X-NeuNAcSubtrate for chromogeneic assay of neuraminidase activity CAS# 160369-85-7 |
- Dacomitinib (PF299804, PF299)
Catalog No.:BCC3683
CAS No.:1110813-31-4
- AG-1478
Catalog No.:BCC3717
CAS No.:153436-53-4
- OSI-420
Catalog No.:BCC4472
CAS No.:183320-51-6
- Gefitinib hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1591
CAS No.:184475-55-6
- Lapatinib Ditosylate
Catalog No.:BCC2083
CAS No.:388082-78-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 160369-85-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71307251 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H21BrClN2NaO9 | M.Wt | 559.72 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | >28mg/mL in DMSO | ||
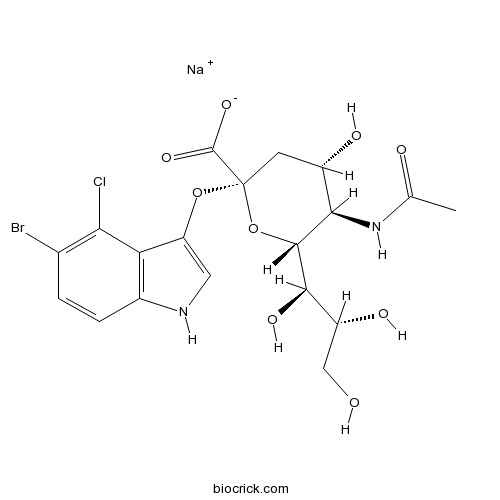
| Chemical Name | sodium;(2S,4S,5R,6R)-5-acetamido-2-[(5-bromo-4-chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)oxy]-4-hydroxy-6-[(1R,2R)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]oxane-2-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)NC1C(CC(OC1C(C(CO)O)O)(C(=O)[O-])OC2=CNC3=C2C(=C(C=C3)Br)Cl)O.[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MNWWXEDVLXNFDD-GNZCRVNMSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H22BrClN2O9.Na/c1-7(25)23-15-10(26)4-19(18(29)30,32-17(15)16(28)11(27)6-24)31-12-5-22-9-3-2-8(20)14(21)13(9)12;/h2-3,5,10-11,15-17,22,24,26-28H,4,6H2,1H3,(H,23,25)(H,29,30);/q;+1/p-1/t10-,11+,15+,16+,17+,19+;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

X-NeuNAc Dilution Calculator

X-NeuNAc Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7866 mL | 8.933 mL | 17.8661 mL | 35.7322 mL | 44.6652 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3573 mL | 1.7866 mL | 3.5732 mL | 7.1464 mL | 8.933 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1787 mL | 0.8933 mL | 1.7866 mL | 3.5732 mL | 4.4665 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0357 mL | 0.1787 mL | 0.3573 mL | 0.7146 mL | 0.8933 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0179 mL | 0.0893 mL | 0.1787 mL | 0.3573 mL | 0.4467 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Km: 0.89 mM for neuraminidase
X-Neu5Ac is a new substrate for chromogenic assay of neuraminidase activity in bacterial expression systems.
Many studies have focused on the functional role of cell surface gangliosides, which are thought to facilitate antigenicity, cell-cell recognition and cell growth regulation. Nacetyl neuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) within gangliosides Plays a key function in these roles. Chromogenic substrates, such as Neu5Ac, are used routinely for cytologic, histologic and spectroscopic analyses of enzyme activity.
In vitro: X-Neu5Ac was hydrolyzed by neuraminidase to release a halogenated product undergoing rapid aerobic oxidation to form the dark blue pigment. Preliminary kinetic studies indicated that X-Neu5Ac was a good and stable substrate for neuraminidase. In addition, X-Neu5Ac would also be hydrolyzed mutant enzymes [1].
In vivo: To visualize extracellular sialidase activity on the membrane surface in the rat brain, acute brain slices were incubated with X-Neu5Ac at pH 7.3. After 1h, myelin-abundant regions showed intense fluorescence in the rat brain. Although the hippocampus showed weak fluorescence in the brain, mossy fiber terminals in the hippocampus showed relatively intense fluorescence. In addition, the fluorescence intensities caused by X-Neu5Ac was correlated with the sialidase activity. Therefore, staining with X-Neu5Ac was specific for sialidase and useful for quantitative analysis of sialidase activities [1].
Clinical trial: N/A
References:
[1] Fujii I,Iwabuchi Y,Teshima T,Shiba T,Kikuchi M. X-Neu5Ac: a novel substrate for chromogenic assay of neuraminidase activity in bacterial expression systems. Bioorg Med Chem.1993 Aug;1(2):147-9.
[2] Minami A,Shimizu H,Meguro Y,Shibata N,Kanazawa H,Ikeda K,Suzuki T. Imaging of sialidase activity in rat brain sections by a highly sensitive fluorescent histochemical method. Neuroimage.2011 Sep 1;58(1):34-40.
- Bisdehydroneotuberostemonine
Catalog No.:BCN7072
CAS No.:160333-27-7
- L-368,899 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7438
CAS No.:160312-62-9
- 8-Hydroxybergapten
Catalog No.:BCN2732
CAS No.:1603-47-0
- SB 205384
Catalog No.:BCC7095
CAS No.:160296-13-9
- 14-Deoxy-11-hydroxyandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN4702
CAS No.:160242-09-1
- SR 11302
Catalog No.:BCC3607
CAS No.:160162-42-5
- BIM 23127
Catalog No.:BCC5822
CAS No.:160161-61-5
- 7-Chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepin-5-one
Catalog No.:BCC8779
CAS No.:160129-45-3
- L-BMAA hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7400
CAS No.:16012-55-8
- 2-Iminopiperidine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6862
CAS No.:16011-96-4
- SCH 58261
Catalog No.:BCC7306
CAS No.:160098-96-4
- Cryptofolione
Catalog No.:BCN7197
CAS No.:160098-78-2
- 3',5,5',7-Tetrahydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN1710
CAS No.:160436-10-2
- 30-Oxopseudotaraxasterol
Catalog No.:BCN7135
CAS No.:160481-71-0
- THZ1
Catalog No.:BCC4005
CAS No.:1604810-83-4
- THZ2
Catalog No.:BCC3986
CAS No.:1604810-84-5
- Antirhine
Catalog No.:BCN4003
CAS No.:16049-28-8
- Bisandrographolide A
Catalog No.:BCN4701
CAS No.:160498-00-0
- 12S-hydroxyandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN4700
CAS No.:869593-50-0
- BW 723C86 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6915
CAS No.:160521-72-2
- 5,7,3',4'-Tetrahydroxy-3-methoxy-8-geranylflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6847
CAS No.:1605304-56-0
- Zarzissine
Catalog No.:BCN6456
CAS No.:160568-14-9
- DMP 543
Catalog No.:BCC7331
CAS No.:160588-45-4
- Villosin
Catalog No.:BCN1711
CAS No.:160598-92-5
Glycolipid acceptor specificity of a human Gal beta(1-3/1-4) GlcNAc alpha 2,3-sialyltransferase.[Pubmed:8554608]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Dec 26;217(3):852-8.
A human Gal beta(1-3/1-4)GlcNAc alpha 2,3-sialyltransferase, called ST-4, is a sialyltransferase involved in the in vivo biosynthesis of sialyl Lewis X (NeuNAc alpha 2-3Gal beta 1-4(Fuc alpha 1-3)GlcNAc) determinant. The ST-4 enzyme could utilize nLc4Cer (Gal beta 1-4GlcNAc beta 1-3Gal beta 1-4Glc beta 1-1'Cer) containing type 2 sugar chain, Lc4Cer (Gal beta 1-3GlcNAc beta 1-3Gal beta 1-4Glc beta 1-1'Cer) containing type 1 sugar chain, Gg4Cer (Gal beta 1-3GalNAc beta 1-3Gal beta 1-4Glc beta 1-1'Cer), and LacCer as glycolipid acceptor substrates, but not other neutral glycolipids (GalCer, GlcCer, Gb3Cer, Gg3Cer, Gb4Cer) and gangliosides (GM1a, GM2, GM3, GD1a, GD1b, and GT1b) as substrates. The order of sialic acid incorporation into glycolipids for the enzyme was nLc4Cer > Gg4Cer > Lc4Cer > LacCer. The apparent Km values of ST-4 for nLc4Cer and Gg4Cer were 0.47 and 2.5 mM, respectively. Thus, the ST-4 could efficiently utilize both nLc4Cer and Gg4Cer as glycolipid acceptor substrates in vitro, suggesting that the substrate specificity of the enzyme may be similar to that of a glycolipid sialyltransferase (SAT-3), which is defined as the enzyme that uses both nLc4Cer and Gg4Cer as glycolipid acceptor substrates.
NAN fusions: a synthetic sialidase reporter gene as a sensitive and versatile partner for GUS.[Pubmed:12410816]
Plant J. 2002 Nov;32(3):391-400.
GUS continues to be the reporter of choice for many gene fusion applications, due to the unparalleled sensitivity of the encoded enzyme and the ease with which it can be quantified in cell-free extracts and visualized histochemically in cells and tissues. A compatible and functionally equivalent reporter gene would facilitate dual promoter studies and internal standardization of expression analyses in the same plant. A search for a candidate enzyme activity not found in plants, which might form the basis of a novel GUS-compatible reporter system, led us to investigate nanH, a Clostridium perfringens gene which encodes the so-called 'small' cytoplasmic sialidase. Expression of the native, AT-rich nanH gene in transgenic plants did not, however, result in detectable sialidase activity. For this reason, a codon-optimized derivative, NAN, was synthesized which possesses a GC content similar to that found in highly expressed plant genes. NAN enzyme activity was expressed at high levels in both stably and transiently transformed cells, possessed kinetic and stability properties similar to those of GUS, and showed optimal activity in GUS buffer. Moreover, NAN and GUS activity could be visualized simultaneously in polyacrylamide gels using the corresponding methylumbelliferone-based substrates, and in whole seedlings and tissue sections using the histochemical substrates 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl alpha-d-N-acetylneuraminic acid (X-NeuNAc) and 5-bromo-6-chloro-3-indolyl beta-d-glucuronide (X-GlucM), respectively.
Molecular cloning of a fourth member of a human alpha (1,3)fucosyltransferase gene family. Multiple homologous sequences that determine expression of the Lewis x, sialyl Lewis x, and difucosyl sialyl Lewis x epitopes.[Pubmed:1339443]
J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24575-84.
We and others have previously described the isolation of three human alpha (1,3)fucosyltransferase genes which form the basis of a nascent glycosyltransferase gene family. We now report the molecular cloning and expression of a fourth homologous human alpha (1,3)fucosyltransferase gene. When transfected into mammalian cells, this fucosyltransferase gene is capable of directing expression of the Lewis x (Gal beta 1-->4[Fuc alpha 1-->3]GlcNAc), sialyl Lewis x (NeuNAc alpha 2-->3Gal beta 1-->4 [Fuc alpha 1-->3]GlcNAc), and difucosyl sialyl Lewis x (NeuNAc alpha 2-->3Gal beta 1-->4[Fuc alpha 1-->3]GlcNAc beta 1-->3 Gal beta 1-->4[Fuc alpha 1-->3]GlcNAc) epitopes. The enzyme shares 85% amino acid sequence identity with Fuc-TIII and 89% identity with Fuc-TV but differs substantially in its acceptor substrate requirements. Polymerase chain reaction analyses demonstrate that the gene is syntenic to Fuc-TIII and Fuc-TV on chromosome 19. Southern blot analyses of human genomic DNA demonstrate that these four alpha (1,3)fucosyltransferase genes account for all DNA sequences that cross-hybridize at low stringency with the Fuc-TIII catalytic domain. Using similar methods, a catalytic domain probe from Fuc-TIV identifies a new class of DNA fragments which do not cross-hybridize with the chromosome 19 fucosyltransferase probes. These results extend the molecular definition of a family of human alpha (1,3)fucosyltransferase genes and provide tools for examining fucosyltransferase gene expression.


