Lenalidomide hydrochlorideTNF-α secretion inhibitor CAS# 1243329-97-6 |
- Lenalidomide (CC-5013)
Catalog No.:BCC2245
CAS No.:191732-72-6
- Celastrol
Catalog No.:BCN5986
CAS No.:34157-83-0
- Necrostatin 2 racemate
Catalog No.:BCC2077
CAS No.:852391-15-2
- Necrostatin 2
Catalog No.:BCC1793
CAS No.:852391-19-6
- Necrostatin 2 S enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC2078
CAS No.:852391-20-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1243329-97-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44234581 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H14ClN3O3 | M.Wt | 295.72 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CC-5013 hydrochloride | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 52 mg/ml in DMSO | ||
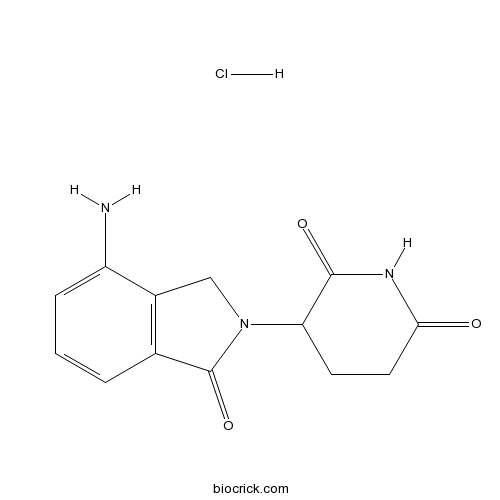
| Chemical Name | 3-(7-amino-3-oxo-1H-isoindol-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | C1CC(=O)NC(=O)C1N2CC3=C(C2=O)C=CC=C3N.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RYWZLJSDFZVVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H13N3O3.ClH/c14-9-3-1-2-7-8(9)6-16(13(7)19)10-4-5-11(17)15-12(10)18;/h1-3,10H,4-6,14H2,(H,15,17,18);1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Lenalidomide hydrochloride is a potent inhibitor of TNF-α and has antiangiogenic effect. Lenalidomide functions as a protein homeostatic modulator (PHM) linking casein kinase 1A1 (CKIα) to the human E3 ligase cereblon.In Vitro:Lenalidomide is potent in stimulating T cell proliferation and IFN-γ and IL-2 production. Lenalidomide has been shown to inhibit production of pro inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-12 and elevate the production of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 from human PBMCs. Lenalidomide downregulates the production of IL-6 directly and also by inhibiting multiple myeloma (MM) cells and bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) interaction, which augments the apoptosis of myeloma cells[2]. Dose-dependent interaction with the CRBN-DDB1 complex is observed with Thalidomide, Lenalidomide and Pomalidomide, with IC50 values of ~30 μM, ~3 μM and ~3 μM, respectively, These reduced CRBN expression cells (U266-CRBN60 and U266-CRBN75) are less responsive than the parental cells to antiproliferative effects Lenalidomide across a dose-response range of 0.01 to 10 μM[3]. Lenalidomide, a thalidomide analog, functions as a molecular glue between the human E3 ubiquitin ligase cereblon and CKIα is shown to induce the ubiquitination and degradation of this kinase, thus presumably killing leukemic cells by p53 activation[5].In Vivo:The toxicity of Lenalidomide doses up to 15, 22.5, and 45 mg/kg via IV, IP, and PO routes of administration. Limited by solubility in our PBS dosing vehicle, these maximum achievable Lenalidomide doses are well tolerated with the exception of one mouse death (of four total dosed) at the 15 mg/kg IV dose. Notably, no other toxicities are observed in the study at IV doses of 15 mg/kg (n=3) or 10 mg/kg (n=45) or at any other dose level through IV, IP, and PO routes[4]. References: | |||||

Lenalidomide hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

Lenalidomide hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3816 mL | 16.9079 mL | 33.8158 mL | 67.6315 mL | 84.5394 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6763 mL | 3.3816 mL | 6.7632 mL | 13.5263 mL | 16.9079 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3382 mL | 1.6908 mL | 3.3816 mL | 6.7632 mL | 8.4539 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0676 mL | 0.3382 mL | 0.6763 mL | 1.3526 mL | 1.6908 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0338 mL | 0.1691 mL | 0.3382 mL | 0.6763 mL | 0.8454 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50 Value: 13 nM [1] Lenalidomideis a derivative of thalidomide introduced in 2004. Lenalidomide (Revlimid, CC-5013) is a TNF-α secretion inhibitor with IC50 of 13 nM. in vitro: Lenalidomide strongly induces IL-2 and sIL-2R production. Lenalidomide-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of CD28 on T cells is followed by a down-stream activation of NF-κB [2]. Lenalidomide and pomalidomide inhibits autoubiquitination of CRBN in HEK293 T cells expressing thalidomide-binding competent wild-type CRBN, but not thalidomide-binding defective CRBN (YW/AA). Overexpression of CRBN wild-type protein, but not CRBN (YW/AA) mutant protein, in KMS12 myeloma cells, amplifies pomalidomide-mediated reductions in c-myc and IRF4 expression and increases in p21(WAF-1) expression. Long-term selection for Lenalidomide resistance in H929 myeloma cell lines is accompanied by a reduction in CRBN, while in DF15R myeloma cells resistant to both pomalidomide and Lenalidomide, CRBN protein is undetectable [3]. in vivo: Pharmacokinetic studies evaluated doses of 0.5, 1.5, 5, and 10 mg/kg IV and 0.5 and 10 mg/kg doses for IP and oral routes. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was used to quantify lenalidomide in plasma, brain, lung, liver, heart, kidney, spleen, and muscle [4]. Treatment with either thalidomide or lenalidomide attenuated weight loss, enhanced motor performance, decreased motor neuron cell death, and significantly increased the life span in G93A transgenic mice [5]. Toxicity: International Staging System III received a combination therapy of lenalidomide (15 mg, Day 1 - 21) with dexamethasone (40 mg, Day 1, 8, 15, 22). After 4 days on chemotherapy, he experienced worsened dyspnea and was urgently hospitalized because of acute respiratory failure [6]. Clinical trial: Lenalidomide As Immune Adjuvant In Patient's With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Phase 2
- Paucinervin A
Catalog No.:BCN7308
CAS No.:1243249-16-2
- LGK-974
Catalog No.:BCC5103
CAS No.:1243244-14-5
- Wnt-C59
Catalog No.:BCC3965
CAS No.:1243243-89-1
- RN486
Catalog No.:BCC3921
CAS No.:1242156-23-5
- 12-Ursene-3,16,22-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6126
CAS No.:1242085-06-8
- Laxiracemosin H
Catalog No.:BCN6910
CAS No.:1241871-28-2
- 6-O-Vanilloylajugol
Catalog No.:BCN6125
CAS No.:124168-04-3
- (R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7726
CAS No.:1241675-76-2
- Alcesefoliside
Catalog No.:BCN2933
CAS No.:124151-38-8
- Scutebarbatine O
Catalog No.:BCN8377
CAS No.:960302-88-9
- 2-Hydroxytetracosanoic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1599
CAS No.:124111-47-3
- 1-Caffeoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5911
CAS No.:1241-87-8
- 9-(1H-Benzotriazol-1-ylmethyl)-9H-carbazole
Catalog No.:BCC8792
CAS No.:124337-34-4
- MG 149
Catalog No.:BCC5149
CAS No.:1243583-85-8
- Cannabidiolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6127
CAS No.:1244-58-2
- CGS 21680 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4316
CAS No.:124431-80-7
- VU 0364739 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7875
CAS No.:1244640-48-9
- 16R-sitsirikine
Catalog No.:BCN3492
CAS No.:1245-00-7
- 2,2'-Bicinchoninic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8487
CAS No.:1245-13-2
- Retusin
Catalog No.:BCN7794
CAS No.:1245-15-4
- 16-Oxoalisol A
Catalog No.:BCN3460
CAS No.:124515-98-6
- PI4KIII beta inhibitor 3
Catalog No.:BCC1310
CAS No.:1245319-54-3
- Glucocorticoid receptor agonist
Catalog No.:BCC1596
CAS No.:1245526-82-2
- NVP-BGT226
Catalog No.:BCC3827
CAS No.:1245537-68-1
Phase 1 dose-ranging study of ezatiostat hydrochloride in combination with lenalidomide in patients with non-deletion (5q) low to intermediate-1 risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).[Pubmed:22546242]
J Hematol Oncol. 2012 Apr 30;5:18.
BACKGROUND: Ezatiostat, a glutathione S-transferase P1-1 inhibitor, promotes the maturation of hematopoietic progenitors and induces apoptosis in cancer cells. RESULTS: Ezatiostat was administered to 19 patients with non-deletion(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) at one of two doses (2000 mg or 2500 mg/day) in combination with 10 mg of lenalidomide on days 1-21 of a 28-day cycle. No unexpected toxicities occurred and the incidence and severity of adverse events (AEs) were consistent with that expected for each drug alone. The most common non-hematologic AEs related to ezatiostat in combination with lenalidomide were mostly grade 1 and 2 fatigue, anorexia, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting; hematologic AEs due to lenalidomide were thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and anemia. One of 4 evaluable patients (25%) in the 2500/10 mg dose group experienced an erythroid hematologic improvement (HI-E) response by 2006 MDS International Working Group (IWG) criteria. Four of 10 evaluable patients (40%) in the 2000 mg/10 mg dose group experienced an HI-E response. Three of 7 (43%) red blood cell (RBC) transfusion-dependent patients became RBC transfusion independent, including one patient for whom prior lenalidomide monotherapy was ineffective. Three of 5 (60%) thrombocytopenic patients had an HI-platelet (HI-P) response. Bilineage HI-E and HI-P responses occurred in 3 of 5 (60%), 1 of 3 with HI-E and HI-N (33%), and 1 of 3 with HI-N and HI-P (33%). One of 3 patients (33%) with pancytopenia experienced a complete trilineage response. All multilineage responses were observed in the 2000/10 mg doses recommended for future studies. CONCLUSIONS: The tolerability and activity profile of ezatiostat co-administered with lenalidomide supports the further development of ezatiostat in combination with lenalidomide in MDS and also encourages studies of this combination in other hematologic malignancies where lenalidomide is active.


