VillosinCAS# 160598-92-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 160598-92-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16733738 | Appearance | Powder |
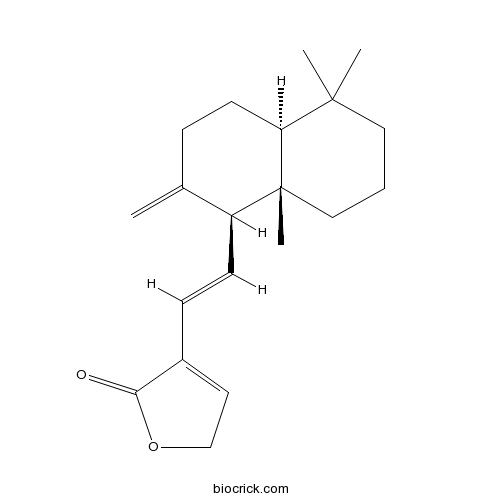
| Formula | C20H28O2 | M.Wt | 300.4 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-[(E)-2-[(1S,4aS,8aS)-5,5,8a-trimethyl-2-methylidene-3,4,4a,6,7,8-hexahydro-1H-naphthalen-1-yl]ethenyl]-2H-furan-5-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCCC2(C1CCC(=C)C2C=CC3=CCOC3=O)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HVTQZHAAIRBKHO-YSLAMIOMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H28O2/c1-14-6-9-17-19(2,3)11-5-12-20(17,4)16(14)8-7-15-10-13-22-18(15)21/h7-8,10,16-17H,1,5-6,9,11-13H2,2-4H3/b8-7+/t16-,17-,20+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Villosin shows inhibitory effects against nitric oxide production in LPS and IFN-γ-induced RAW 264.7 murine macrophages with IC50 values of 5.99 ± 1.20 ug/ml. 2. Villosin exhibits potent cytotoxic activity , it may be used as a potential lead molecule for antitumor therapeutic development. |
| Targets | NO |

Villosin Dilution Calculator

Villosin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3289 mL | 16.6445 mL | 33.2889 mL | 66.5779 mL | 83.2224 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6658 mL | 3.3289 mL | 6.6578 mL | 13.3156 mL | 16.6445 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3329 mL | 1.6644 mL | 3.3289 mL | 6.6578 mL | 8.3222 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0666 mL | 0.3329 mL | 0.6658 mL | 1.3316 mL | 1.6644 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0333 mL | 0.1664 mL | 0.3329 mL | 0.6658 mL | 0.8322 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- DMP 543
Catalog No.:BCC7331
CAS No.:160588-45-4
- Zarzissine
Catalog No.:BCN6456
CAS No.:160568-14-9
- 5,7,3',4'-Tetrahydroxy-3-methoxy-8-geranylflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6847
CAS No.:1605304-56-0
- BW 723C86 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6915
CAS No.:160521-72-2
- 12S-hydroxyandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN4700
CAS No.:869593-50-0
- Bisandrographolide A
Catalog No.:BCN4701
CAS No.:160498-00-0
- Antirhine
Catalog No.:BCN4003
CAS No.:16049-28-8
- THZ2
Catalog No.:BCC3986
CAS No.:1604810-84-5
- THZ1
Catalog No.:BCC4005
CAS No.:1604810-83-4
- 30-Oxopseudotaraxasterol
Catalog No.:BCN7135
CAS No.:160481-71-0
- 3',5,5',7-Tetrahydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN1710
CAS No.:160436-10-2
- X-NeuNAc
Catalog No.:BCC2063
CAS No.:160369-85-7
- 1,4,6-Trihydroxy-5-methoxy-7-prenylxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN1548
CAS No.:160623-47-2
- 2,3-Dihydro-3alpha-methoxynimbolide
Catalog No.:BCN7093
CAS No.:1607828-35-2
- Ardisicrenoside B
Catalog No.:BCN8078
CAS No.:160791-12-8
- Indirubin-3'-oxime
Catalog No.:BCC7185
CAS No.:160807-49-8
- AMG319
Catalog No.:BCC6510
CAS No.:1608125-21-8
- H-Thr(Bzl)-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2577
CAS No.:160841-03-2
- Ethyl 2-(3-cyano-4-isobutoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-5-thiazolecarboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC8967
CAS No.:160844-75-7
- Chrysin 8-C-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7982
CAS No.:160880-89-7
- Fmoc-Valinol
Catalog No.:BCC2694
CAS No.:160885-98-3
- Hosenkoside F
Catalog No.:BCN2520
CAS No.:160896-45-7
- Hosenkoside G
Catalog No.:BCN2272
CAS No.:160896-46-8
- Hosenkoside K
Catalog No.:BCN2577
CAS No.:160896-49-1
New Labdane diterpenes from Hedychium yunnanense with cytotoxicity and inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production.[Pubmed:26965832]
Nat Prod Res. 2016 Dec;30(23):2669-2674.
Two new labdane diterpenes, hedychenoids A (1) and B (2), were isolated from the rhizomes of Hedychium yunnanense, together with four known ones hedychenone (3), forrestin A (4), Villosin (5) and calcaratarin C (6). Their structures were determined on the basis of NMR (1D and 2D) and mass spectroscopic analysis. Compounds 2, 3 and 5 exhibited cytotoxicity against SGC-7901 with IC50 values of 14.88 +/- 0.52, 7.08 +/- 0.21 and 7.76 +/- 0.21 mug/ml, 3 and 5 against HeLa with IC50 values of 9.76 +/- 0.48 and 13.24 +/- 0.63 mug/ml, respectively. Compounds 2, 5 showed inhibitory effects against nitric oxide production in LPS and IFN-gamma-induced RAW 264.7 murine macrophages with IC50 values of 6.57 +/- 0.88 and 5.99 +/- 1.20 mug/ml, respectively.
Abietane diterpenoids from Clerodendrum trichotomum and correction of NMR data of Villosin C and B.[Pubmed:25230490]
Nat Prod Commun. 2014 Jul;9(7):907-10.
Nine abietane diterpenoids (1-9) were isolated from the stems of Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb. and identified by spectroscopic methods. Furthermore, corrected NMR data is provided for Villosin C (1) and B (2) whose absolute configurations were elucidated from circular dichroism (CD) data. All isolates were tested for cytotoxicity against four cancer cell lines (A549, HepG-2, MCF-7 and 4T1). Compounds 1, 2, 3, 4 and 8 were found to have remarkable cytotoxic effects with IC50 values ranging from 8.79 to 35.46 microM.
Rubus fruticosus (blackberry) use as an herbal medicine.[Pubmed:25125882]
Pharmacogn Rev. 2014 Jul;8(16):101-4.
Wild grown European blackberry Rubus fruticosus) plants are widespread in different parts of northern countries and have been extensively used in herbal medicine. The result show that European blackberry plants are used for herbal medicinal purpose such as antimicrobial, anticancer, antidysentery, antidiabetic, antidiarrheal, and also good antioxidant. Blackberry plant (R. fruticosus) contains tannins, gallic acid, Villosin, and iron; fruit contains vitamin C, niacin (nicotinic acid), pectin, sugars, and anthocyanins and also contains of berries albumin, citric acid, malic acid, and pectin. Some selected physicochemical characteristics such as berry weight, protein, pH, total acidity, soluble solid, reducing sugar, vitamin C, total antioxidant capacity, antimicrobial screening of fruit, leaves, root, and stem of R. fruticosus, and total anthocyanins of four preselected wild grown European blackberry (R. fruticosus) fruits are investigated. Significant differences on most of the chemical content detect among the medicinal use. The highest protein content (2%), the genotypes with the antioxidant activity of standard butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) studies 85.07%. Different cultivars grown in same location consistently show differences in antioxidant capacity.
Labdane-type diterpenes from Hedychium gardnerianum with potent cytotoxicity against human small cell lung cancer cells.[Pubmed:19960422]
Phytother Res. 2010 Jul;24(7):1009-13.
Seven labdane-type diterpenes, coronarin E, coronarin A, yunnancoronarin A, yunnancoronarin B, hedyforrestin B, Villosin, and hedyforrestin C were isolated from the rhizome of Hedychium gardnerianum and evaluated for cytotoxic activity against human small cell lung cancer (NCI-H187) and non-cancerous Vero cells. The results showed that Villosin exhibited potent cytotoxic activity with IC(50) of 0.40 microM, which was higher than that of the drug ellipticine (IC(50) 1.79 microM). Moreover, ellipticine was very toxic to Vero cells (IC(50) 7.47 microM) whereas the toxicity of Villosin was undetectable at concentration lower than 166.42 microM. The results have indicated that the lactone ring is essential for high cytotoxic activity and that the presence of a hydroxyl group at the 6 or 7 position causes decrease in activity. The very high cytotoxicity against the NCI-H187 cells and the exceptionally high selectivity index (>416) of Villosin suggested that this compound may be used as a potential lead molecule for antitumor therapeutic development.


