Moxifloxacin HClFluoroquinolone antibiotic CAS# 186826-86-8 |
- Orbifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4689
CAS No.:113617-63-3
- Cisplatin
Catalog No.:BCN1552
CAS No.:14283-03-5
- Ciclopirox ethanolamine
Catalog No.:BCC4372
CAS No.:41621-49-2
- Carbenicillin
Catalog No.:BCC5192
CAS No.:4697-36-3
- Sulconazole Nitrate
Catalog No.:BCC4853
CAS No.:61318-91-0
- Sertaconazole nitrate
Catalog No.:BCC4716
CAS No.:99592-39-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 186826-86-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 101526 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H25ClFN3O4 | M.Wt | 437.89 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 31 mg/mL (70.79 mM) H2O : 16.67 mg/mL (38.07 mM; Need ultrasonic) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
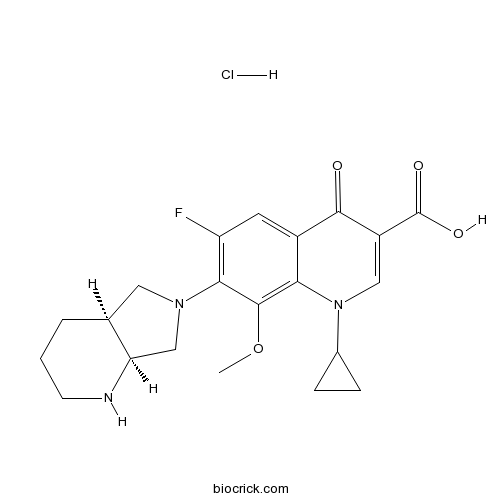
| Chemical Name | 7-[(4aS,7aS)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,7a-octahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C2C(=CC(=C1N3CC4CCCNC4C3)F)C(=O)C(=CN2C5CC5)C(=O)O.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IDIIJJHBXUESQI-DFIJPDEKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H24FN3O4.ClH/c1-29-20-17-13(19(26)14(21(27)28)9-25(17)12-4-5-12)7-15(22)18(20)24-8-11-3-2-6-23-16(11)10-24;/h7,9,11-12,16,23H,2-6,8,10H2,1H3,(H,27,28);1H/t11-,16+;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Moxifloxacin (Hydrochloride) is a synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic agent.
Target: Antibacterial
Moxifloxacin is an extended-spectrum fluoroquinolone which has improved coverage against gram-positive cocci and atypical pathogens compared with older fluoroquinolone agents, while retaining good activity against gram-negative bacteria. The antibacterial spectrum of moxifloxacin includes all major upper and lower respiratory tract pathogens; it is one of the most active fluoroquinolones against pneumococci, including penicillin- and macrolide-resistant strains [1]. Moxifloxacin has limited phototoxic potential. In clinical trials, moxifloxacin had clinical success rates of 88-97% and bacteriologic eradication rates of 90-97%. Moxifloxacin is a safe and effective antimicrobial that will be useful for treating acute sinusitis, acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, and community-acquired pneumonia [2]. Moxifloxacin possibly stimulates lipid peroxidation and enhances phagocytosis, as depicted by MDA production and survival prolongation, without being toxic as depicted by white blood cell count [3].
Clinical indications: Abdominal abscess; Acute bronchitis; Acute sinusitis; Bacterial infection
Toxicity: Symptoms of overdose include CNS and gastrointestinal effects such as decreased activity, somnolence, tremor, convulsions, vomiting, and diarrhea. The minimal lethal intravenous dose in mice and rats is 100 mg/kg. References: | |||||

Moxifloxacin HCl Dilution Calculator

Moxifloxacin HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2837 mL | 11.4184 mL | 22.8368 mL | 45.6736 mL | 57.092 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4567 mL | 2.2837 mL | 4.5674 mL | 9.1347 mL | 11.4184 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2284 mL | 1.1418 mL | 2.2837 mL | 4.5674 mL | 5.7092 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0457 mL | 0.2284 mL | 0.4567 mL | 0.9135 mL | 1.1418 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0228 mL | 0.1142 mL | 0.2284 mL | 0.4567 mL | 0.5709 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Moxifloxacin HCl is anti-infective compound with a broad antibacterial spectrum.[1]
Moxifloxacin is a fourth generation fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent with a broad antibacterial spectrum against Gram positive bacteria and Gram negative bacteria in vitro.[1] The antibacterial activity of moxifloxacin is from the inhibition effect of DNA topoisomerase II and topoisomerase IV which are involved in bacterial DNA replication, transcription, recombination and repair[2]. The oral bioavailability of moxifloxacin is absolutely good which can be up to 90%. There are no many potenti[al drug interactions because that moxifloxacin is not a inhibitor or substrate of the hepatic cytochrome P-450 isoenzyme system. Moxifloxacin had bacteriologic eradication rates about 90–97% and clinical success rates of 88–97%. The MIC90s of moxifloxacin for the ciprofloxacin-susceptible isolates were ≤0.6 μg/mL. The MIC90s of moxifloxacin for enterococci range from 1 to 4 μg/mL. The reported MIC90s of moxifloxacin for Haemophilus parainfluenzae are from 0.03 to 0.125μg/mL. The MIC90s of moxifloxacin for B. fragilisrange 0.25–4 μg/mL and 4 μg/mL for other bacteroides species. [3]
Moxifloxacin also inhibits hPON1 (human serum paraoxonase-1) enzyme activity with Ki value of 2.641±0.004 mM in vitro.[4]
References:
[1]. Cruz LA, Hall R: Enantiomeric purity assay of moxifloxacin hydrochloride by capillary electrophoresis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2005, 38(1):8-13.
[2]. Kamruzzaman M, Alam AM, Lee SH, Ragupathy D, Kim YH, Park SR, Kim SH: Spectrofluorimetric study of the interaction between europium(III) and moxifloxacin in micellar solution and its analytical application. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 2012, 86:375-380.
[3]. Culley CM, Lacy MK, Klutman N, Edwards B: Moxifloxacin: clinical efficacy and safety. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2001, 58(5):379-388.
[4]. Turkes C, Soyut H, Beydemir S: Human serum paraoxonase-1 (hPON1): in vitro inhibition effects of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, levofloxacin hemihidrate, cefepime hydrochloride, cefotaxime sodium and ceftizoxime sodium. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2014:1-7.
- ML 10302 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7695
CAS No.:186826-17-5
- Ginsenoside Rg5
Catalog No.:BCN3551
CAS No.:186763-78-0
- Alisol A 24-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN2344
CAS No.:18674-16-3
- N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
Catalog No.:BCC6495
CAS No.:1867-73-8
- Ketamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5982
CAS No.:1867-66-9
- H-D-Tyr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3137
CAS No.:186698-58-8
- Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202)
Catalog No.:BCC1105
CAS No.:186692-46-6
- 2-NBDG
Catalog No.:BCC6530
CAS No.:186689-07-6
- 4-Methylcinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5034
CAS No.:1866-39-3
- Allyl cinnamate
Catalog No.:BCC8812
CAS No.:1866-31-5
- 1,2-Bis(3-indenyl)ethane
Catalog No.:BCC8413
CAS No.:18657-57-3
- LY 344864
Catalog No.:BCC1716
CAS No.:186544-26-3
- 2B-(SP)
Catalog No.:BCC5817
CAS No.:186901-17-7
- Pafuramidine
Catalog No.:BCC1832
CAS No.:186953-56-0
- Sinapine
Catalog No.:BCN1815
CAS No.:18696-26-9
- N,N'-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)oxamide
Catalog No.:BCC9061
CAS No.:1871-89-2
- NS309
Catalog No.:BCC1809
CAS No.:18711-16-5
- Clauszoline M
Catalog No.:BCN4683
CAS No.:187110-72-1
- Luliconazole
Catalog No.:BCC1711
CAS No.:187164-19-8
- Cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3114
CAS No.:18719-76-1
- Oseltamivir acid
Catalog No.:BCC1826
CAS No.:187227-45-8
- PA-824
Catalog No.:BCC1106
CAS No.:187235-37-6
- Kimcuongin
Catalog No.:BCN7472
CAS No.:1872403-23-0
- Z-VAD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1126
CAS No.:187389-52-2
Chitosan-Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Matrices as Carriers for Hydrodynamically Balanced Capsules of Moxifloxacin HCl.[Pubmed:27142106]
Curr Drug Deliv. 2017;14(1):83-90.
BACKGROUND: In recent years, gastroretentive, hydrodynamically balanced system (HBS) for stomach-specific floating sustained drug release has gained a lot of importance in improving absorption of drugs especially those absorbed from stomach and small intestine. OBJECTIVE: The objective of the current investigation is to evaluate chitosan-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) based on polymeric matrices as a carrier for single-unit capsules based on HBS for stomach- specific floating sustained drug release using Moxifloxacin HCl (MX) as a model drug. METHOD: Various HBS capsules of MX were prepared by physical blending of MX with chitosan (low or medium molecular mass) or HPMC (K4M or K15M) or chitosan-HPMC combinations in varying proportions followed by encapsulation into size 0 capsules made of hard gelatin. The in vitro buoyancy and drug release in 0.1 N HCl (pH 1.2) were evaluated. RESULTS: HBS capsules based on chitosan (low and medium molecular weight and their combination) as polymer matrix failed to float on 0.1 N HCl (pH 1.2). Whereas, formulations containing HPMC (K4M or K15M) or their mixture with chitosan, remained buoyant and released MX over 9 h in the acidic dissolution medium following zero-order kinetics. CONCLUSION: HPMC (K4M, K15M, blend of K4M and K15M) or their mixture with low/medium molecular mass chitosan may constitute excellent carrier systems for the stomach-specific sustained delivery of MX over a longer period.
Design and Development of Thermoreversible Ophthalmic In Situ Hydrogel of Moxifloxacin HCl.[Pubmed:20497100]
Curr Drug Deliv. 2010 Jul;7(3):238-43.
Conventional eye drops show relatively low bioavailability due to poor precorneal contact time. In situ hydrogels are of great importance in providing sustained ocular drug delivery. By exhibiting elastic properties they resist ocular drainage of the drug leading to longer contact times. In the present study an in situ gelling thermoreversible mucoadhesive gel was formulated of an antibacterial agent, Moxifloxacin HCl using a combination of poloxamer 407 and poloxamer 188 with different mucoadhesive polymers such as Xanthan gum and Sodium alginate with a view to increase gel strength and bioadhesion force and thereby increased precorneal contact time and bioavailability of the drug. Formulations were evaluated for physical parameters like clarity, pH, spreadability, drug content, gelation temperature, gel strength, bioadhesion force and in vitro drug release study. Formulations were found transparent, uniform in consistency and had good spreadability within a pH range of 6.8 to 7.4. A satisfactory bioadhesion (3298 to 4130 Dyne/cm2) on the sheeps corneal surface and good gel strength (95 to 128 sec) was also observed. As the concentration of mucoadhesive polymers in the gel formulation increased, the rate of drug release decreased. The order of drug release was in order: Xanthan gum > Sodium alginate. It was concluded that a thermoreversible in situ gel of Moxifloxacin HCl can be formulated by combining with mucoadhesive polymers and used effectively as safe and sustained ocular drug delivery. This combination provided greater bioadhesion force and gel strength as compared to the thermoreversible polymers i.e., poloxamer 407 (PF 127) or 188 (PF 68) when used alone.
Studies on Poloxamer Based Mucoadhesive Insitu Ophthalmic Hydrogel of Moxifloxacin HCL.[Pubmed:20158483]
Curr Drug Deliv. 2010 Feb 17. pii: BSP-CDD-EPUB-00045.
Conventional eye drops shows relatively low bioavailability due to poor precorneal contact time. In situ hydrogels are of great importance in providing sustained ocular drug delivery due to their elastic properties hydrogels resist ocular drainage leading to longer contact times. In the present study an in situ gelling thermoreversible mucoadhesive gel was formulated of an antibacterial agent Moxifloxacin HCl using combination of poloxamer 407 and poloxamer 188 with different mucoadhesive polymers such as Xanthan gum and Sodium alginate with a view to increase in gel strength and bioadhesion force and thereby increase in precorneal contact time and there by increase in bioavailability of the drug. The formulations were evaluated for physical parameters like Clarity, pH, spreadability, drug content, gelation temperature, gel strength, bioadhesion force and in vitro drug release study. The formulated gels were transparent, uniform in consistency and had spreadability with a pH range of 6.8 to 7.4. A satisfactory bioadhesion (3298 to 4130 Dyne/cm(2)) on the sheep's corneal surface and good gel strength (95 to 128 sec) were also observed. As the concentration of mucoadhesive polymers in the gel formulation increases, the rate of drug release decreases. The order of drug release was Xanthan gum>Sodium alginate. It was concluded that a thermoreversible in situ gel formulation with Moxifloxacin HCl can be formulated by combining with mucoadhesive polymers and can effectively be used in safe and sustained ocular drug delivery with greater bioadhesion force and gel strength as compared to the thermoreversible polymers poloxamer 407 or 188 when used alone.
An Improvement of the Efficacy of Moxifloxacin HCl for the Treatment of Bacterial Keratitis by the Formulation of Ocular Mucoadhesive Microspheres.[Pubmed:23641344]
Sci Pharm. 2013 Jan-Mar;81(1):259-80.
The aim of this study was to prepare novel ocular mucoadhesive microspheres of Moxifloxacin HCl to increase its residence time on the ocular surface and to enhance its therapeutic efficacy in ocular bacterial keratitis. Microspheres were fabricated with different grades of Methocel and Sodium CMC as polymers. Microspheres were evaluated for their particle size, morphology, encapsulation efficiency, mucoadhesion, antimicrobial efficacy, and in vitro drug release studies. In vivo studies were carried out for the promising formulation on eyes of albino rabbits by inducing bacterial keratitis. A sterile microspheres suspension in light mineral oil was applied to infected eyes twice a day. A marketed conventional eye drop was used as a positive control. Eyes were examined daily for improvement of clinical signs of bacterial keratitis by an ophthalmologist. The average particle size of microspheres was found to be less than 80 mum. Methocel microspheres were found to have a smoother surface than Sodium CMC. Entrapment efficiency was enhanced with an increased polymer concentration and viscosity. The formulation containing Methocel K100M with a drug: polymer ratio of 1:2 exerted longer corneal and conjunctival mucoadhesion time of 8.45+/-0.15 h and 9.40+/-0.53 h respectively. In vitro release of Moxifloxacin HCl from microspheres was retarded with increased viscosity and concentration of polymers, and was controlled by diffusion as well as polymer relaxation. All formulations showed comparable antimicrobial activity in comparison with conventional marketed eye drops. The formulation containing Methocel K100M with a drug: polymer ratio of 1:2 was found to be a promising formulation and was used for the in vivo studies. The in vivo studies revealed that microspheres demonstrated significantly lower clinical scores and reduced the total duration of therapy than the marketed Moxifloxacin HCl eye drops. In vitro and in vivo studies showed that ocular mucoadhesive microspheres of Moxifloxacin HCl were found to have an improved efficacy in the treatment of ocular bacterial keratitis in comparison with the marketed formulation.


