ProtionamideCAS# 14222-60-7 |
- Laminin (925-933)
Catalog No.:BCC1015
CAS No.:110590-60-8
- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Peptide (985-996)
Catalog No.:BCC1014
CAS No.:96249-43-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 14222-60-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 666418 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H12N2S | M.Wt | 180.27 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Protionamide | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM | ||
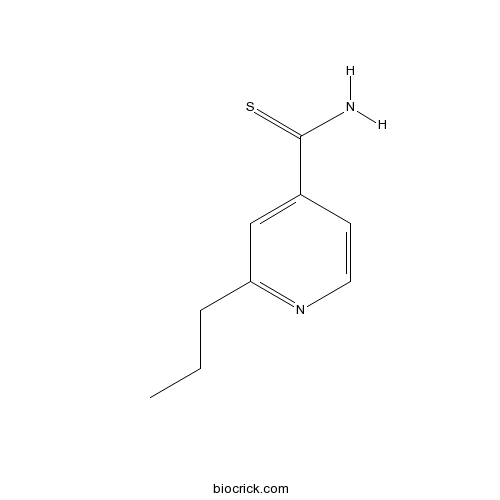
| Chemical Name | 2-propylpyridine-4-carbothioamide | ||
| SMILES | CCCC1=NC=CC(=C1)C(=S)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VRDIULHPQTYCLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H12N2S/c1-2-3-8-6-7(9(10)12)4-5-11-8/h4-6H,2-3H2,1H3,(H2,10,12) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Protionamide (or prothionamide) is a drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis; has also been tested for use in the treatment of leprosy.
Target: Anti tuberculosis
Although ETH and PTH are both potent drugs against M. tuberculosis (MIC = ~0.5 μg/ml) (24), they do not affect E. coli growth, even at very high concentrations (100 μg/ml), which is primarily caused by the absence of an EthA homologue in E. coli [1]. Clinical improvement was noted in 74% of the patients treated with ethionamide and in 83% of those treated with prothionamide. Therapy was well tolerated and drug-related hepatotoxicity did not require discontinuation of therapy. The 500-mg dose of both ethionamide and prothionamide resulted in loss in Mycobacterium leprae viability more rapidly than did the 250-mg dose, and prothionamide at both dose levels was superior to the equivalent dose of ethionamide [2]. References: | |||||

Protionamide Dilution Calculator

Protionamide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.5472 mL | 27.7362 mL | 55.4723 mL | 110.9447 mL | 138.6809 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1094 mL | 5.5472 mL | 11.0945 mL | 22.1889 mL | 27.7362 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5547 mL | 2.7736 mL | 5.5472 mL | 11.0945 mL | 13.8681 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1109 mL | 0.5547 mL | 1.1094 mL | 2.2189 mL | 2.7736 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0555 mL | 0.2774 mL | 0.5547 mL | 1.1094 mL | 1.3868 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Protionamide
- Catestatin
Catalog No.:BCC5935
CAS No.:142211-96-9
- 9-Dihydro-13-acetylbaccatin III
Catalog No.:BCC1315
CAS No.:142203-65-4
- Taxumairol B
Catalog No.:BCN6940
CAS No.:142203-64-3
- KPT-276
Catalog No.:BCC4445
CAS No.:1421919-75-6
- GZD824
Catalog No.:BCC4389
CAS No.:1421783-64-3
- Hederacoside C
Catalog No.:BCN2329
CAS No.:14216-03-6
- Sweroside
Catalog No.:BCN6219
CAS No.:14215-86-2
- LY3039478
Catalog No.:BCC2105
CAS No.:1421438-81-4
- AZ5104
Catalog No.:BCC6389
CAS No.:1421373-98-9
- AZD-9291 mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4121
CAS No.:1421373-66-1
- AZD-9291
Catalog No.:BCC4120
CAS No.:1421373-65-0
- Mutant EGFR inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4119
CAS No.:1421373-62-7
- 2'-Rhamnoechinacoside
Catalog No.:BCN8219
CAS No.:1422390-59-7
- Rauvotetraphylline A
Catalog No.:BCN7052
CAS No.:1422506-49-7
- Rauvotetraphylline B
Catalog No.:BCN7056
CAS No.:1422506-50-0
- Rauvotetraphylline C
Catalog No.:BCN7055
CAS No.:1422506-51-1
- Rauvotetraphylline D
Catalog No.:BCN7054
CAS No.:1422506-52-2
- Rauvotetraphylline E
Catalog No.:BCN7051
CAS No.:1422506-53-3
- Kenpaullone
Catalog No.:BCC7047
CAS No.:142273-20-9
- Shizukaol B
Catalog No.:BCN6983
CAS No.:142279-40-1
- Shizukaol C
Catalog No.:BCN6225
CAS No.:142279-41-2
- Shizukaol D
Catalog No.:BCN6226
CAS No.:142279-42-3
- Teuvincenone H
Catalog No.:BCN6227
CAS No.:142299-73-8
- L-701,324
Catalog No.:BCC6842
CAS No.:142326-59-8
Simple, rapid and sensitive determination of protionamide in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed:9613970]
J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1998 Apr 10;707(1-2):338-41.
A simple high-performance liquid chromatography method has been developed that allows the sensitive determination of Protionamide (2-n-propyl-pyridine-4-carboxylic acid thioamide, PTH) in human serum. After pretreatment of the serum with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and centrifugation the supernatants were neutralized using NaHCO3. PTH was separated on a Kromasil 100 C4 column (acetonitrile-sodium tetraborate buffer pH 8-dibutylamine) and determined photometrically at 291 nm. The lower limit of quantification for 300 microl serum precipitated with 60 microl TCA and injection of 50 microl was 27 microg/l and linearity was observed up to 15 mg/l.
[Clinical analysis of protionamide and para-aminosalicylic acid induced hepatotoxicity in 129 cases].[Pubmed:24433800]
Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2013 Oct;36(10):737-40.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate drug-induced liver injury (DILI) in tuberculosis (TB) patients treated with Protionamide (Pto) and (or) para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS), and therefore to provide data for using second-line anti-tuberculosis drugs and risk prediction of liver damage. METHODS: A retrospective analysis was performed for TB patients treated with regimens containing Pto and (or) PAS in Beijing Chest Hospital during Jan. 2008 to Jan. 2013. Cases with DILI were identified, and associated factors including patients' age and gender, time of onset, severity, clinical manifestations and prognosis of DILI were analyzed. The 2 groups were compared with chi(2) test. P < 0.05 was considered to be significant. RESULTS: A total of 1714 cases were admitted, among whom 226 experienced liver damage during treatment, of which 97 cases were excluded because of underlying alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis B and C. Finally, 129 cases were diagnosed as having DILI, resulting in an overall incidence of 7.5% (129/1714), being 9.2% (59/641) in females, and 6.5% (70/1073) in males (chi(2) = 4.143, P < 0.05). DILI in most patients occurred between 1 week to 2 months, with 30.2% (39/129) within 2-4 weeks. 47.3% (61/129) of the patients showed no obvious clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Among different regimens, combination of Pto, PAS and PZA resulted in the highest rate of DILI (20.7%, 19/92), while the rate was 9.8% (8/82) for the combination of Pto and PZA, P < 0.05. CONCLUSIONS: DILI caused by Pto and PAS should be taken into account, especially in female patients and for multi-drug combination therapy. Liver function should be monitored even in patients without related clinical manifestations for early identification and treatment, and therefore avoiding severe liver damage.
New forms of multidrug therapy for the treatment of leprosy. First report for the practice on rifampicin + sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim + protionamide and rifampicin + sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim + isoniazid.[Pubmed:2758869]
Chemotherapy. 1989;35(2):133-9.
Since 1970, when the lifelong monotherapy with dapsone (DDS) in leprosy could be replaced by short-term combination therapy with rifampicin + isoniazid + Protionamide + DDS (Isoprodian-RMP), chemotherapeutic research was faced with two problems: (1) to find alternative treatment regimens for cases of intolerance, and (2) to work out forms of therapy allowing a further reduction of the average treatment time of 2 years. The present paper describes the attempts made to find solutions to these problems. With two new combinations, alternatives have become available, and the average treatment time is shortened to 6 months. Both combinations are also effective in tuberculosis.
[Ofloxacin-cycloserine-protionamide-INH combination against treatment refractory lung tuberculosis].[Pubmed:7724506]
Pneumologie. 1995 Feb;49(2):72-6.
Multiresistant tuberculoses are on the increase. The conversion rates in "additional" therapy are only modest. 17 multiresistant patients and 6 treatment-refractory tuberculoses were treated by us with ofloxacin-cycloserin-Protionamide-INH. 16 of these patients were HIV positive. 21 patients converted after 3 months of treatment by the latest. 3 patients died of HIV syndrome. There was otherwise no difference between HIV positive and HIV negative patients. As a rule, the combination was well tolerated. In multiresistant tuberculosis, it is mandatory to administer at least 3 drugs to which there is no resistance.


