AG-1478EGFR inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 153436-53-4 |
- Lapatinib
Catalog No.:BCC3633
CAS No.:231277-92-2
- Lapatinib Ditosylate
Catalog No.:BCC2083
CAS No.:388082-78-8
- AEE788 (NVP-AEE788)
Catalog No.:BCC2520
CAS No.:497839-62-0
- AC480 (BMS-599626)
Catalog No.:BCC1252
CAS No.:714971-09-2
- BMS-690514
Catalog No.:BCC1430
CAS No.:859853-30-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 153436-53-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2051 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H14ClN3O2 | M.Wt | 315.75 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Tyrphostin AG-1478; NSC 693255 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (316.71 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
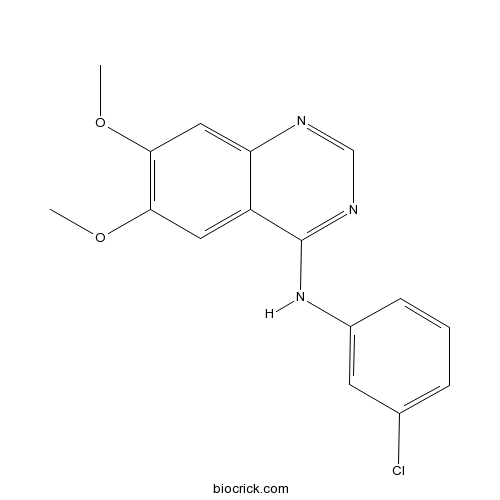
| Chemical Name | N-(3-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C(=NC=N2)NC3=CC(=CC=C3)Cl)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GFNNBHLJANVSQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H14ClN3O2/c1-21-14-7-12-13(8-15(14)22-2)18-9-19-16(12)20-11-5-3-4-10(17)6-11/h3-9H,1-2H3,(H,18,19,20) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AG-1478 (Tyrphostin AG-1478) is a selective inhibitor of EGFR with an IC50 values of 3 nM. | |||||
| Targets | EGFR | HER2 | PDGFR | |||
| IC50 | 3 nM | >100 μM | >100 μM | |||

AG-1478 Dilution Calculator

AG-1478 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1671 mL | 15.8353 mL | 31.6706 mL | 63.3413 mL | 79.1766 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6334 mL | 3.1671 mL | 6.3341 mL | 12.6683 mL | 15.8353 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3167 mL | 1.5835 mL | 3.1671 mL | 6.3341 mL | 7.9177 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0633 mL | 0.3167 mL | 0.6334 mL | 1.2668 mL | 1.5835 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0317 mL | 0.1584 mL | 0.3167 mL | 0.6334 mL | 0.7918 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AG-1478 is an inhibitor of EGFR which acts on EGF-stimulated Erk1/2 phosphorylation with IC50 value of 10 uM using ovarian cell line Ishikawa [1].
EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) belongs to human HER-1 family, which is a cell surface receptor and recognized by EGF-family (epidermal growth factor family). Many studies have shown that EGFR is over-expressed in a variety of solid tumors and its over-expression means bad prognosis for cancer patients [1]. AG1478 works as EGFR kinase inhibitor through blocking EGFR phosphorylation and superoxide anion production [2].
Treating human hepatocellular carcinoma HA22T/VGH cells could reduce its anti-tumor activity compared with control group [3]. When tested with ovarian cancer cell lines CAOV-3 or SKOV-3, EGFR signaling was diminished [4]. When human colorectal SW480 was treated with AG-1478, both EGFR phosphorylation and cell proliferation were reduced [5].
In nu/nu mice model with CAOV-3 cells xenografted, treatment with AG-1478 could diminish EGFR phosphorylation thus limited the growth of tumor [4].
Gong XD, et al. had shown that AG-1478 also could reduce the expression of FOXM1 via FOXO3a using a NSCLC cell lines A549, and the A549 cells showed increased chemosensitivity[6].
References:
1.Takai, N., et al., Synergistic anti-neoplastic effect of AG1478 in combination with cisplatin or paclitaxel on human endometrial and ovarian cancer cells. Mol Med Rep, 2010. 3(3): p. 479-84.
2.D'Anneo, A., et al., Parthenolide induces superoxide anion production by stimulating EGF receptor in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol, 2013. 43(6): p. 1895-900.
3.Bondi, M.L., et al., Entrapment of an EGFR inhibitor into nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) improves its antitumor activity against human hepatocarcinoma cells. J Nanobiotechnology, 2014. 12(21): p. 1477-3155.
4.Yu, Y., et al., Synergistic effects of combined platelet-activating factor receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in ovarian cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol, 2014. 7(1): p. 1756-8722.
5.Yagublu, V., et al., Combination of the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478 and 5-FU: no synergistic effect on EGFR phosphorylation, cell proliferation and apoptosis induction. Anticancer Res, 2013. 33(9): p. 3753-8.
6.Gong, X.D., et al., [Effects of AG1478 on the expression of FOXM1 gene via FOXO3a in non-small cell lung cancer cells]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2013. 35(8): p. 572-8.
- Gavestinel
Catalog No.:BCC7340
CAS No.:153436-38-5
- Taxcultine
Catalog No.:BCN6948
CAS No.:153415-46-4
- Taxol C
Catalog No.:BCN6941
CAS No.:153415-45-3
- 7-Epi-docetaxel
Catalog No.:BCC5411
CAS No.:153381-68-1
- Ginkgolide K
Catalog No.:BCN8209
CAS No.:153355-70-5
- SCR7
Catalog No.:BCC3978
CAS No.:1533426-72-0
- DFB
Catalog No.:BCC7130
CAS No.:15332-10-2
- 4,4'-Bis(2-benzoxazolyl)stilbene
Catalog No.:BCC8656
CAS No.:1533-45-5
- ML355
Catalog No.:BCC8060
CAS No.:1532593-30-8
- Cilomilast
Catalog No.:BCC2283
CAS No.:153259-65-5
- Taxayunnansin A
Catalog No.:BCN1685
CAS No.:153229-31-3
- Thiamphenicol
Catalog No.:BCC4736
CAS No.:15318-45-3
- PD153035 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3617
CAS No.:153436-54-5
- WHI-P180 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4243
CAS No.:153437-55-9
- Fexofenadine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4542
CAS No.:153439-40-8
- Desmethoxy yangonin
Catalog No.:BCN2295
CAS No.:15345-89-8
- Carbazeran citrate
Catalog No.:BCC6173
CAS No.:153473-94-0
- Xanthinin
Catalog No.:BCN1686
CAS No.:153483-31-9
- Cevimeline hydrochloride hemihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1471
CAS No.:153504-70-2
- [D-Trp34]-Neuropeptide Y
Catalog No.:BCC7690
CAS No.:153549-84-9
- Bexarotene
Catalog No.:BCC3737
CAS No.:153559-49-0
- D-Menthol
Catalog No.:BCN4973
CAS No.:15356-60-2
- DL-Menthol
Catalog No.:BCN5950
CAS No.:15356-70-4
- 13-Hydroxylupanine
Catalog No.:BCN3204
CAS No.:15358-48-2
Niflumic acid and AG-1478 reduce cigarette smoke-induced mucin synthesis: the role of hCLCA1.[Pubmed:17426222]
Chest. 2007 Apr;131(4):1149-56.
BACKGROUND: Cigarette smoke induces bronchial mucus secretion. However, the mechanism of this induction is still unidentified. In this study, we investigated the role of the putative calcium-activated chloride channel 1 (CLCA1) and its blocker, niflumic acid, in cigarette smoke-induced mucin synthesis both in vivo and in vitro. METHODS AND RESULTS: Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to cigarette smoke for 4 weeks. The CLCA1, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and MUC5AC expressions were increased in the trachea and lung tissues. Goblet-cell hyperplasia with marked mucin staining was detected in the tracheal and bronchial epithelium. In the human bronchial epithelial cell line NCI-H292, cigarette smoke solution also induced mucin production as well as the RNA and protein expressions of CLCA1, EGFR, and MUC5AC. Both in vivo and in vitro, the induction of MUC5AC and mucin synthesis were inhibited by niflumic acid, and/or a selective EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, AG-1478. Niflumic acid also blocked the epidermal growth factor-induced MUC5AC and mucin staining in the NCI-H292 cell line. CONCLUSION: Both EGFR and niflumic acid-sensitive chloride channels (probably CLCA1) are dependently affecting the mucin production as a part of a single complex signaling pathway. CLCA1 may be a key signaling member that can be targeted with pharmacologic interventions to treat mucus hypersecretion.
The EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor tyrphostin AG-1478 causes hypomagnesemia and cardiac dysfunction.[Pubmed:22646904]
Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 Aug;90(8):1145-9.
We determined whether the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) N-(3-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinazolinamine (tyrphostin AG-1478) causes hypomagnesemia and cardiac dysfunction in rats. Tyrphostin was administered (3 times per week, intraperitoneal injection, to achieve 21.4 mg.(kg body mass)(-1).day(-1)) to normomagnesemic rats for 5 weeks. Levels of magnesium in the plasma of the tyrphostin-treated rats decreased significantly by the following amount: 17% at week 1, 27% at week 2, and 26%-35% between weeks 3 to 5. Levels of the plasma lipid peroxidation marker 8-isoprostane rose significantly: by 58% at week 1, 168% at week 3, and 113% at week 5. At week 5, blood neutrophils from the tyrphostin-treated group displayed a 2.26-fold higher basal level of O(2)(.-) generation; the ratio of oxidized glutathione (glutathione disulfide; GSSG) to reduced glutathione (GSH) in the red blood cells increased 2.5-fold. At week 5, echocardiography revealed that TKI treatment resulted in significant cardiac systolic dysfunction, with impaired diastolic function and dilated cardiomyopathy. Since hypomagnesemia alone can trigger oxidative stress and cardiac injury, we suggest that inhibition of EGFR-TK caused magnesium wasting, which partly contributed to decreased cardiac contractility.
Fluorescence and analytical ultracentrifugation analyses of the interaction of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor, tyrphostin AG 1478-mesylate, with albumin.[Pubmed:15913535]
Anal Biochem. 2005 Jul 15;342(2):292-9.
Quantifying the interaction of drugs with carrier proteins in plasma is of importance for understanding effective drug delivery to disease-affected tissues. In this study, we employed analytical ultracentrifugation and steady-state fluorescence spectroscopy to characterize the interaction of a potential new anticancer drug, AG 1478-mesylate, with plasma proteins in a suspension of normal serum albumin (NSA). We found that mesylate salt of AG 1478, an epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor, sediments in 0.1%(w/v) NSA as a complex with a sedimentation coefficient of 3.8 S. This is consistent with the size of human serum albumin. This interaction was quantitated by meniscus depletion sedimentation and fluorescence titration analyses. AG 1478-mesylate binds to albumin with an apparent single-site affinity (K(d)) of 120 microM. In this article, we show that the cyclodextrin carrier molecule, Captisol, increases the apparent affinity of the hydrophobic AG 1478-mesylate for albumin (K(d)=4-6 microM), and we propose that the AG 1478-mesylate-Captisol (1:1) complex binds to albumin with at least 10-fold higher affinity than does AG 1478-mesylate ligand alone. A fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-sulfonic acid (FMS) derivative of the 6-aminoquinazoline analog of AG 1478, which was designed to have improved serum-binding properties, was shown by fluorescence analysis to bind with approximately 100-fold greater affinity than the parent compound. This has significant implications in the effective delivery of therapeutic agents in vivo.
UV-Vis spectroscopy and solvatochromism of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG-1478.[Pubmed:27092736]
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2016 Jul 5;164:128-32.
The effect of twenty-one solvents on the UV-Vis spectrum of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG-1478 was investigated. The absorption spectrum in the range 300-360nm consisted of two partially overlapping bands at approximately 340nm and 330nm. The higher energy absorption band was more sensitive to solvent and exhibited a peak position that varied from 327nm to 336nm, while the lower energy absorption band demonstrated a change in peak position from 340nm to 346nm in non-chlorinated solvents. The fluorescence spectrum of AG-1478 was particularly sensitive to solvent. The wavelength of peak intensity varied from 409nm to 495nm with the corresponding Stokes shift in the range of 64nm to 155nm (4536cm(-1) to 9210cm(-1)). We used a number of methods to assess the relationship between spectroscopic properties and solvent properties. The detailed analysis revealed that for aprotic solvents, the peak position of the emission spectrum in wavenumber scale correlated with the polarity (dielectric constant or ET(30)) of the solvent. In protic solvents, a better correlation was observed between the hydrogen bonding power of the solvent and the position of the emission spectrum. Moreover, the fluorescence quantum yields were larger in aprotic solvents as compared to protic solvents. This analysis underscores the importance of polarity and hydrogen-bonding environment on the spectroscopic properties of AG-1478. These studies will assume relevance in understanding the interaction of AG-1478 in vitro and in vivo.


