Dacomitinib (PF299804, PF299)HER inhibitor CAS# 1110813-31-4 |
- Icotinib Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1639
CAS No.:1204313-51-8
- WZ8040
Catalog No.:BCC1075
CAS No.:1214265-57-2
- AZD-9291
Catalog No.:BCC4120
CAS No.:1421373-65-0
- PD168393
Catalog No.:BCC1157
CAS No.:194423-15-9
- Pelitinib (EKB-569)
Catalog No.:BCC1118
CAS No.:257933-82-7
- AZD8931 (Sapitinib)
Catalog No.:BCC3734
CAS No.:848942-61-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1110813-31-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11511120 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H25ClFN5O2 | M.Wt | 469.94 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | PF-00299804; PF-299804 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 41.67 mg/mL (88.67 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
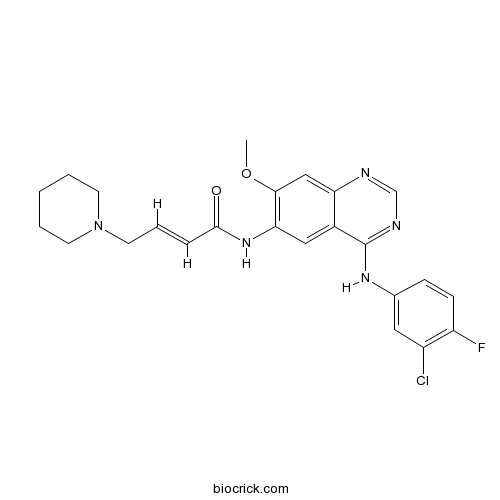
| Chemical Name | (E)-N-[4-(3-chloro-4-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yl]-4-piperidin-1-ylbut-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)N=CN=C2NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)F)Cl)NC(=O)C=CCN4CCCCC4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LVXJQMNHJWSHET-AATRIKPKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H25ClFN5O2/c1-33-22-14-20-17(24(28-15-27-20)29-16-7-8-19(26)18(25)12-16)13-21(22)30-23(32)6-5-11-31-9-3-2-4-10-31/h5-8,12-15H,2-4,9-11H2,1H3,(H,30,32)(H,27,28,29)/b6-5+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | PF-299804 is a potent, irreversible inhibitor of ErbB for EGFR with IC50 of 6 nM. | |||||
| Targets | ErbB1 | ErbB2 | ErbB4 | |||
| IC50 | 6 nM | 45.7 nM | 73.7 nM | |||

Dacomitinib (PF299804, PF299) Dilution Calculator

Dacomitinib (PF299804, PF299) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1279 mL | 10.6397 mL | 21.2793 mL | 42.5586 mL | 53.1983 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4256 mL | 2.1279 mL | 4.2559 mL | 8.5117 mL | 10.6397 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2128 mL | 1.064 mL | 2.1279 mL | 4.2559 mL | 5.3198 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0426 mL | 0.2128 mL | 0.4256 mL | 0.8512 mL | 1.064 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0213 mL | 0.1064 mL | 0.2128 mL | 0.4256 mL | 0.532 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 6 nM (EGFR); 45.7 nM (ERBB2); 73.7 nM (ERBB4)
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; ErbB-1; HER1 in humans) is the cell-surface receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family (EGF-family) of extracellular protein ligands. The epidermal growth factor receptor is a member of the ErbB family of receptors, a subfamily of four closely related receptor tyrosine kinases: EGFR (ErbB-1), HER2/c-neu (ErbB-2), Her 3 (ErbB-3) and Her 4 (ErbB-4). Mutations affecting EGFR expression or activity could result in cancer. Dacomitinib (PF-00299804) is an irreversible small molecule pan-HER inhibitor.
In vitro: Dacomitinib reduced the phosphorylation of HER2, EGFR, HER4, AKT, andERKin the majority of sensitive lines. Dacomitinib exerted its antiproliferative effect through a combined G0–G1 arrest and an induction of apoptosis. Dacomitinib inhibited growth in several HER2-amplified lines with de novo and acquired resistance to trastuzumab. Dacomitinib maintained a high activity in lines with acquired resistance to lapatinib. This study identifies HER2-amplified breast cancer lines as most sensitive to the antiproliferative effect of dacomitinib and provides a strong rationale for its clinical testing in HER2-amplified breast cancers resistant to trastuzumab and lapatinib [1].
In vivo: To evaluate the in vivo efficacy of PF00299804, the authors generated xenografts in nu/nu mice using HCC827 GFP and HCC827 Del/T790M cells and treated the mice with PF00299804. PF00299804 effectively inhibited the growth of HCC827 GFP xenografts. PF00299804 treatment was substantially more effective at inhibiting growth of this xenograft model than gefinitib. Thus, these preclinical models suggest that PF00299804 may be quite effective against lung cancers that become resistant to gefitinib or erlotinib via acquisition of a T790M mutation in EGFR [2].
Clinical trial: Dacomitinib (PF-00299804) is an experimental drug candidate under development by Pfizer for the treatment of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. It is a selective and irreversible inhibitor of EGFR. Dacomitinib has advanced to several Phase III clinical trials. The results of the first trials were disappointing, with a failure to meet the study goals. Additional Phase III trials are ongoing (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dacomitinib).
References:
[1] Kalous O, Conklin D, Desai AJ, O'Brien NA, Ginther C, Anderson L, Cohen DJ, Britten CD, Taylor I, Christensen JG, Slamon DJ, Finn RS. Dacomitinib (PF-00299804), an irreversible Pan-HER inhibitor, inhibits proliferation of HER2-amplified breast cancer cell lines resistant to trastuzumab and lapatinib. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(9):1978-87.
[2] Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Gale CM, Lifshits E, Gonzales AJ, Shimamura T, Zhao F, Vincent PW, Naumov GN, Bradner JE, Althaus IW, Gandhi L, Shapiro GI, Nelson JM, Heymach JV, Meyerson M, Wong KK, J?nne PA. PF00299804, an irreversible pan-ERBB inhibitor, is effective in lung cancer models with EGFR and ERBB2 mutations that are resistant to gefitinib. Cancer Res. 2007;67(24):11924-32.
- Fmoc-Ser(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3546
CAS No.:111061-56-4
- Fmoc-D-Lys(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2594
CAS No.:111061-54-2
- N-Benzoyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1622
CAS No.:111059-46-2
- Ginkgolic acid C17:1
Catalog No.:BCN5334
CAS No.:111047-30-4
- 2-(2'-Hydroxy-4'-methylphenyl)propionic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7980
CAS No.:111044-84-9
- Annonacin
Catalog No.:BCN4734
CAS No.:111035-65-5
- Ruthenium Red
Catalog No.:BCC7067
CAS No.:11103-72-3
- Vitamin A2
Catalog No.:BCC8367
CAS No.:11103-57-4
- Pioglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC4927
CAS No.:111025-46-8
- Muricatide
Catalog No.:BCN1780
CAS No.:111025-01-5
- 2-Amino-1-phenylethanol
Catalog No.:BCN1779
CAS No.:7568-93-6
- Efonidipine hydrochloride monoethanolate
Catalog No.:BCC7767
CAS No.:111011-76-8
- FERb 033
Catalog No.:BCC7701
CAS No.:1111084-78-6
- 14-Hydroxy sprengerinin C
Catalog No.:BCN2777
CAS No.:1111088-89-1
- NF 110
Catalog No.:BCC7404
CAS No.:111150-22-2
- PF-04880594
Catalog No.:BCC3998
CAS No.:1111636-35-1
- 1,2-O-Dilinoleoyl-3-O-beta-D-galactopyranosylracglycerol
Catalog No.:BCN6768
CAS No.:111187-15-6
- 7,3',4'-Trihydroxy-3-benzyl-2H-chromene
Catalog No.:BCN1621
CAS No.:1111897-60-9
- CGS 20625
Catalog No.:BCC7375
CAS No.:111205-55-1
- Episappanol
Catalog No.:BCN7940
CAS No.:111254-18-3
- Sappanol
Catalog No.:BCN3735
CAS No.:111254-19-4
- Lestaurtinib
Catalog No.:BCC2440
CAS No.:111358-88-4
- Zileuton
Catalog No.:BCC2515
CAS No.:111406-87-2
- Azadirachtin
Catalog No.:BCC8123
CAS No.:11141-17-6
Preclinical Test of Dacomitinib, an Irreversible EGFR Inhibitor, Confirms Its Effectiveness for Glioblastoma.[Pubmed:25939761]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Jul;14(7):1548-58.
Glioblastomas (GBM) are devastating tumors in which there has been little clinical improvement in the last decades. New molecularly directed therapies are under development. EGFR is one of the most promising targets, as this receptor is mutated and/or overexpressed in nearly half of the GBMs. However, the results obtained with first-generation tyrosine-kinase inhibitors have been disappointing with no clear predictive markers of tumor response. Here, we have tested the antitumoral efficacy of a second-generation inhibitor, dacomitinib (PF299804, Pfizer), that binds in an irreversible way to the receptor. Our results confirm that dacomitinib has an effect on cell viability, self-renewal, and proliferation in EGFR-amplified +/- EGFRvIII GBM cells. Moreover, systemic administration of dacomitinib strongly impaired the in vivo tumor growth rate of these EGFR-amplified cell lines, with a decrease in the expression of stem cell-related markers. However, continuous administration of the compound was required to maintain the antitumor effect. The data presented here confirm that dacomitinib clearly affects receptor signaling in vivo and that its strong antitumoral effect is independent of the presence of mutant receptor isoforms although it could be affected by the PTEN status (as it is less effective in a PTEN-deleted GBM line). Dacomitinib is being tested in second line for EGFR-amplified GBMs. We hope that our results could help to select retrospectively molecular determinants of this response and to implement future trials with dacomitinib (alone or in combination with other inhibitors) in newly diagnosed GBMs.
Resistance to irreversible EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors through a multistep mechanism involving the IGF1R pathway.[Pubmed:23172312]
Cancer Res. 2013 Jan 15;73(2):834-43.
The clinical efficacy of EGF receptor (EGFR) kinase inhibitors gefitinib and erlotinib is limited by the development of drug resistance. The most common mechanism of drug resistance is the secondary EGFR T790M mutation. Strategies to overcome EGFR T790M-mediated drug resistance include the use of mutant selective EGFR inhibitors, including WZ4002, or the use of high concentrations of irreversible quinazoline EGFR inhibitors such as PF299804. In the current study, we develop drug-resistant versions of the EGFR-mutant PC9 cell line, which reproducibly develops EGFR T790M as a mechanism of drug resistance to gefitinib. Neither PF299804-resistant nor WZ4002-resistant clones of PC9 harbor EGFR T790M. Instead, they have shown activated insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) signaling as a result of loss of expression of IGFBP3 with the IGF1R inhibitor, BMS 536924, restoring EGFR inhibitor sensitivity. Intriguingly, prolonged exposure to either PF299804 or WZ4002 results in the emergence of a more drug-resistant subclone that exhibits ERK activation. A MEK inhibitor, CI-1040, partially restores sensitivity to the EGFR/IGF1R inhibitor combination. Moreover, an IGF1R or MEK inhibitor used in combination with either PF299804 or WZ4002 completely prevents the emergence of drug-resistant clones in this model system. Our studies suggest that more effective means of inhibiting EGFR T790M will prevent the emergence of this common drug resistance mechanism in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. However, multiple drug resistance mechanisms can still emerge. Preventing the emergence of drug resistance, by targeting pathways that become activated in resistant cancers, may be a more effective clinical strategy.


