KenpaulloneGSK-3 inhibitor. Also inhibits cdks CAS# 142273-20-9 |
- Rocilinostat (ACY-1215)
Catalog No.:BCC2144
CAS No.:1316214-52-4
- LY 294002
Catalog No.:BCC3659
CAS No.:154447-36-6
- (±)-Bay K 8644
Catalog No.:BCC3918
CAS No.:71145-03-4
- Omeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1254
CAS No.:73590-58-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 142273-20-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3820 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H11BrN2O | M.Wt | 327.18 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 9-Bromopaullone; NSC-664704 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 35 mg/mL (106.97 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
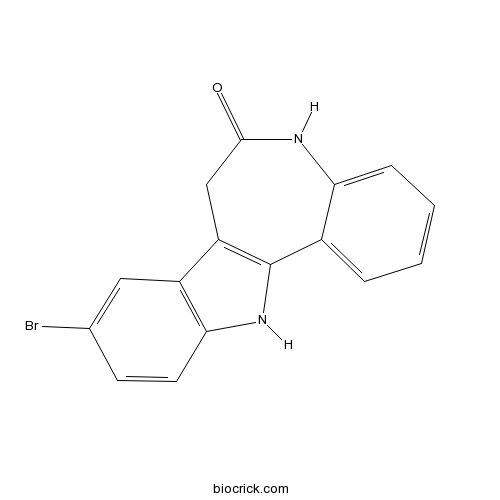
| Chemical Name | 9-bromo-7,12-dihydro-5H-indolo[3,2-d][1]benzazepin-6-one | ||
| SMILES | C1C2=C(C3=CC=CC=C3NC1=O)NC4=C2C=C(C=C4)Br | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QQUXFYAWXPMDOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H11BrN2O/c17-9-5-6-14-11(7-9)12-8-15(20)18-13-4-2-1-3-10(13)16(12)19-14/h1-7,19H,8H2,(H,18,20) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent inhibitor of CDK1/cyclin B and GSK-3β (IC50 values are 0.4 and 0.23 μM respectively). Also inhibits CDK2/cyclin A, CDK2/cyclin E and CDK5/cyclin/p35 (IC50 values are 0.68, 7.5 and 0.85 μM respectively). Selective over c-src (IC50 = 15 μM), casein kinase 2 (IC50 = 20 μM), ERK1 (IC50 = 20 μM), ERK2 (IC50 = 9 μM) and a range of other protein kinases (IC50 values > 35 μM). Generates induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from somatic cells when used in combination with reprogramming factors; can replace Klf4. |

Kenpaullone Dilution Calculator

Kenpaullone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0564 mL | 15.2821 mL | 30.5642 mL | 61.1284 mL | 76.4105 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6113 mL | 3.0564 mL | 6.1128 mL | 12.2257 mL | 15.2821 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3056 mL | 1.5282 mL | 3.0564 mL | 6.1128 mL | 7.6411 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0611 mL | 0.3056 mL | 0.6113 mL | 1.2226 mL | 1.5282 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0306 mL | 0.1528 mL | 0.3056 mL | 0.6113 mL | 0.7641 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Kenpaullone is a potent inhibitor of CDK1/cyclin B and GSK-3β, with IC50s of 0.4 μM and 23 nM, and also inhibits CDK2/cyclin A, CDK2/cyclin E, and CDK5/p25 with IC50s of 0.68 μM, 7.5 μM, 0.85 μM, respectively.
In Vitro:Kenpaullone shows much less effect on c-src (IC50, 15 μM), casein kinase 2 (IC50, 20 μM), erk 1 (IC50, 20 μM), and erk 2 (IC50, 9 μM). Kenpaullone acts by competitive inhibition of ATP binding, and the apparent Ki is 2.5 μM. Kenpaullone can inhibit the growth of tumor cells in culture (mean GI50, 43 μM) and causes altered cell cycle progression most clearly revealed under conditions of recovery from serum starvation[1]. Kenpaullone demonstrates a wide range of biological utility, extending from maintenance of pancreatic β cell survival and proliferation to the induction of apoptosis in cancer cells[2].
References:
[1]. Zaharevitz DW, et al. Discovery and initial characterization of the paullones, a novel class of small-molecule inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases. Cancer Res. 1999 Jun 1;59(11):2566-9.
[2]. Lyssiotis CA, et al. Reprogramming of murine fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells with chemical complementation of Klf4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jun 2;106(22):8912-7.
- Rauvotetraphylline E
Catalog No.:BCN7051
CAS No.:1422506-53-3
- Rauvotetraphylline D
Catalog No.:BCN7054
CAS No.:1422506-52-2
- Rauvotetraphylline C
Catalog No.:BCN7055
CAS No.:1422506-51-1
- Rauvotetraphylline B
Catalog No.:BCN7056
CAS No.:1422506-50-0
- Rauvotetraphylline A
Catalog No.:BCN7052
CAS No.:1422506-49-7
- 2'-Rhamnoechinacoside
Catalog No.:BCN8219
CAS No.:1422390-59-7
- Protionamide
Catalog No.:BCC4834
CAS No.:14222-60-7
- Catestatin
Catalog No.:BCC5935
CAS No.:142211-96-9
- 9-Dihydro-13-acetylbaccatin III
Catalog No.:BCC1315
CAS No.:142203-65-4
- Taxumairol B
Catalog No.:BCN6940
CAS No.:142203-64-3
- KPT-276
Catalog No.:BCC4445
CAS No.:1421919-75-6
- GZD824
Catalog No.:BCC4389
CAS No.:1421783-64-3
- Shizukaol B
Catalog No.:BCN6983
CAS No.:142279-40-1
- Shizukaol C
Catalog No.:BCN6225
CAS No.:142279-41-2
- Shizukaol D
Catalog No.:BCN6226
CAS No.:142279-42-3
- Teuvincenone H
Catalog No.:BCN6227
CAS No.:142299-73-8
- L-701,324
Catalog No.:BCC6842
CAS No.:142326-59-8
- Adefovir Dipivoxil
Catalog No.:BCC5025
CAS No.:142340-99-6
- H-D-Phe-pNA
Catalog No.:BCC3015
CAS No.:14235-18-8
- SP2509
Catalog No.:BCC5578
CAS No.:1423715-09-6
- FR 139317
Catalog No.:BCC5733
CAS No.:142375-60-8
- 7alpha-Hydroxy-4,11-cadinadiene-3,8-dione
Catalog No.:BCN7057
CAS No.:1423809-64-6
- Didemethylpseudoaspidin AA
Catalog No.:BCN3777
CAS No.:142382-28-3
- Mesterolone
Catalog No.:BCC9023
CAS No.:1424-00-6
New thiophene analogues of kenpaullone: synthesis and biological evaluation in breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:16122578]
Eur J Med Chem. 2005 Aug;40(8):757-63.
Thieno analogues of Kenpaullone have been synthesized using an established method. We investigated the effect of five structural analogues of Kenpaullone on vincristine sensitive and resistant MCF7 (human mammary adenocarcinoma) cells. One analogue, 8-Bromo-6,11-dihydro-thieno-[3',2':2,3]azepino[4,5-b]indol-5(4H)-one (3a), showed an antiproliferative activity in the drug sensitive cell line that led to cell accumulation in G2/M phase. In addition, repression of cdk1, a G2/M transition key regulator, as well as induction of p21 were observed at the mRNA level. Programmed cell death (apoptosis) was induced in early time treatments and was accompanied by p53 mRNA induction. The antiproliferative and proapoptotic properties of 3a make this CDK inhibitor an interesting candidate for further investigations.
Reprogramming of murine fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells with chemical complementation of Klf4.[Pubmed:19447925]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jun 2;106(22):8912-7.
Ectopic expression of defined transcription factors can reprogram somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, but the utility of iPS cells is hampered by the use of viral delivery systems. Small molecules offer an alternative to replace virally transduced transcription factors with chemical signaling cues responsible for reprogramming. In this report we describe a small-molecule screening platform applied to identify compounds that functionally replace the reprogramming factor Klf4. A series of small-molecule scaffolds were identified that activate Nanog expression in mouse fibroblasts transduced with a subset of reprogramming factors lacking Klf4. Application of one such molecule, Kenpaullone, in lieu of Klf4 gave rise to iPS cells that are indistinguishable from murine embryonic stem cells. This experimental platform can be used to screen large chemical libraries in search of novel compounds to replace the reprogramming factors that induce pluripotency. Ultimately, such compounds may provide mechanistic insight into the reprogramming process.
Cell cycle molecular targets in novel anticancer drug discovery.[Pubmed:10788588]
Curr Pharm Des. 2000 Mar;6(4):379-92.
A number of potential molecular targets for novel anticancer drug discovery have been identified in cell cycle control mechanisms. Prominent among these are the regulatory proteins, cyclins and their effector counterparts the cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs). Aberrant expression of these proteins, particularly cyclins involved in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, namely the D and E cyclins, has been associated with a variety of human cancers, including breast and colorectal cancer, B-lymphoma, prostate and non-small cell lung cancer. Inhibition of CDK kinase activity has turned out to be the most productive strategy for the discovery and design novel anticancer agents specifically targeting the cell cycle. Other potentially useful cell cycle areas for exploration include cyclin-CDK interactions, Cdc25 activation of cyclin-CDK complexes, ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of cyclins, cell cycle check point kinases like Chk1, and recently identified oncogenic cell cycle-related aurora and polo-like kinases. Potent specific inhibitors have been identified that bind to the ATP site of CDKs, mainly cyclin B-CDK1, cyclin A-CDK2, and cyclin D-CDK4 complexes, and inhibit kinase activity. X-ray crystallographic data of CDKs, and their complexes with inhibitors have played a major role in the success of drug discovery efforts. Combinatorial chemistry, highthroughput screening, functional genomics and informatics have also contributed. CDK inhibitors currently under investigation include flavopiridol, olomoucine, roscovitine, puvalanol B, the dihydroindolo[3,2-d][1]benzazepinone Kenpaullone, indirubin-3 -monoxime and novel diaminothiazoles such as AG12275. The anticancer therapeutic potential of CDK inhibitors has been demonstrated in preclinical studies, and Phases I and II clinical trials in cancer patients are currently underway.
Paullones, a series of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: synthesis, evaluation of CDK1/cyclin B inhibition, and in vitro antitumor activity.[Pubmed:10425100]
J Med Chem. 1999 Jul 29;42(15):2909-19.
The paullones represent a novel class of small molecule cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors. To investigate structure-activity relationships and to develop paullones with antitumor activity, derivatives of the lead structure Kenpaullone (9-bromo-7,12-dihydroindolo[3,2-d][1]benzazepin-6(5H)-one, 4a) were synthesized. Paullones with different substituents in the 2-, 3-, 4-, 9-, and 11-positions were prepared by a Fischer indole reaction starting from 1H-[1]benzazepine-2,5(3H,4H)-diones 5. Selective substitutions at either the lactam or the indole nitrogen atom were accomplished by treating Kenpaullone with alkyl halides in the presence of sodium hydride/THF or potassium hydroxide/acetone, respectively. S-Methylation of the Kenpaullone-derived thiolactam 18 yielded the methylthioimidate 19, which gave the hydroxyamidine 20 upon reaction with hydroxylamine. The new paullones were tested both in a CDK1/cyclin B inhibition assay and in the in vitro antitumor cell line-screening program of the National Cancer Institute (NCI). With respect to the CDK1/cyclin B inhibition, electron-withdrawing substituents in the 9-position as well as a 2,3-dimethoxy substitution on the paullone basic scaffold turned out to be favorable. A 9-trifluoromethyl substituent was found to be equivalent to the 9-bromo substituent of Kenpaullone. Replacement of the 9-bromo substituent of Kenpaullone by a 9-cyano or 9-nitro group produced a substantial increase in enzyme-inhibiting potency. Substitutions in other positions or the replacement of the lactam moiety led to decreased CDK1 inhibition. Noteworthy in vitro antitumor activities (GI(50) values between 1 and 10 microM) were found with the 9-bromo-2,3-dimethoxy-7,12-dihydroindolo[3, 2-d][1]benzazepin-6(5H)-one (4t), its 9-trifluoromethyl analogue 4u, the 12-Boc-substituted paullone15, and the methylthioimidate 19, respectively. The 9-nitro-7,12-dihydroindolo[3, 2-d][1]benzazepin-6(5H)-one (4j, named alsterpaullone) showed a high CDK1/cyclin B inhibitory activity (IC(50) = 0.035 microM) and exceeded the in vitro antitumor potency of the other paullones by 1 order of magnitude (log GI(50) mean graph midpoint = -6.4 M).
Discovery and initial characterization of the paullones, a novel class of small-molecule inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases.[Pubmed:10363974]
Cancer Res. 1999 Jun 1;59(11):2566-9.
Analysis of the National Cancer Institute Human Tumor Cell Line Anti-Cancer Drug Screen data using the COMPARE algorithm to detect similarities in the pattern of compound action to flavopiridol, a known inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), has suggested several possible novel CDK inhibitors. 9-Bromo-7,12-dihydro-indolo[3,2-d][1]benzazepin-6(5H)-one, NSC-664704 (Kenpaullone), is reported here to be a potent inhibitor of CDK1/cyclin B (IC50, 0.4 microM). This compound also inhibited CDK2/cyclin A (IC50, 0.68 microM), CDK2/cyclin E (IC50, 7.5 microM), and CDK5/p25 (IC50, 0.85 microM) but had much less effect on other kinases; only c-src (IC50, 15 microM), casein kinase 2 (IC50, 20 microM), erk 1 (IC50, 20 microM), and erk 2 (IC50, 9 microM) were inhibited with IC50s less than 35 microM. Kenpaullone acts by competitive inhibition of ATP binding. Molecular modeling indicates that Kenpaullone can bind in the ATP binding site of CDK2 with residue contacts similar to those observed in the crystal structures of other CDK2-bound inhibitors. Analogues of Kenpaullone, in particular 10-bromopaullone (NSC-672234), also inhibited various protein kinases including CDKs. Cells exposed to Kenpaullone and 10-bromopaullone display delayed cell cycle progression. Kenpaullone represents a novel chemotype for compounds that preferentially inhibit CDKs.


