SCR7DNA ligase IV inhibitor CAS# 1533426-72-0 |
- L189
Catalog No.:BCC7707
CAS No.:64232-83-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1533426-72-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 72708496 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H14N4OS | M.Wt | 334.39 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 45 mg/mL (134.57 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
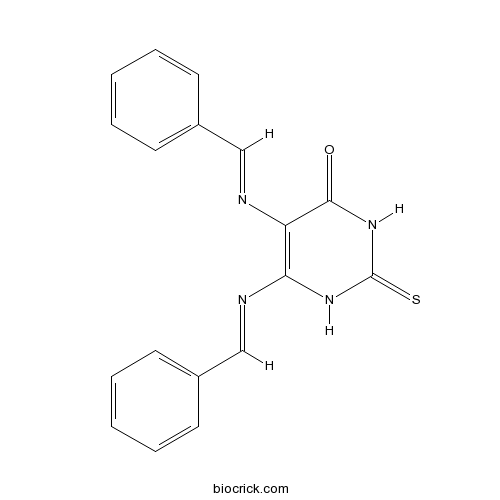
| Chemical Name | 5-(benzylideneamino)-6-[(E)-benzylideneamino]-2-sulfanylidene-1H-pyrimidin-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C=NC2=C(NC(=S)NC2=O)N=CC3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NEEVCWPRIZJJRJ-LWRDCAMISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H14N4OS/c23-17-15(19-11-13-7-3-1-4-8-13)16(21-18(24)22-17)20-12-14-9-5-2-6-10-14/h1-12H,(H2,21,22,23,24)/b19-11?,20-12+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | SCR7 is a DNA Ligase IV inhibitor, blocks nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ). SCR7 increases CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing frequency.In Vitro:SCR7 inhibits joining of double-strand breaks (DSBs) in cell-free repair system. SCR7 blocks Ligase IV-mediated joining by interfering with its DNA binding but not that of T4 DNA Ligase or Ligase I. SCR7 inhibits NHEJ in a Ligase IV-dependent manner within cells, and activates the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Results show a dose-dependent decrease in cell proliferation of MCF7, A549, and HeLa with an IC50 of 40, 34, and 44 μM, respectively, which is further confirmed by DIC imaging in MCF7. T47D, A2780, and HT1080 are also sensitive to SCR7, with an IC50 of 8.5, 120, and 10 μM, respectively[1].In Vivo:SCR7 treatment (10 mg/kg, six doses) significantly reduces breast adenocarcinoma-induced tumor. Untreated tumor animals survived only for 52 days, whereas treated animals exhibit ~4-fold increase in lifespan[1]. References: | |||||
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | Epithelial (A549) and melanoma (MelJuSo) cell line derivatives |
| Preparation method | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 24 hours at 37oC |
| Applications | Scr7 increases the efficiency of insertional mutagenesis in cell lines. In A549 cells, 0.01 μM Scr7 improves the efficiency of insertion at the target site about threefold relative to the untreated control. In Scr7-treated MelJuSo cells, the insertion efficiency is also enhanced in a dose-dependent manner up to 19-fold. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
| Animal models | Kell-LPETG mice |
| Dosage form | CRISPR components mixture (Cas9 mRNA, sgRNA and targeting template) and 10 mM of Scr7 NHEJ inhibitor (to 1 mM final) were injected into the cytoplasm at the pronuclear stage. The injected zygotes were transferred at the 2-cell stage into the pseudo-pregnant females. |
| Application | Co-injection of Scr7 increases the efficiency of precise genome editing in mouse embryos. The insertion efficiency with Scr7 co-injection is significantly higher (P = 0.0012) compared to blastocysts not injected with Scr7. The insertion efficiency in Scr7-co-injected E10 embryos is also significantly enhanced compared to E10 embryos not injected with Scr7 (P = 0.003). |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: 1. Maruyama T, Dougan SK, Truttmann MC et al. Increasing the efficiency of precise genome editing with CRISPR-Cas9 by inhibition of nonhomologous end joining. Nat Biotechnol. 2015 May;33(5):538-42. | |

SCR7 Dilution Calculator

SCR7 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9905 mL | 14.9526 mL | 29.9052 mL | 59.8104 mL | 74.763 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5981 mL | 2.9905 mL | 5.981 mL | 11.9621 mL | 14.9526 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2991 mL | 1.4953 mL | 2.9905 mL | 5.981 mL | 7.4763 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0598 mL | 0.2991 mL | 0.5981 mL | 1.1962 mL | 1.4953 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0299 mL | 0.1495 mL | 0.2991 mL | 0.5981 mL | 0.7476 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Scr7 is a DNA ligase IV inhibitor, initially identified as an anti-cancer agent [1].
Scr7 targets the DNA binding domain of DNA ligase IV, reducing its affinity for double strand breaks (DSBs) and inhibiting its function. Scr7 also inhibits DNA ligase III (but not DNA ligase I), albeit less efficiently. Cells were treated with doxycycline to induce Cas9 expression, with various concentrations of Scr7 for 24 h. Scr7 maintained cells capable of entering S/G2 phase, which is necessary for HDR. [1] Treatment of mice with Scr7 affects lymphocyte development, as DNA ligase IV plays a key role in the joining of coding ends during V(D)J recombination by means of C-NHEJ16. The defects in lymphocyte development upon Scr7 treatment are transient and reversible, due to the noncovalent mode of binding of Scr7. Scr7 enhanced the frequency of HDR by transiently blocking NHEJ (with the exception of DNA ligase I–dependent alt-NHEJ), resulting in precise genome editing by CRISPR-Cas9 in both cultured cells and in mice. [2]
References:
[1]. Srivastava M, Nambiar M, Sharma S et al. An inhibitor of nonhomologous end-joining abrogates double-strand break repair and impedes cancer progression. Cell. 2012 Dec 21;151(7):1474-87. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.054.
[2]. Maruyama T, Dougan SK, Truttmann MC et al.Increasing the efficiency of precise genome editing with CRISPR-Cas9 by inhibition of nonhomologous end joining. Nat Biotechnol. 2015 Mar 23. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3190. [Epub ahead of print]
- DFB
Catalog No.:BCC7130
CAS No.:15332-10-2
- 4,4'-Bis(2-benzoxazolyl)stilbene
Catalog No.:BCC8656
CAS No.:1533-45-5
- ML355
Catalog No.:BCC8060
CAS No.:1532593-30-8
- Cilomilast
Catalog No.:BCC2283
CAS No.:153259-65-5
- Taxayunnansin A
Catalog No.:BCN1685
CAS No.:153229-31-3
- Thiamphenicol
Catalog No.:BCC4736
CAS No.:15318-45-3
- N-Methyltaxol C
Catalog No.:BCN7343
CAS No.:153083-53-5
- Diclofenac
Catalog No.:BCC5249
CAS No.:15307-86-5
- Diclofenac Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4439
CAS No.:15307-79-6
- SR 140333
Catalog No.:BCC6098
CAS No.:153050-21-6
- Precursor of cefcapene diisopropylanmine salt
Catalog No.:BCC9127
CAS No.:153012-37-4
- Serotonin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4715
CAS No.:153-98-0
- Ginkgolide K
Catalog No.:BCN8209
CAS No.:153355-70-5
- 7-Epi-docetaxel
Catalog No.:BCC5411
CAS No.:153381-68-1
- Taxol C
Catalog No.:BCN6941
CAS No.:153415-45-3
- Taxcultine
Catalog No.:BCN6948
CAS No.:153415-46-4
- Gavestinel
Catalog No.:BCC7340
CAS No.:153436-38-5
- AG-1478
Catalog No.:BCC3717
CAS No.:153436-53-4
- PD153035 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3617
CAS No.:153436-54-5
- WHI-P180 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4243
CAS No.:153437-55-9
- Fexofenadine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4542
CAS No.:153439-40-8
- Desmethoxy yangonin
Catalog No.:BCN2295
CAS No.:15345-89-8
- Carbazeran citrate
Catalog No.:BCC6173
CAS No.:153473-94-0
- Xanthinin
Catalog No.:BCN1686
CAS No.:153483-31-9
SCR7 is neither a selective nor a potent inhibitor of human DNA ligase IV.[Pubmed:27235626]
DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Jul;43:18-23.
DNA ligases are attractive therapeutics because of their involvement in completing the repair of almost all types of DNA damage. A series of DNA ligase inhibitors with differing selectivity for the three human DNA ligases were identified using a structure-based approach with one of these inhibitors being used to inhibit abnormal DNA ligase IIIalpha-dependent repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSB)s in breast cancer, neuroblastoma and leukemia cell lines. Raghavan and colleagues reported the characterization of a derivative of one of the previously identified DNA ligase inhibitors, which they called SCR7 (designated SCR7-R in our experiments using SCR7). SCR7 appeared to show increased selectivity for DNA ligase IV, inhibit the repair of DSBs by the DNA ligase IV-dependent non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway, reduce tumor growth, and increase the efficacy of DSB-inducing therapeutic modalities in mouse xenografts. In attempting to synthesize SCR7, we encountered problems with the synthesis procedures and discovered discrepancies in its reported structure. We determined the structure of a sample of SCR7 and a related compound, SCR7-G, that is the major product generated by the published synthesis procedure for SCR7. We also found that SCR7-G has the same structure as the compound (SCR7-X) available from a commercial vendor (XcessBio). The various SCR7 preparations had similar activity in DNA ligation assay assays, exhibiting greater activity against DNA ligases I and III than DNA ligase IV. Furthermore, SCR7-R failed to inhibit DNA ligase IV-dependent V(D)J recombination in a cell-based assay. Based on our results, we conclude that SCR7 and the SCR7 derivatives are neither selective nor potent inhibitors of DNA ligase IV.
Enhanced efficacy of pluronic copolymer micelle encapsulated SCR7 against cancer cell proliferation.[Pubmed:25515310]
Macromol Biosci. 2015 Apr;15(4):521-34.
5,6-Bis(benzylideneamino)-2-mercaptopyrimidin-4-ol (SCR7) is a new anti cancer molecule having capability to selectively inhibit non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), one of the DNA double strand break (DSB) repair pathways inside the cells. In spite of the promising potential as an anticancer agent, hydrophobicity of SCR7 decreases its bioavailability. Herein the entrapment of SCR7 in Pluronic copolymer is reported. The size of the aggregates was determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) which yields an average diameter of 23 nm. SCR7 encapsulated micelles (ES) were also characterized by small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). Evaluation of its biological properties by using a variety of techniques, including Trypan blue, MTT and Live-dead cell assays, reveal that encapsulated SCR7 can induce cytotoxicity in cancer cell lines, being more effective in breast cancer cell line. Encapsulated SCR7 treatment resulted in accumulation of DNA breaks within the cells, resulting in cell cycle arrest at G1 phase and activation of apoptosis. More importantly, we found approximately 5 fold increase in cell death, when encapsulated SCR7 was used in comparison with SCR7 alone.
DNA repair of myeloma plasma cells correlates with clinical outcome: the effect of the nonhomologous end-joining inhibitor SCR7.[Pubmed:27443291]
Blood. 2016 Sep 1;128(9):1214-25.
DNA repair activity of malignant cells seems to influence therapeutic outcome and patients' survival. Herein, we investigated the mechanistic basis for the link between DNA repair efficiency and response to antimyeloma therapy. Nucleotide excision repair (NER), interstrand cross-links repair (ICL/R), double-strand breaks repair (DSB/R), and chromatin structure were evaluated in multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (melphalan-sensitive RPMI8226; melphalan-resistant LR5) and bone marrow plasma cells (BMPCs) from MM patients who responded (n = 17) or did not respond (n = 9) to subsequent melphalan therapy. The effect of DSB/R inhibition was also evaluated. Responders' BMPCs showed slower rates of NER and DSB/R (P <0022), similar rates of ICL/R, and more condensed chromatin structure compared with nonresponders. Moreover, apoptosis rates of BMPCs were inversely correlated with individual DNA repair efficiency and were higher in responders' cells compared with those of nonresponders (P = .0011). Similarly, RPMI8226 cells showed slower rates of NER and DSB/R, comparable rates of ICL/R, more condensed chromatin structure, and higher sensitivity than LR5 cells. Interestingly, cotreatment of BMPCs or cell lines with DSB/R inhibitors significantly reduced the rates of DSB/R and increased melphalan sensitivity of the cells, with the nonhomologous end-joining inhibitor SCR7 showing the strongest effect. Together, responders' BMPCs are characterized by lower efficiencies of NER and DSB/R mechanisms, resulting in higher accumulation of the extremely cytotoxic ICLs and DSBs lesions, which in turn triggers the induction of the apoptotic pathway. Moreover, the enhancement of melphalan cytotoxicity by DSB/R inhibition offers a promising strategy toward improvement of existing antimyeloma regimens.
Pluronic copolymer encapsulated SCR7 as a potential anticancer agent.[Pubmed:25608025]
Faraday Discuss. 2015;177:155-61.
Nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) inside cells can be selectively inhibited by 5,6-bis-(benzylideneamino)-2-mercaptopyrimidin-4-ol (SCR7) which possesses anticancer properties. The hydrophobicity of SCR7 decreases its bioavailability which is a major setback in the utilization of this compound as a therapeutic agent. In order to circumvent the drawback of SCR7, we prepared a polymer encapsulated form of SCR7. The physical interaction of SCR7 and Pluronic(R) copolymer is evident from different analytical techniques. The in vitro cytotoxicity of the drug formulations is established using the MTT assay.


