous treatment with the same amount of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO, n = 4) or the same amount of normal saline (n = 4). After 3 days, liver tissue was harvested for histopathological analysis and measurements of apoptosis. Survival rates were measured in a separate experiment in which animals underwent the same protocol. The animals received endotoxin (15 mg/kg) in the afternoon of the third postoperative day. Animals were observed for 48 h and the survival rates were recorded. RESULTS: When compared with sham operation, common bile duct ligation with ZFA-fmk (placebo) significantly increased hepatocyte apoptosis (P < 0.001). When compared with the OBZFA group, Boc-D-FMK significantly diminished the increased hepatocyte apoptosis in the OBBOC-D group (P < 0.001). There is no difference in hepatocyte apoptosis (P = 0.05) between OBBOC-D and SHAM groups. After endotoxin challenge, the 48 h survival rates were 100%, 87.5% and 62.5% for the SHAM, OBBOC-D and OBZFA groups, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: Boc-D-FMK-fmk effectively attenuated the hepatocyte apoptosis in bile duct-ligated rats and may improve the survival rates after endotoxin challenge.


