Lenalidomide (CC-5013)Antineoplastic agent,inhibits angiogenesis CAS# 191732-72-6 |
- Lenalidomide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1697
CAS No.:1243329-97-6
- Necrostatin-1
Catalog No.:BCC2247
CAS No.:4311-88-0
- Roquinimex
Catalog No.:BCC5355
CAS No.:84088-42-6
- Lenalidomide hemihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4198
CAS No.:847871-99-2
- Necrostatin 2 racemate
Catalog No.:BCC2077
CAS No.:852391-15-2
- Necrostatin 2 S enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC2078
CAS No.:852391-20-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 191732-72-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 216326 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H13N3O3 | M.Wt | 259.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Revlimid; Revimid; CC-5013 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 35 mg/mL (135.00 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
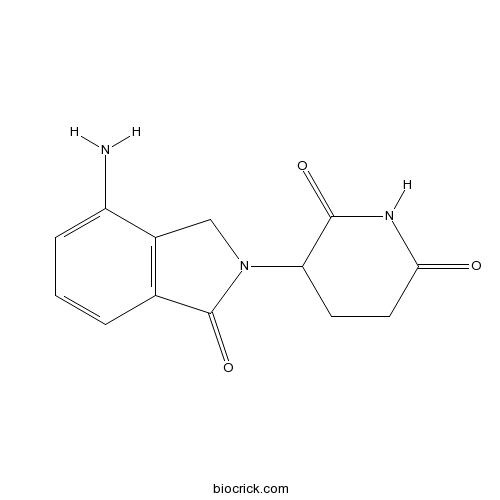
| Chemical Name | 3-(7-amino-3-oxo-1H-isoindol-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione | ||
| SMILES | C1CC(=O)NC(=O)C1N2CC3=C(C2=O)C=CC=C3N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GOTYRUGSSMKFNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H13N3O3/c14-9-3-1-2-7-8(9)6-16(13(7)19)10-4-5-11(17)15-12(10)18/h1-3,10H,4-6,14H2,(H,15,17,18) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Lenalidomide (CC-5013) is an inhibitor of TNF-α secretion with IC50 of 13 nM. | |||||
| Targets | TNF-α | |||||
| IC50 | 13 nM | |||||
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
| Cell lines | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 10 μM, 7 days |
| Applications | The cells were incubated with the dye at 37°C for 10 min and treated for 7 days in RPMI culture medium with lenalidomide. Cells were surface stained with anti-CD4-PerCP and anti-CD25-APC, followed by intracellular staining with anti-FOXP3-PE. Lenalidomide inhibited the expression of CD4+CD25high CTLA-4+FOXP3+ cells. Incubation with lenalidomide significantly decreases expression of the T regulatory cell population after 7 days of culture. The drug decreased the percentage of CD4+CD25high cells expressing both CTLA-4 and FOXP3 from 25 to 12%. |
| Animal experiment: [2] | |
| Animal models | Male Sprague–Dawley rats |
| Dosage form | Oral administration, 50 mg/kg or 250 mg/kg, |
| Application | In the rat mesenteric window assay (RMWA), representative differences between vehicle and 50 or 250 mg/kg lenalidomide-treated rats were visualized by staining with an antibody against rat endothelium in bFGF-induced angiogenic windows. The induction of angiogenesis by bFGF was significantly inhibited by oral treatment of lenalidomide in a dose-dependent manner. Lenalidomide significantly decreased the percentage of vascularized area from 5.16% in the control group to 2.58 and 1.69 in the 50 and 250 mg/kg group, respectively. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Galustian C, Meyer B, Labarthe M C, et al. The anti-cancer agents lenalidomide and pomalidomide inhibit the proliferation and function of T regulatory cells. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 2009, 58(7): 1033-1045. [2] Dredge K, Horsfall R, Robinson S P, et al. Orally administered lenalidomide (CC-5013) is anti-angiogenic in vivo and inhibits endothelial cell migration and Akt phosphorylation in vitro. Microvascular research, 2005, 69(1): 56-63. | |

Lenalidomide (CC-5013) Dilution Calculator

Lenalidomide (CC-5013) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8565 mL | 19.2827 mL | 38.5654 mL | 77.1307 mL | 96.4134 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7713 mL | 3.8565 mL | 7.7131 mL | 15.4261 mL | 19.2827 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3857 mL | 1.9283 mL | 3.8565 mL | 7.7131 mL | 9.6413 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0771 mL | 0.3857 mL | 0.7713 mL | 1.5426 mL | 1.9283 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0386 mL | 0.1928 mL | 0.3857 mL | 0.7713 mL | 0.9641 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Lenalidomide (also known as CC-5013), an oral derivative of thalidomide, is an antineoplastic agent exhibiting antitumor activity through a variety of mechanisms, including immune system activation, angiogenesis inhibition, and direct antineoplastic effects. It has been extensively studied for the treatment of multiple myeloma and myelodysplastic syndrome as well as lymphoproliferative disorders including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. According to recent studies, Lnalidomide promotes and restores immune system function in CLL patients by inducing an overexpression of costimulatory molecules in leukemic lymphocytes to restore the humoral immunity and immunoglobulins production as well as improving the ability of T cells and leukemic cells to form synapses with T lymphocytes.
Reference
Ana Pilar Gonzalez-Rodriguez, Angel R. Payer, Andrea Acebes-Huerta, Leticia Hergo-Zapico, Monica Villa-Alvarez, Esther Gonzalez-Garcia, and Segundo Gonzalez. Lenalidomide and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. BioMed Research International 2013.
- Tenacissoside H
Catalog No.:BCN2570
CAS No.:191729-45-0
- Tenacissoside I
Catalog No.:BCN4681
CAS No.:191729-44-9
- Tenacissoside G
Catalog No.:BCN4682
CAS No.:191729-43-8
- Pomalidomide (CC-4047)
Catalog No.:BCC2246
CAS No.:19171-19-8
- SIB 1553A hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6284
CAS No.:191611-89-9
- Trimethylgallic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN3369
CAS No.:1916-07-0
- 2-Deacetoxytaxinine B
Catalog No.:BCN1181
CAS No.:191547-12-3
- Epieriocalyxin A
Catalog No.:BCN1180
CAS No.:191545-24-1
- 2-Hydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7545
CAS No.:1915-98-6
- Isoficusin A
Catalog No.:BCN6865
CAS No.:1914963-20-4
- LY 379268
Catalog No.:BCC7368
CAS No.:191471-52-0
- AGN 195183
Catalog No.:BCC5419
CAS No.:191469-29-1
- Cyclo(Pro-Gly)
Catalog No.:BCN2417
CAS No.:19179-12-5
- Deoxypodophyllotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN1182
CAS No.:19186-35-7
- BIBO 3304 trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC7355
CAS No.:191868-14-1
- Flutax 1
Catalog No.:BCC7298
CAS No.:191930-58-2
- NTNCB hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7270
CAS No.:191931-56-3
- HIV-1 Tat Protein Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC4417
CAS No.:191936-91-1
- 12-Hydroxymyricanone
Catalog No.:BCN8046
CAS No.:191999-68-5
- Hinokiflavone
Catalog No.:BCN2989
CAS No.:19202-36-9
- Tenulin
Catalog No.:BCN7961
CAS No.:19202-92-7
- MRS 1334
Catalog No.:BCC5753
CAS No.:192053-05-7
- Harpagoside
Catalog No.:BCN4995
CAS No.:19210-12-9
- Prazosin
Catalog No.:BCC4081
CAS No.:19216-56-9
Lenalidomide (Revlimid, CC-5013) in myelodysplastic syndromes: is it any good?[Pubmed:15865869]
Curr Hematol Rep. 2005 May;4(3):182-5.
The myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) can be divided into "early" and "advanced" disease by evaluation of prognostic variables such as the number of cytopenias, karyotype, and percentage of myeloblasts. Patients with an isolated interstitial deletion of chromosome 5q31 represent a distinct subset who may derive particular benefit from immunomodulatory drugs. Goals of therapy for early MDS focus on hematologic improvement and maximizing quality of life. Thalidomide, the prototype of the immunomodulatory drugs, yields major erythroid responses in some patients with early MDS, but dose-limiting neurologic toxicities limit its potential clinical benefit. Lenalidomide, a more potent and non-neurotoxic derivative, has shown promising results in early MDS, yielding hematologic improvement in almost half of patients, and transfusion independence with cytogenetic remissions in approximately two thirds of patients harboring the chromosome 5q31 deletion.
Orally administered lenalidomide (CC-5013) is anti-angiogenic in vivo and inhibits endothelial cell migration and Akt phosphorylation in vitro.[Pubmed:15797261]
Microvasc Res. 2005 Jan;69(1-2):56-63.
The thalidomide analogue and immunomodulatory drug (IMiD) lenalidomide (CC-5013, REVLIMID) is emerging as a useful treatment for a number of cancers and has recently entered phase III trials for multiple myeloma. It has been suggested that the anti-tumor effect of lenalidomide is related to its anti-angiogenic potency. In this regard, we have previously shown that lenalidomide inhibits angiogenesis in both rat and human in vitro models but does not affect endothelial cell proliferation. We now show that oral administration of lenalidomide attenuates growth factor-induced angiogenesis in vivo; the rat mesenteric window assay was utilized to show that lenalidomide significantly inhibits vascularization in a dose-dependent manner. We also found that lenalidomide significantly inhibits growth factor-induced endothelial cell migration. This correlates with the inhibitory effect of lenalidomide on growth factor-induced Akt phosphorylation, thereby providing a potential mechanism for its anti-migratory and subsequent anti-angiogenic effects. These data further support the use of lenalidomide as an orally administered drug for the effective treatment of angiogenesis-dependent conditions, including cancer, and suggest a potential mechanism of action.
Lenalidomide (Revlimid, CC-5013) in myelodysplastic syndromes: Is it any good?[Pubmed:20425326]
Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2006 Mar;1(1):16-9.
The myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) can be divided into "early" and "advanced" disease by evaluation of prognostic variables such as the number of cytopenias, karyotype, and percentage of myeloblasts. Patients with an isolated interstitial deletion of chromosome 5q31 represent a distinct subset who may derive particular benefit from immunomodulatory drugs. Goals of therapy for early MDS focus on hematologic improvement and maximizing quality of life. Thalidomide, the prototype of the immunomodulatory drugs, yields major erythroid responses in some patients with early MDS, but doselimiting neurologic toxicities limit its potential clinical benefit. Lenalidomide, a more potent and non-neurotoxic derivative, has shown promising results in early MDS, yielding hematologic improvement in almost half of patients and transfusion independence with cytogenetic remissions in approximately two thirds of patients harboring the chromosome 5q31 deletion.
Immunomodulatory drug lenalidomide (CC-5013, IMiD3) augments anti-CD40 SGN-40-induced cytotoxicity in human multiple myeloma: clinical implications.[Pubmed:16357183]
Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 15;65(24):11712-20.
SGN-40, a humanized immoglobulin G1 (IgG1) anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody, mediates cytotoxicity against human multiple myeloma (MM) cells via suppression of interleukin (IL)-6-induced proliferative and antiapoptotic effects as well as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). Here, we studied the clinical significance of an immunomodulatory drug lenalidomide on SGN-40-induced cytotoxicity against CD138(+)CD40(+) MM lines and patient MM cells. Pretreatment with lenalidomide sensitized MM cells to SGN-40-induced cell death. Combined lenalidomide and SGN-40 significantly induced MM apoptosis, evidenced by enhanced cleavage of caspase-3/8/poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase and increased sub-G(0) cells, compared with either single agent at the same doses. Pretreatment of effector cells with lenalidomide augmented SGN-40-induced MM cell lysis, associated with an increased number of CD56(+)CD3(-) natural killer (NK) cells expressing CD16 and LFA-1. Importantly, pretreatment with lenalidomide or lenalidomide and SGN-40 markedly enhanced NK-cell-mediated lysis of autologous patient MM cells triggered by SGN-40. Lenalidomide also up-regulated CD40L on CD56(+)CD3(-) NK cells, facilitating IL-2-mediated activation of NK cells. In addition, lenalidomide induced the CD56(dim) NK subset, which are more potent mediators of ADCC against target MM cells than the CD56(bright) NK subset. Finally, pretreatment of both effector and target MM cells with lenalidomide markedly enhanced SGN-40-mediated ADCC against CD40-expressing MM cells. These studies, therefore, show that the addition of lenalidomide to SGN-40 enhances cytotoxicity against MM cells, providing the framework for combined lenalidomide and SGN-40 in a new treatment paradigm to both target MM cells directly and induce immune effectors against MM.


