AZD-9291Mutated forms EGFR inhibitor CAS# 1421373-65-0 |
- Dacomitinib (PF299804, PF299)
Catalog No.:BCC3683
CAS No.:1110813-31-4
- CO-1686 (AVL-301)
Catalog No.:BCC1490
CAS No.:1374640-70-6
- Compound 56
Catalog No.:BCC3615
CAS No.:171745-13-4
- Erlotinib Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3645
CAS No.:183319-69-9
- Gefitinib hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1591
CAS No.:184475-55-6
- BIBX 1382
Catalog No.:BCC1418
CAS No.:196612-93-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1421373-65-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71496458 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C28H33N7O2 | M.Wt | 499.61 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Osimertinib; Mereletinib | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (200.16 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
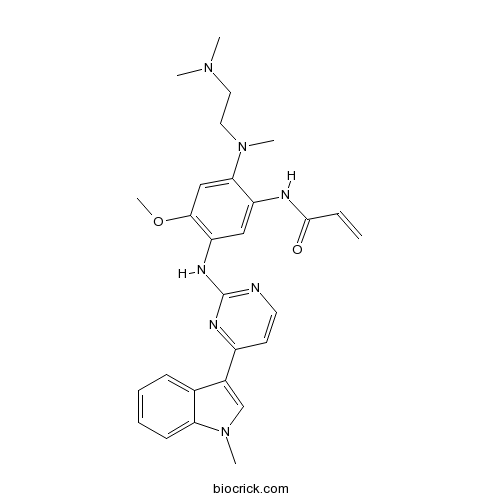
| Chemical Name | N-[2-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl-methylamino]-4-methoxy-5-[[4-(1-methylindol-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]phenyl]prop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | CN1C=C(C2=CC=CC=C21)C3=NC(=NC=C3)NC4=C(C=C(C(=C4)NC(=O)C=C)N(C)CCN(C)C)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DUYJMQONPNNFPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C28H33N7O2/c1-7-27(36)30-22-16-23(26(37-6)17-25(22)34(4)15-14-33(2)3)32-28-29-13-12-21(31-28)20-18-35(5)24-11-9-8-10-19(20)24/h7-13,16-18H,1,14-15H2,2-6H3,(H,30,36)(H,29,31,32) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AZD9291 is a novel oral, potent and selective third generation irreversible inhibitor of mutated forms EGFR with IC50 values of 12.92 nM, 11.44 nM and 493.8 nM for Exon 19 deletion EGFR, L858R/T790M EGFR and wild type EGFR, respectively. | |||||
| Targets | Exon 19 deletion EGFR | L858R/T790M EGFR | wild type EGFR | |||
| IC50 | 12.92 nM | 11.44 nM | 493.8 nM | |||
| Cell experiment[1]: | |
| Cell lines | Human lung cancer cells with EGFR-mutations or wild type EGFR stable expression |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Applications | AZD9291 potently inhibits EGFR phosphorylation in EGFRm+ (e.g. PC9; < 25 nM) and EGFR m+/T790M (e.g. H1975; < 25 nM) cell lines in vitro, whilst demonstrating much less activity against wild-type EGFR lines (e.g. LoVo; > 500 nM). Consistently, AZD9291 showed significantly more potent inhibition of proliferation in mutant EGFR cell lines compared to wild-type in vitro. |
| Animal experiment[1]: | |
| Animal models | EGFRm+ and EGFRm+/T790M transgenic mice |
| Dosage form | 5 mg/kg |
| Application | AZD9291 administered once daily orally at 5 mg/kg caused profound regression of tumours across EGFRm+ (PC9; 178% growth inhibition) and EGFRm+/T790M (H1975; 119% growth inhibition) tumour models in vivo, after 14 days dosing. Furthermore 5 mg/kg AZD9291 was sufficient to cause significant shrinkage of EGFRm+ and EGFRm+/T790M transgenic mouse lung tumours. Tumour growth inhibition was associated with profound inhibition of EGFR phosphorylation and key downstream signaling pathways such as AKT and ERK. Chronic long-term treatment of PC9 and H1975 xenograft tumours with AZD9291 led to a complete and sustained macroscopic response, with no visible tumours after 40 days dosing, and being maintained beyond 100 days. Furthermore, pre-clinical data also indicates that AZD9291 could target tumours that have acquired resistance to the more recently identified HER2-amplification mechanism, thus potentially extending its benefit in TKI resistant patients. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: 1. Darren Cross1, Sue Ashton1, Caroline Nebhan2 et al. AZD9291: an irreversible, potent and selective third generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) targeting EGFR activating (EGFRm+) and resistance (T790M) mutations in advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 2013;12(11 Suppl):A109. | |

AZD-9291 Dilution Calculator

AZD-9291 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0016 mL | 10.0078 mL | 20.0156 mL | 40.0312 mL | 50.039 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4003 mL | 2.0016 mL | 4.0031 mL | 8.0062 mL | 10.0078 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2002 mL | 1.0008 mL | 2.0016 mL | 4.0031 mL | 5.0039 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.04 mL | 0.2002 mL | 0.4003 mL | 0.8006 mL | 1.0008 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.02 mL | 0.1001 mL | 0.2002 mL | 0.4003 mL | 0.5004 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AZD-9291 is an irreversible inhibitor of mutant EGFR kinase with IC50 values of 15nM, 17nM and 480nM, respectively for L858R/T790M, ex19del and wild-type EGFR [1].
A series of mutations cause the resistance of EGFR, AZD-9291 is developed for an irreversible and selective inhibitor of the mutant EGFR. AZD-9291 binds to the ATP binding site of EGFR by targeting Cys 797. In EGFR recombinant enzyme assay, AZD-9291 shows about 200 times greater potency against the mutant EGFR than wild-type EGFR. AZD-9291 does not exhibit significant activity towards other receptor kinase. In vitro assays show that AZD-9291can inhibit EGFR phosphorylation with lower IC50 value in cell lines harboring sensitising EGFR mutants than in wild-type cell lines. Additionally, AZD9291 can induce profound shrinkage in mutant EGFR at low doses in xenograft models. This also happens in transgenic mouse tumor models. Mice treated with AZD9291 at the dose of 5 mg/kg/day display 80% reduction in tumor volume [1].
References:
[1] Darren A. E. Cross, Susan E Ashton, Serban Ghiorghiu, et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discovery. 2014, June.
- Mutant EGFR inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4119
CAS No.:1421373-62-7
- Mutated EGFR-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5444
CAS No.:1421372-66-8
- CYM 50769
Catalog No.:BCC6337
CAS No.:1421365-63-0
- (+)-Ketoconazole
Catalog No.:BCC4249
CAS No.:142128-59-4
- WS6
Catalog No.:BCC5566
CAS No.:1421227-53-3
- WS 3
Catalog No.:BCC7519
CAS No.:1421227-52-2
- Isosalvianolic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN3476
CAS No.:142115-17-1
- BIM 189
Catalog No.:BCC5934
CAS No.:142062-55-3
- Caproic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9218
CAS No.:142-62-1
- NVP-TNKS656
Catalog No.:BCC6541
CAS No.:1419949-20-4
- NSC 625987
Catalog No.:BCC7269
CAS No.:141992-47-4
- Methyl 4-Hydroxyphenylacetate
Catalog No.:BCN1571
CAS No.:14199-15-6
- AZD-9291 mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4121
CAS No.:1421373-66-1
- AZ5104
Catalog No.:BCC6389
CAS No.:1421373-98-9
- LY3039478
Catalog No.:BCC2105
CAS No.:1421438-81-4
- Sweroside
Catalog No.:BCN6219
CAS No.:14215-86-2
- Hederacoside C
Catalog No.:BCN2329
CAS No.:14216-03-6
- GZD824
Catalog No.:BCC4389
CAS No.:1421783-64-3
- KPT-276
Catalog No.:BCC4445
CAS No.:1421919-75-6
- Taxumairol B
Catalog No.:BCN6940
CAS No.:142203-64-3
- 9-Dihydro-13-acetylbaccatin III
Catalog No.:BCC1315
CAS No.:142203-65-4
- Catestatin
Catalog No.:BCC5935
CAS No.:142211-96-9
- Protionamide
Catalog No.:BCC4834
CAS No.:14222-60-7
- 2'-Rhamnoechinacoside
Catalog No.:BCN8219
CAS No.:1422390-59-7
Small-molecule EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer.[Pubmed:24921970]
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014 Oct;23(10):1333-48.
INTRODUCTION: EGFR has been implicated in various malignancies such as NSCLC, breast, head and neck, and pancreatic cancer. Numerous drugs have been developed in order to target the tyrosine domain of EGFR as an approach in cancer treatment. AREAS COVERED: This article focuses on the different generations of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). This spans from the emergence of the first-generation EGFR-TKIs to overcoming drug resistance using second-generation EGFR-TKIs and to reducing adverse effect (AE) using mutant-selective third-generation EGFR-TKIs. EXPERT OPINION: Current TKI treatment is frequently accompanied by drug resistance and/or serious AEs. There has been the promise of advancements in second-generation EGFR-TKIs that could overcome drug resistance, acting as second- or third-line salvage treatment, but this promise has yet to be met. That being said, both issues are currently being addressed with mutant-selective EGFR-TKIs with the expectation of bringing more EGFR-targeted therapy into the next phase of cancer therapy in the future.


