(R)-DRF053 dihydrochloridecdk/CK1 inhibitor,potent and ATP-competitive CAS# 1241675-76-2 |
- Anguizole
Catalog No.:BCC1365
CAS No.:442666-98-0
- Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
Catalog No.:BCC1374
CAS No.:630420-16-5
- Balapiravir
Catalog No.:BCC1396
CAS No.:690270-29-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1241675-76-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71433624 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H29Cl2N7O | M.Wt | 490.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
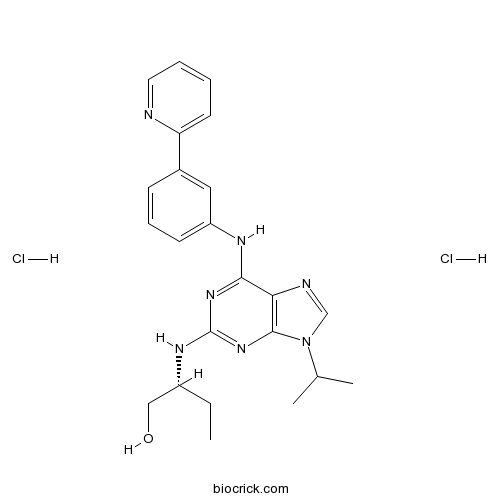
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-[[9-propan-2-yl-6-(3-pyridin-2-ylanilino)purin-2-yl]amino]butan-1-ol;dihydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCC(CO)NC1=NC2=C(C(=N1)NC3=CC=CC(=C3)C4=CC=CC=N4)N=CN2C(C)C.Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BQPRBNGSDBTKAK-ZEECNFPPSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H27N7O.2ClH/c1-4-17(13-31)27-23-28-21(20-22(29-23)30(14-25-20)15(2)3)26-18-9-7-8-16(12-18)19-10-5-6-11-24-19;;/h5-12,14-15,17,31H,4,13H2,1-3H3,(H2,26,27,28,29);2*1H/t17-;;/m1../s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, ATP-competitive inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) and casein kinase 1 (CK1) (IC50 values are 220, 80 and 14 nM for cdk1/cyclin B, cdk5/p25 and CK1 respectively). Selective over GSK-3 αβ (IC50= 4.1 μM). Also shown to inhibit amyloid-β production in N2A-APP695 cells. |

(R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride Dilution Calculator

(R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.039 mL | 10.1951 mL | 20.3903 mL | 40.7805 mL | 50.9757 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4078 mL | 2.039 mL | 4.0781 mL | 8.1561 mL | 10.1951 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2039 mL | 1.0195 mL | 2.039 mL | 4.0781 mL | 5.0976 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0408 mL | 0.2039 mL | 0.4078 mL | 0.8156 mL | 1.0195 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0204 mL | 0.102 mL | 0.2039 mL | 0.4078 mL | 0.5098 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Alcesefoliside
Catalog No.:BCN2933
CAS No.:124151-38-8
- Scutebarbatine O
Catalog No.:BCN8377
CAS No.:960302-88-9
- 2-Hydroxytetracosanoic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1599
CAS No.:124111-47-3
- 1-Caffeoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5911
CAS No.:1241-87-8
- (-)-Hydroxydihydrobovolide
Catalog No.:BCN7890
CAS No.:124097-54-7
- 16-Epikoumidine
Catalog No.:BCN3915
CAS No.:124096-81-7
- Etomoxir
Catalog No.:BCC1564
CAS No.:124083-20-1
- 7',8'-Dihydroobolactone
Catalog No.:BCN7196
CAS No.:1240403-82-0
- AZD3514
Catalog No.:BCC1070
CAS No.:1240299-33-5
- Kobophenol A
Catalog No.:BCN3444
CAS No.:124027-58-3
- 1beta,10beta-Epoxydesacetoxymatricarin
Catalog No.:BCN7307
CAS No.:124020-39-9
- Triamcinolone
Catalog No.:BCC4741
CAS No.:124-94-7
- 6-O-Vanilloylajugol
Catalog No.:BCN6125
CAS No.:124168-04-3
- Laxiracemosin H
Catalog No.:BCN6910
CAS No.:1241871-28-2
- 12-Ursene-3,16,22-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6126
CAS No.:1242085-06-8
- RN486
Catalog No.:BCC3921
CAS No.:1242156-23-5
- Wnt-C59
Catalog No.:BCC3965
CAS No.:1243243-89-1
- LGK-974
Catalog No.:BCC5103
CAS No.:1243244-14-5
- Paucinervin A
Catalog No.:BCN7308
CAS No.:1243249-16-2
- Lenalidomide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1697
CAS No.:1243329-97-6
- 9-(1H-Benzotriazol-1-ylmethyl)-9H-carbazole
Catalog No.:BCC8792
CAS No.:124337-34-4
- MG 149
Catalog No.:BCC5149
CAS No.:1243583-85-8
- Cannabidiolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6127
CAS No.:1244-58-2
- CGS 21680 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4316
CAS No.:124431-80-7
Palladium(II) complexes with R(2)edda derived ligands. Part IV. O,O'-dialkyl esters of (S,S)-ethylenediamine-N,N'-di-2-(4-methyl)-pentanoic acid dihydrochloride and their palladium(II) complexes: synthesis, characterization and in vitro antitumoral activity against chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells.[Pubmed:20570025]
Eur J Med Chem. 2010 Sep;45(9):3601-6.
Four novel bidentate N,N'-ligand precursors, including O,O'-dialkyl esters (alkyl = ethyl, n-propyl, n-butyl and n-pentyl), L1 x 2 HCl-L4 x 2 HCl, of (S,S)-ethylenediamine-N,N'-di-2-(4-methyl)-pentanoic acid dihydrochloride [(S,S)-H(4)eddl]Cl(2) and the corresponding palladium(II) complexes 1-4, were prepared and characterized by IR, (1)H NMR and (13)C NMR spectroscopy and elemental analysis. In vitro cytotoxicity of all compounds was determined against chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells (CLL). The compounds were found to exhibit higher antitumoral activity than cisplatin. The most active compound 2, [PdCl(2){(S,S)-nPr(2)eddl}], was found to be 13.6 times more active than cisplatin on CLL cells.
Evolving patient selection and clinical benefit criteria for sapropterin dihydrochloride (Kuvan(R)) treatment of PKU patients.[Pubmed:22310224]
Mol Genet Metab. 2012 Apr;105(4):672-6.
PURPOSE: To understand current patient selection, dosing, and response criteria used for sapropterin dihydrochloride (sapropterin, Kuvan(R)) to treat phenylketonuria (PKU). METHODS: Results of a 2010 survey of twenty-nine academic medical centers are reported to describe practice patterns in comparison to results of a survey done in 2008 and to what is reported in the literature. RESULTS/CONCLUSIONS: In addition to reduction in blood phenylalanine (Phe) levels, clinicians report using broader disease-management approaches when evaluating clinical benefit of sapropterin, including consideration of increased Phe tolerance and behavioral changes. Similar approaches are reported in the literature.
Screening of bulk drug samples and anti-tuberculosis products for the presence of therapeutically less active diasteriomeric (R,S) form of ethambutol dihydrochloride.[Pubmed:19295106]
Indian J Tuberc. 2008 Oct;55(4):192-8.
BACKGROUND: The present study was carried out to screen various ethambutol dihydrochloride (EB2HCI) bulk drug samples and anti-tuberculosis (anti-TB) products for the presence of less active (R,S)-EB2HCl. METHODOLOGY: Samples of pure EB2HCl were received gratis from various companies and the formulations were procured from local market, and also from a Directly Observed Treatment Short-course (DOTS) centre. Some products available in the institute from Global Drug Facility were also included in the study. In total, 5 API samples and 35 formulations containing EB2HCI were investigated. These were subjected to evaluation for the presence of (R,S)-EB2HCl using a previously published differential scanning calorimetric method. The thermograms were recorded between 25 degrees C and 250 degrees C at a rate of 10 degrees C/min. RESULTS: 1 API sample and 12 formulations were found to contain (R,S)-EB2HCI up to an extent of 30-100%. One of the DOTS centres supply was also found to contain approximately 97% of the less active isomer. CONCLUSION: The presence of therapeutically inactive form of the EB2HCl from 30-100% in approximately 30% of the products in the local market is an alarming finding, which means low quality anti-TB products are in circulation. The same may be contributory to the developing resistance of the drugs against the mycobacterium.
The percutaneous permeation of a combination of 0.1% octenidine dihydrochloride and 2% 2-phenoxyethanol (octenisept(R)) through skin of different species in vitro.[Pubmed:21835019]
BMC Vet Res. 2011 Aug 11;7:44.
BACKGROUND: A water based combination of 0.1% octenidine dihydrochloride and 2% 2 - phenoxyethanol is registered in many European countries as an antiseptic solution (octenisept(R)) for topical treatment with high antimicrobial activity for human use, but octenidine based products have not been registered for veterinary use yet. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether octenidine dihydrochloride or 2 -phenoxyethanol, the two main components of this disinfectant, permeate through animal skin in vitro. Therefore, permeation studies were conducted using Franz-type diffusion cells. 2 ml of the test compound were applied onto 1.77 cm2 split skin of cats, dogs, cows and horses. To simulate wounded skin, cattle skin was treated with adhesive tapes 100 times, as well. Up to an incubation time of 28 hours samples of the acceptor chamber were taken and were analysed by UV-HPLC. Using the method of the external standard, the apparent permeability coefficient, the flux Jmax, and the recovery were calculated. Furthermore, the residues of both components in the skin samples were determined after completion of the diffusion experiment. RESULTS: After 28 hours no octenidine dihydrochloride was found in the receptor chamber of intact skin samples, while 2.7% of the topical applied octenidine dihydrochloride permeated through barrier disrupted cattle skin. 2 - phenoxyethanol permeated through all skin samples with the highest permeability in equine, followed by bovine, canine to feline skin. Furthermore, both components were found in the stratum corneum and the dermis of all split skin samples with different amounts in the examined species. CONCLUSION: For 2-phenoxyethanol the systemic impact of the high absorption rate and a potential toxicological risk have to be investigated in further studies. Due to its low absorption rates through the skin, octenidine dihydrochloride is suitable for superficial skin treatment in the examined species.


