LapatinibEGFR/HER2 inhibitor,potent,selective and reversible CAS# 231277-92-2 |
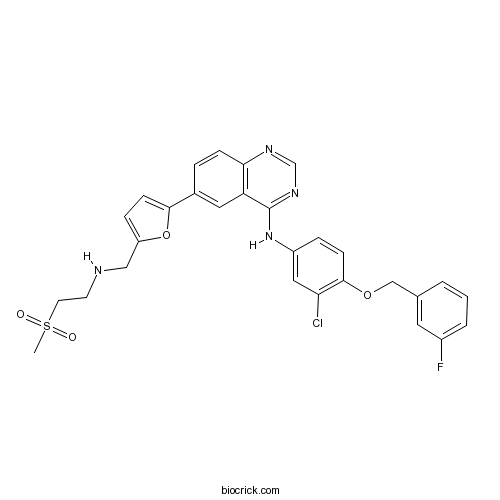
- WZ4002
Catalog No.:BCC1074
CAS No.:1213269-23-8
- CO-1686 (AVL-301)
Catalog No.:BCC1490
CAS No.:1374640-70-6
- Mutant EGFR inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4119
CAS No.:1421373-62-7
- Erlotinib Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3645
CAS No.:183319-69-9
- Lapatinib Ditosylate
Catalog No.:BCC2083
CAS No.:388082-78-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 231277-92-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 208908 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C29H26ClFN4O4S | M.Wt | 581.06 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | GW572016 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 39 mg/mL (67.12 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | N-[3-chloro-4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-6-[5-[(2-methylsulfonylethylamino)methyl]furan-2-yl]quinazolin-4-amine | ||
| SMILES | CS(=O)(=O)CCNCC1=CC=C(O1)C2=CC3=C(C=C2)N=CN=C3NC4=CC(=C(C=C4)OCC5=CC(=CC=C5)F)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BCFGMOOMADDAQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C29H26ClFN4O4S/c1-40(36,37)12-11-32-16-23-7-10-27(39-23)20-5-8-26-24(14-20)29(34-18-33-26)35-22-6-9-28(25(30)15-22)38-17-19-3-2-4-21(31)13-19/h2-10,13-15,18,32H,11-12,16-17H2,1H3,(H,33,34,35) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Lapatinib is a potent inhibitor of EGFR and ErbB2 with IC50 of 10.8 and 9.2 nM, respectively. | |||||
| Targets | EGFR | ErbB2 | ||||
| IC50 | 10.8 nM | 9.2 nM | ||||

Lapatinib Dilution Calculator

Lapatinib Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.721 mL | 8.605 mL | 17.2099 mL | 34.4199 mL | 43.0248 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3442 mL | 1.721 mL | 3.442 mL | 6.884 mL | 8.605 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1721 mL | 0.8605 mL | 1.721 mL | 3.442 mL | 4.3025 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0344 mL | 0.1721 mL | 0.3442 mL | 0.6884 mL | 0.8605 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0172 mL | 0.086 mL | 0.1721 mL | 0.3442 mL | 0.4302 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Lapatinib (also known as GW572016), a member of the 4-anilinoquinazoline class of kinase inhibitors, is a potent, reversible and selective small-molecule inhibitor of both epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) tyrosine kinases that inhibits recombinant EGFR and HER-2 tyrosine kinases in cell-free biochemical kinase assays with values of 50% inhibition concentration IC50 of 10.8 nmol/L and 9.3 nmol/L respectively. Lapatinib interferes with the adenosine triphosphate binding in the tyrosine kinases domains of both EGFR and HER-2 resulting in the inhibition of auto-phosphorylation and resultant downstream signaling activities (such as cellular proliferation and survival).
Reference
Alison Reid, Laura Vidal, Heather Shaw and Johann de Bono. Dual inhibition of ErbB1 (EGFR/HER1) and ErbB2 (HER2/neu). European Journal of Cancer 43 (2007) 481-489
Norio Kondo, Mamoru Tsukuda, Yukari Ishiguro, Machiko Kimura, Kyoko Fujita, Atsuko Sakakibara, Hideaki Takahashi, Gabor Toth and Hideki Matsuda. Antitumor effects of lapatinib (GW572016), a dual inhibitor of EGFR and HER-2, in combination with cisplatin or paclitaxel on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology Reports 23: 957-963, 2010
Zev A. Wainberg, Adrian Anghel, Amrita J. Desai, Raul Ayala, Tong Luo, Brent Safran, Marlena S. Fejzo, J. Randolph Hecht, Denni J. Slamon and Richard S. Finn. Lapatinib, a dual EGFR and HER2 kinase inhibitor, selectively inhibits HER2-amplified human gastric cancer cells and is synergistic with trastuzumab in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16(5): 1509-1519
- Methylxanthoxylin
Catalog No.:BCC8212
CAS No.:23121-32-6
- Fumagillin
Catalog No.:BCC2347
CAS No.:23110-15-8
- UK 370106
Catalog No.:BCC2379
CAS No.:230961-21-4
- UK 356618
Catalog No.:BCC2378
CAS No.:230961-08-7
- Neuropeptide SF (mouse, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC6054
CAS No.:230960-31-3
- Chebulagic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3262
CAS No.:23094-71-5
- Corilagin
Catalog No.:BCN2322
CAS No.:23094-69-1
- 2-amino-3-(3-bromo-5-chloro-4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8284
CAS No.:
- Sitosteryl palmitate
Catalog No.:BCN5078
CAS No.:2308-85-2
- Xylazine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4341
CAS No.:23076-35-9
- 4-Amino-N-methylphthalimide
Catalog No.:BCC8686
CAS No.:2307-00-8
- PD 102807
Catalog No.:BCC7145
CAS No.:23062-91-1
- N-[3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)phenyl]-6-iodoquinazolin-4-amine
Catalog No.:BCC9068
CAS No.:231278-20-9
- 5-(4-((3-chloro-4-((3-fluorobenzyl)oxy)phenyl)amino)quinazolin-6-yl)furan-2-carbaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCC8719
CAS No.:231278-84-5
- Mudanpioside H
Catalog No.:BCC9049
CAS No.:231280-71-0
- 6'-O-xylosyl-glycitin
Catalog No.:BCN8169
CAS No.:231288-18-9
- Tectorigenin 7-O-xylosylglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN2903
CAS No.:231288-19-0
- Heveaflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5079
CAS No.:23132-13-0
- Physalin B
Catalog No.:BCN7921
CAS No.:23133-56-4
- Strictosamide
Catalog No.:BCN5080
CAS No.:23141-25-5
- Vincosamide
Catalog No.:BCN5081
CAS No.:23141-27-7
- Pentoxyverine Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC4697
CAS No.:23142-01-0
- Oxymetazoline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4333
CAS No.:2315-02-8
- H-Glu(OMe)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2932
CAS No.:23150-65-4
Phase Ib dose-finding trial of lapatinib plus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in advanced HER2-positive breast cancer.[Pubmed:28341957]
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017 May;79(5):863-871.
PURPOSE: Combination of anthracyclines with trastuzumab is hampered by cardiotoxicity. Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and Lapatinib could represent a safer alternative to combination therapy. METHODS: In this phase Ib study with 3 + 3 dose escalation design, patients with HER2-positive advanced breast cancer received pegylated liposomal doxorubicin 30 mg/m(2) intravenously on day 1 plus Lapatinib 1250 (level 1) or 1500 (level 2) mg/day orally on days 1-21 of each 21-day cycle. The aims were to establish the maximum tolerated dose at first cycle, and the activity and safety of multiple cycles. RESULTS: Nine patients out of 11 enrolled were evaluable: 3 at level 1 and 6 at level 2. No dose-limiting toxicities occurred at dose level 1, while 1 (grade 3 diarrhea) occurred at dose level 2, leading to the expansion of this cohort to 6 patients, with no further dose-limiting toxicities. Main grade 1-2 toxicities at first cycle were leucopenia, diarrhea, elevated transaminases, mucositis. Three patients had grade 3 toxicities at subsequent cycles, including colitis, anorexia, stomatitis plus hand-foot syndrome. One partial response, 5 disease stabilizations, and 3 disease progressions were reported. CONCLUSIONS: Combination of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and Lapatinib is feasible and potentially active in pretreated HER2-positive advanced breast cancer patients. TRIAL REGISTRATION: NCT02131506 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier).
FOXO1 Suppression is a Determinant of Acquired Lapatinib-Resistance in HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer Cells Through MET Upregulation.[Pubmed:28343375]
Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jan;50(1):239-254.
PURPOSE: Lapatinib is a candidate drug for treatment of trastuzumab-resistant, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive gastric cancer (GC). Unfortunately, Lapatinib resistance renders this drug ineffective. The present study investigated the implication of forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) signaling in the acquired Lapatinib resistance in HER2-positive GC cells. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Lapatinib-resistant GC cell lines (SNU-216 LR2-8) were generated in vitro by chronic exposure of Lapatinib-sensitive, HER2-positive SNU-216 cells to Lapatinib. SNU-216 LR cells with FOXO1 overexpression were generated by stable transfection of a constitutively active FOXO1 mutant (FOXO1A3). HER2 and MET in SNU-216 LR cells were downregulated using RNA interference. The sensitivity of GC cells to Lapatinib and/or cisplatin was determined by crystal violet assay. In addition, Western blot analysis, luciferase reporter assay and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction were performed. RESULTS: SNU-216 LR cells showed upregulations of HER2 and MET, but downregulation of FOXO1 compared to parental SNU-216 cells. FOXO1 overexpression in SNU-216 LR cells significantly suppressed resistance to Lapatinib and/or cisplatin. In addition, FOXO1 negatively controlled HER2 and MET at the transcriptional level and was negatively controlled by these molecules at the post-transcriptional level. A positive crosstalk was shown between HER2 and MET, each of which increased resistance to Lapatinib and/or cisplatin. CONCLUSION: FOXO1 serves as an important linker between HER2 and MET signaling pathways through negative crosstalks and is a key regulator of the acquired Lapatinib resistance in HER2-positive GC cells. These findings provide a rationale for establishing a novel treatment strategy to overcome Lapatinib resistance in a subtype of GC patients.
HR+HER2- breast cancers with growth factor receptor-mediated EMT have a poor prognosis and lapatinib downregulates EMT in MCF-7 cells.[Pubmed:28349782]
Tumour Biol. 2017 Mar;39(3):1010428317695028.
Despite an overall good prognosis, a significant proportion of patients with hormone receptor positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative breast cancers develop distant metastases. The metastatic potential of epithelial cells is known to be regulated by tumor-stromal interaction and mediated by epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Hormone receptor positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative tumors were used to estimate markers of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and the luminal breast cancer cell line MCF-7 was used to examine the interactions between integrins and growth factor receptors in causation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. A total of 140 primary tumors were sub-divided into groups enriched for the markers of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (snail family transcriptional repressor 2 and integrin beta6) versus those with low levels. Within the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition+ tumors, there was a positive correlation between the transcripts of integrin beta6 and growth factor receptors-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and epidermal growth factor receptor. In tumors enriched for epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers, patients with tumors with the highest quartile of growth factor receptor transcripts had a shorter disease-free survival compared to patients with low growth factor receptor expression by Kaplan-Meier analysis (log rank, p = 0.03). Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition was induced in MCF-7 cells by treatment with transforming growth factor beta 1 and confirmed by upregulation of SNAI1 and SNAI2 transcripts, increase of vimentin and integrin beta6 protein, and repression of E-cadherin. Treatment of these cells with the dual-specificity tyrosine-kinase inhibitor Lapatinib led to downregulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition as indicated by lower levels of SNAI1 and SNAI2 transcripts, integrin alphavbeta6, and matrix metalloproteinase 9 protein. The results suggest that synergistic interactions between growth factor receptors and integrin beta6 could mediate epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration in a subset of luminal breast cancers and Lapatinib might be effective in disrupting this interaction.


