Oseltamivir acidInfluenza neuraminidase inhibitor CAS# 187227-45-8 |
- Peramivir Trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4956
CAS No.:1041434-82-5
- Zanamivir
Catalog No.:BCC4946
CAS No.:139110-80-8
- X-NeuNAc
Catalog No.:BCC2063
CAS No.:160369-85-7
- Oseltamivir
Catalog No.:BCC1825
CAS No.:196618-13-0
- Oseltamivir phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC4690
CAS No.:204255-11-8
- Peramivir
Catalog No.:BCC1846
CAS No.:330600-85-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 187227-45-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 449381 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H24N2O4 | M.Wt | 284.35 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | GS 4071; Ro 64-0802; oseltamivir carboxylate | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 230 mg/mL (808.86 mM) H2O : ≥ 56 mg/mL (196.94 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
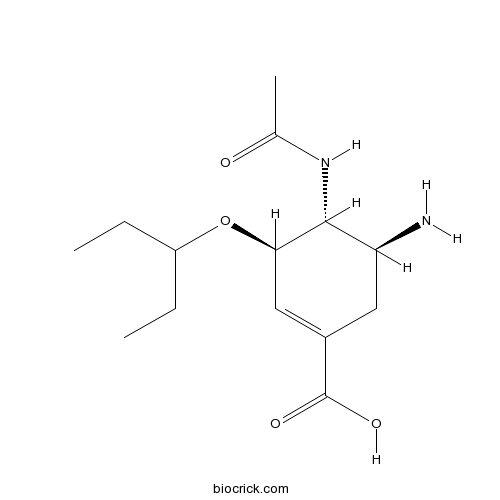
| Chemical Name | (3R,4R,5S)-4-acetamido-5-amino-3-pentan-3-yloxycyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCC(CC)OC1C=C(CC(C1NC(=O)C)N)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NENPYTRHICXVCS-YNEHKIRRSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H24N2O4/c1-4-10(5-2)20-12-7-9(14(18)19)6-11(15)13(12)16-8(3)17/h7,10-13H,4-6,15H2,1-3H3,(H,16,17)(H,18,19)/t11-,12+,13+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Oseltamivir acid is an active metabolite of Oseltamivir, which is a potent and selective inhibitor of influenza A and B virus neuraminidases.In Vitro:Oseltamivir acid inhibits virus replication in vitro and in vivo. Influenza B and A/H1N1 viruses appeare to be sensitive to Oseltamivir (mean B IC50 value: 13 nM; mean H1N1 IC50 value: 1.34 nM), while A/H1N2 and A/H3N2 viruses are more sensitive to Oseltamivir (mean H3N2 IC50 value: 0.67 nM; mean H1N2 IC50 value: 0.9 nM)[1]. In neuraminidases inhibition assays with influenza A viruses, the median 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of RWJ-270201 (approximately 0.34 nM) is comparable to that of Oseltamivir carboxylate (0.45 nM) For influenza B virus isolates, the IC50 of RWJ-270201 (1.36 nM) is comparable to that of Zanamivir (2.7 nM) and less than that of Oseltamivir carboxylate (8.5 nM)[2].In Vivo:Oseltamivir (0.1, 1, or 10 mg/kg/day, twice daily by oral gavage) produces a dose-dependent antiviral effect against Vietnam/1203/04 (VN1203/04) virus. The 5-day regimen at 10 mg/kg/day protects 50% of mice; deaths in this treatment group are delayed and indicated the replication of residual virus after the completion of treatment. Eight-day regimens improved Oseltamivir efficacy, and dosages of 1 and 10 mg/kg/day significantly reduced virus titers in organs and provided 60% and 80% survival rates, respectively[3]. In the pharmacokinetic study, after the oral administration of 1,000 mg/kg Oseltamivir, peak plasma concentrations are reached at 2 h postdose for Oseltamivir and 8 h for Oseltamivir carboxylate (OC). Rats are exposed to Oseltamivir over the whole sampling interval and had a ~2.7-fold-higher rate of exposure to OC than Oseltamivir. In CSF, peak concentrations are reached at 2 h postdose for Oseltamivir and 6 h for OC. CSF/plasma exposure ratios (AUC0-8 h) are ~0.07 for Oseltamivir and 0.007 for OC. In perfused brain samples, peak concentrations are reached at 8 h postdose for Oseltamivir and 6 h for OC. Brain/plasma exposure ratios (AUC0-8 h) of ~0.12 for Oseltamivir and 0.01 for OC are recorded. Corresponding CSF/brain exposure ratios ranged between ~0.55 and 0.64 for both analytes. A further group of animals that received a single oral administration of Oseltamivir at a lower dose produced similar results[4]. References: | |||||

Oseltamivir acid Dilution Calculator

Oseltamivir acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5168 mL | 17.584 mL | 35.1679 mL | 70.3359 mL | 87.9198 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7034 mL | 3.5168 mL | 7.0336 mL | 14.0672 mL | 17.584 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3517 mL | 1.7584 mL | 3.5168 mL | 7.0336 mL | 8.792 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0703 mL | 0.3517 mL | 0.7034 mL | 1.4067 mL | 1.7584 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0352 mL | 0.1758 mL | 0.3517 mL | 0.7034 mL | 0.8792 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Oseltamivir is an inhibitor of influenza neuraminidase [1].
Oseltamivir is a prodrug that is converted by intestinal and/or hepatic esterases to the neuraminidase inhibitor molecule, oseltamivir carboxylate. Neuraminidase cleaves the terminal a-Neu5Ac residues from the newly synthesized virion progeny and let it elute from the infected cell and seek new host cells to infect. Oseltamivir efficiently block sialidase activity and significantly inhibit the releasing mechanism [1].
In the treatment of adults, oseltamivir reduces the time to first alleviation of symptoms and investigator mediated unverified pneumonia. In prophylaxis trials, oseltamivir reduced symptomatic influenza in participants by 55%. Oseltamivir also has some harm. Adults treated with oseltamivir are associated with an increased risk of nausea. And in prophylaxis trials there is an increased risk of headaches on-treatment [2].
As a neuraminidase inhibitor, the substitution of the amino acid histidine to tyrosine at position 275 (H275Y) in the neuraminidase gene of H1N1 can cause the resistance of oseltamivir [3].
References:
[1] Enguang Feng, Deju Ye, Jian Li, Dengyou Zhang, Jinfang Wang, Fei Zhao, Rolf Hilgenfeld, Mingyue Zheng, Hualiang Jiang and Hong Liu. Recent Advances in Neuraminidase Inhibitor Development as Anti-influenza Drugs. Chem Med Chem 2012, 7: 1527 – 1536.
[2] Tom Jefferson reviewer, Mark Jones, Peter Doshi, Elizabeth A Spencer, Igho Onakpoya, Carl J Heneghan. Oseltamivir for influenza in adults and children: systematic review of clinical study reports and summary of regulatory comment. BMJ. 2014, 348: g2545.
[3] Rashmi Dixit, Gulam Khandaker, Scott Ilgoutz, Harunor Rashid and Robert Booy. Emergence of Oseltamivir Resistance: Control and Management of Influenza before, during and after the Pandemic. Infectious Disorders – Drug Targets. 2013, 13 (1): 34-45.
- Cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3114
CAS No.:18719-76-1
- Luliconazole
Catalog No.:BCC1711
CAS No.:187164-19-8
- Clauszoline M
Catalog No.:BCN4683
CAS No.:187110-72-1
- NS309
Catalog No.:BCC1809
CAS No.:18711-16-5
- N,N'-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)oxamide
Catalog No.:BCC9061
CAS No.:1871-89-2
- Sinapine
Catalog No.:BCN1815
CAS No.:18696-26-9
- Pafuramidine
Catalog No.:BCC1832
CAS No.:186953-56-0
- 2B-(SP)
Catalog No.:BCC5817
CAS No.:186901-17-7
- Moxifloxacin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2507
CAS No.:186826-86-8
- ML 10302 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7695
CAS No.:186826-17-5
- Ginsenoside Rg5
Catalog No.:BCN3551
CAS No.:186763-78-0
- Alisol A 24-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN2344
CAS No.:18674-16-3
- PA-824
Catalog No.:BCC1106
CAS No.:187235-37-6
- Kimcuongin
Catalog No.:BCN7472
CAS No.:1872403-23-0
- Z-VAD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1126
CAS No.:187389-52-2
- Boc-D-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1128
CAS No.:187389-53-3,634911-80-1
- ER 50891
Catalog No.:BCC7783
CAS No.:187400-85-7
- Methylisopelletierine
Catalog No.:BCN1160
CAS No.:18747-42-7
- Sitoindoside I
Catalog No.:BCN1161
CAS No.:18749-71-8
- N-Aminophthalimide
Catalog No.:BCC9085
CAS No.:1875-48-5
- MaxiPost
Catalog No.:BCC7984
CAS No.:187523-35-9
- Ethyl rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCC8976
CAS No.:187539-57-7
- Fmoc-D-Arg(Pbf)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3077
CAS No.:187618-60-6
- Tataramide B
Catalog No.:BCN3897
CAS No.:187655-56-7
Therapeutic designed poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) cylindrical oseltamivir phosphate-loaded implants impede tumor neovascularization, growth and metastasis in mouse model of human pancreatic carcinoma.[Pubmed:26309402]
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Aug 10;9:4573-86.
Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) copolymers have been extensively used in cancer research. PLGA can be chemically engineered for conjugation or encapsulation of drugs in a particle formulation. We reported that oseltamivir phosphate (OP) treatment of human pancreatic tumor-bearing mice disrupted the tumor vasculature with daily injections. Here, the controlled release of OP from a biodegradable PLGA cylinder (PLGA-OP) implanted at tumor site was investigated for its role in limiting tumor neovascularization, growth, and metastasis. PLGA-OP cylinders over 30 days in vitro indicated 20%-25% release profiles within 48 hours followed by a continuous metronomic low dose release of 30%-50% OP for an additional 16 days. All OP was released by day 30. Surgically implanted PLGA-OP containing 20 mg OP and blank PLGA cylinders at the tumor site of heterotopic xenografts of human pancreatic PANC1 tumors in RAGxCgamma double mutant mice impeded tumor neovascularization, growth rate, and spread to the liver and lungs compared with the untreated cohort. Xenograft tumors from PLGA and PLGA-OP-treated cohorts expressed significant higher levels of human E-cadherin with concomitant reduced N-cadherin and host CD31(+) endothelial cells compared with the untreated cohort. These results clearly indicate that OP delivered from PLGA cylinders surgically implanted at the site of the solid tumor show promise as an effective treatment therapy for cancer.
Evaluation of [(11)C]oseltamivir uptake into the brain during immune activation by systemic polyinosine-polycytidylic acid injection: a quantitative PET study using juvenile monkey models of viral infection.[Pubmed:25045603]
EJNMMI Res. 2014 Jul 2;4:24.
BACKGROUND: Abnormal behaviors of young patients after taking the anti-influenza agent oseltamivir (Tamiflu(R), F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Ltd., Basel, Switzerland) have been suspected as neuropsychiatric adverse events (NPAEs). Immune response to viral infection is suspected to cause elevation of drug concentration in the brain of adolescents. In the present study, the effect of innate immune activation on the brain uptake of [(11)C]oseltamivir was quantitatively evaluated in juvenile monkeys. METHODS: Three 2-year-old monkeys underwent positron emission tomography (PET) scans at baseline and immune-activated conditions. Both scans were conducted under pre-dosing of clinically relevant oseltamivir. The immune activation condition was induced by the intravenous administration of polyinosine-polycytidylic acid (poly I:C). Dynamic [(11)C]oseltamivir PET scan and serial arterial blood sampling were performed to obtain [(11)C]oseltamivir kinetics. Brain uptake of [(11)C]oseltamivr was evaluated by its normalized brain concentration, brain-to-plasma concentration ratio, and plasma-to-brain transfer rate. Plasma pro-inflammatory cytokine levels were also measured. RESULTS: Plasma interleukin-6 was elevated after intravenous administration of poly I:C in all monkeys. Brain radioactivity was uniform both at baseline and under poly I:C treatment. The mean brain concentrations of [(11)C]oseltamivir were 0.0033 and 0.0035% ID/cm(3) x kg, the mean brain-to-plasma concentration ratios were 0.58 and 0.65, and the plasma-to-brain transfer rates were 0.0047 and 0.0051 mL/min/cm(3) for baseline and poly I:C treatment, respectively. Although these parameters were slightly changed by immune activation, the change was not notable. CONCLUSIONS: The brain uptake of [(11)C]oseltamivir was unchanged by poly I:C treatment in juvenile monkeys. This study demonstrated that the innate immune response similar to the immune activation of influenza would not notably change the brain concentration of oseltamivir in juvenile monkeys.
[The anti-viral activity of the complex glycyrrhizic acid-alpha-glutamyl-tryptophan against experimental lethal influenza infection in white mice caused by oseltamivir-resistant strain of the virus].[Pubmed:24640167]
Vopr Virusol. 2013 Sep-Oct;58(5):19-26.
Influenza virus is a leading causing factor of infectious respiratory human pathology. The ability to implement the antigenic drift and development of drug resistance makes it important to develop novel anti-influenza drugs of wide spectrum of activity. In this work, we present the results of the study of the activity of a combination of glycyrrhizic acid with dipeptide alpha-glutamyl-tryptophan against oseltamivir-reistant strain of the virus Al Vladivostok/2/09 (H1 N1) on the model of lethal influenza infection in white mice. Application of Orvilax was shown to decrease the specific mortality of animals (index of protection 39-67% depending on the dose of the virus and drugs combination), to increase the mean day of death to 3.7-5.0 days and decrease the infectious titer of the virus in lung tissue to 1.3 Ig EID50/20 mg. The corresponding figures for the reference compound Tamiflu were 8-11%, 0.5-1.5 days, and 0.6 Ig EID50/20 mg. The use of Orvilax also led to reliable increase of the titers of interferon in the blood from 30.4 to 56.5 ME/mL. The results obtained allow the drug to be considered as a promising anti-influenza remedy that is active against the drug-resistant virus strains.
Synthesis and biological evaluation of oseltamivir analogues from shikimic acid.[Pubmed:25230508]
Nat Prod Commun. 2014 Jul;9(7):977-80.
New oseltamivir analogues were designed and synthesized, starting from shikimic acid. Biological evaluation against three human cancer cell lines (KB, MCF7 and Lu-1) showed that many of them exhibited cytotoxic activity. Azides 5 are more active than the corresponding amines 6. Thus, the reduction of the azide group into amine led to the loss of cytotoxicity. The compounds with a cyclohexanemethyloxy group at C-3 were more active than the other investigated compounds belonging to the same series. This cyclohexanemethyloxy group seems to be critical for the cytotoxic activity of this class of compounds. The synthetic oseltamivir analogues 6a-e had no inhibition activity, even at the concentration of 50 microM when they were evaluated for their in vitro influenza A neuraminidase inhibitory activity by an enzymatic assay.


